Prepare for the Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) exam with our comprehensive study guide. Get expert tips, essential resources, and practice tests to earn your CKA certification and advance your career in Kubernetes administration.
Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) is one of the best kubernetes certifications from the Linux Foundation. You could even say it’s the top DevOps certification right now. It is aimed at engineers interested in setting up and managing Kubernetes clusters.
This guide covers everything you need to know about the CKA certification
The official CNCF certification page says:
The purpose of the Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) program is to provide assurance that CKAs have the skills, knowledge, and competency to perform the responsibilities of Kubernetes administrators.
As one of the highest velocity open source projects, Kubernetes is exploding. In this scenario – the demand for skilled DevOps Engineers with Kubernetes cluster administration knowledge is growing.
As per the cncf annual report, in 2023 Certified Certification exam hit 176,000 enrolments.
Therefore, passing the CKA certification can increase your chances of career growth in a wide range of companies and organizations that use Kubernetes
Register for the CKA Certification Exam [Save upto 40% Today]
To begin your journey of becoming a Certified Kubernetes Administrator – start by registering for the exam on the Linux Foundation portal.
Note: Save 30% Today on CKA | CKAD | CKS | KCNA certification using the Voucher code given below. This code expires soon.
CKA Exam Voucher: Use coupon 30COMTECHIES at checkout
If you’re also planning to take the CKS exam, consider buying it as a bundle to save $382 (up to 40% discount)
Code: Use coupon 30COMTECHIES at checkout
Here are some things to keep in mind regarding the exam.
- The CKA exam is to be taken online and it is proctored remotely.
- A score of 66% or above must be earned to pass.
- CKA Certification is valid for two years.
- After registration, you get one year to schedule the exam.
- After registration, you get a maximum of 2 attempts to take the test. If you miss a scheduled exam for any reason – your second attempt gets nullified.
Note: You can always check the latest Kubernetes Certification Coupon Codes to save costs on the CKA, CKAD, CKS and KCNA certification registration
CKA Certification Preparation Guide
This section will go over resources and links that can help you prepare for the CKA exam and pass the CKA certification with very good score.
CKA Exam Prerequisites
CKA does not require any candidate to have any other certification before they can appear for the CKA exam. The only thing required to clear the exam is a conceptual and practical understanding of Kubernetes’s components and native objects. Also a lot of hands-on practice.
CKA Exam details
| Exam Duration | 2 hours |
| Pass Percentage | 66% |
| CKA exam kubernetes version | Kubernetes v1.30 |
| CKA Validity | 2 Years |
| Exam Cost | $395 USD |
The CKA exam is an open-book exam i.e. you can use the following websites while you are taking the exam.
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/
- https://github.com/kubernetes/
- https://kubernetes.io/blog/ and their subdomains. This includes all available language translations of these pages (e.g. https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/)
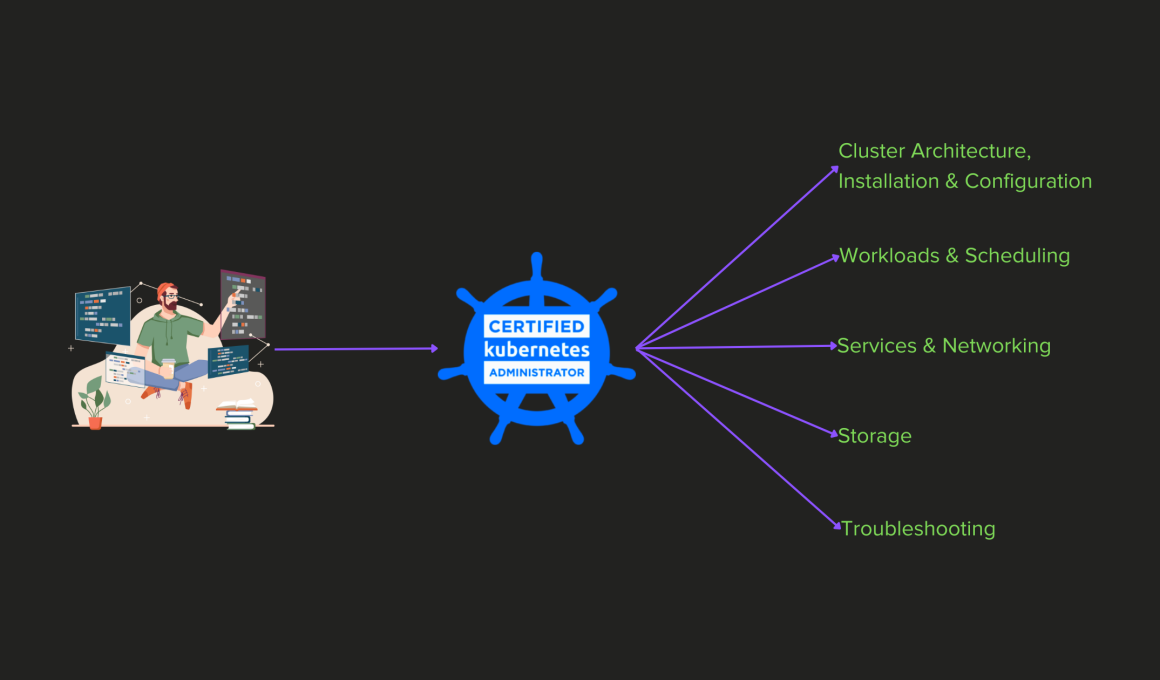
CKA Exam syllabus
The following table has the domains and competencies part of the syllabus along with their respective weightage.
| Topic | Subtopics | Weightage |
| Cluster Architecture, Installation & Configuration | 1. Manage role based access control (RBAC) 2. Use Kubeadm to install a basic cluster 3. Manage a highly-available Kubernetes cluster 4. Provision underlying infrastructure to deploy a Kubernetes cluster 5. Perform a version upgrade on a Kubernetes cluster using Kubeadm 6. Implement etcd backup and restore | 25 % |
| Workloads & Scheduling | 1. Understand deployments and how to perform rolling update and rollbacks 2. Use ConfigMaps and Secrets to configure applications Know how to scale applications 3. Understand the primitives used to create robust, self-healing, application deployments 4. Understand how resource limits can affect Pod scheduling 5. Awareness of manifest management and common templating tools | 15 % |
| Services & Networking | 1. Understand host networking configuration on the cluster nodes 2. Understand connectivity between Pods 3. Understand ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer service types and endpoints 4. Know how to use Ingress controllers and Ingress resources 5. Know how to configure and use CoreDNS 6. Choose an appropriate container network interface plugin | 20 % |
| Storage | 1. Understand storage classes, persistent volumes 2. Understand volume mode, access modes and reclaim policies for volumes 3. Understand persistent volume claims primitive 4. Know how to configure applications with persistent storage | 10 % |
| Troubleshooting | 1. Evaluate cluster and node logging 2. Understand how to monitor applications 3. Manage container stdout & stderr logs 4. Troubleshoot application failure 5. Troubleshoot cluster component failure 6. Troubleshoot networking | 30 % |
CKA Practice Labs
The best way to prepare for the CKA Certification exam is to get a clear understanding of the concepts involved and do a lot of hands-on practice.
Even if you’re actively working in Kubernetes production environments, you’ll still need to practice to pass the exam
The CKA exam doesn’t include multiple-choice questions, so hands-on practice is essential
The following setups will give you a Kubernetes cluster where you can do all the required practice. The exam expects you to solve problems on a live cluster.
Note: I would highly recommend setting up a Kubeadm based cluster. The actual exam also uses kubeadm clusters.
- Killercoda (Browser Based CKA playground)
- Kubernetes Setup using Kubeadm [Self hosted setup based on CKA requirements. This is the recommended setup for learning]
- Minikube
- Kubernetes Vagrant Setup using Kubeadm [ Checkout the Github Repo]
- GKE Cluster using free Google Cloud Credits
- EKS Service on AWS using a Free tier program
- AKS service on Azure using free cloud credits
- Kubernetes Cluster on Digital Ocean[ Get $100 Digital Ocean Free Credits]
Also if you want to get the feel of real exam terminal, you can try all the practicals in the Killercoda remote desktop environment. Each session will be available for one hour. It is more than enough for practice. It takes around 10 minutes for the terminal to be ready. Also, it is similar to the Remote Desktop interface given in the real Exam UI. This way, It will be easy for you when you attempt the exam.
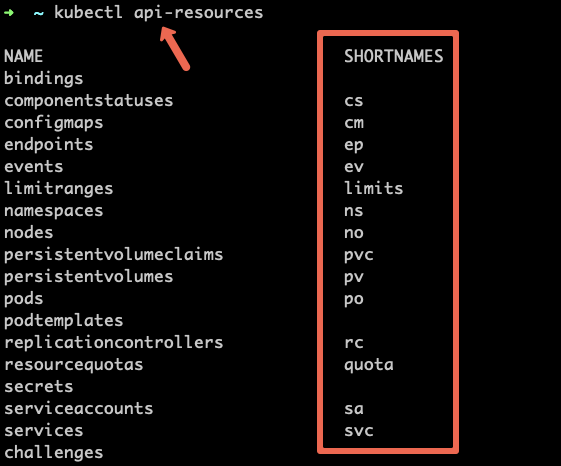
Kubectl Aliases & Shortnames
Once you have the CKA practice lab setup ready, set the following aliases in your practice lab terminal. You can add them to your .bashrc or .zshrc file (depending on your shell), and then run source ~/.bashrc or source ~/.zshrc.
alias k='kubectl'
alias kgp='kubectl get pods'
alias kdr='kubectl --dry-run=client
alias kgs='kubectl get svc'
alias kdesc='kubectl describe'
alias kga='kubectl get all'If you want to use aliases during exams and save time, you need to start practicing with aliases from day one. Whenever you choose a topic to learn, use the aliases during practice sessions.
Also, in the exam terminal you will have the kubectl alias set by default. You can choose to create others if you want to.
Important Note: Command examples give in this guide use kubectl alias and object short-names to make your practice easier.
For example,
k get po --all-namespacesTo know all the available object short names execute the following command.
kubectl api-resourcesNow that you have all the setup ready for the learning, let’s dive into exam syllabus topics and related official resources and tasks.
Guide to CKA Exam: A Syllabus-Based Approach
Here, we will be discussing the CKA syllabus-wise official and useful resources that can be used to prepare for each topic of the CKA exam.
Cluster Architecture, Installation & Configuration [ 25% ]
This section primarily deals with cluster setup, configuration and management.
It is very important to understand the Kubernetes architecture before moving on to hands-on labs.
Manage role-based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control is a method of managing access levels to applications or individual users. It’s a handy tool in the hands of an administrator to give fine-grained controls to others.
| RBAC essentials | Check RBAC Documentation |
Use Kubeadm to Install a Basic Cluster
For the exam: Create a cluster using kubeadm – Practice and use the official documentation as a reference during the exam.
This section focuses on the setting up of a cluster using the kubeadm tool. The candidate must have a clear understanding of the underlying components of Kubernetes such as etcd, Kube API servers, SSL certificate management, etc.
Note: Ensure swap is disabled on all nodes before deploying the Kubeadm cluster.
| Learn About Kubeadm | Kubeadm Documentation |
| Tutorial | Kubeadm Cluster Setup Guide |
Here is what you need to focus on for the exam
- From the official documentation, practice the kubeadm cluster creates commands and their associated parameters.
Manage a Highly-available Kubernetes Cluster
Even though there will not be any questions related to HA for the CKA exam, it is good to know about the high availability architecture.
One of the duties of a Kubernetes administrator is to ensure the high availability of the cluster. This involves proper maintenance tasks on the cluster as well as managing the worker nodes.
| HA Kubernetes Cluster | HA cluster setup using Kubeadm |
Most clusters today are created on AWS, Azure, or GCP where the respective cloud providers take responsibility for cluster availability. However, it is important to understand the logic behind the HA kubernetes cluster.
Provision Underlying Infrastructure to Deploy a Kubernetes cluster
For Kubernetes to work, you need to have the following.
- Certain system configurations
- Container runtime (CRI-O, Containerd, or Docker)
- kubeadm
- kubelet and
- kubectl
During kubeadm cluster installtion you will go through all these configurations.
| Underlying Infrastructure for Kubernetes | Check the Kubeadm installation guide where all the underlying component installation is covered |
Perform a Version upgrade on a Kubernetes Cluster Using Kubeadm
In the exam, you will be asked to upgrade a Kubernetes cluster and nodes using Kubeadm.
Kubernetes is a continuously improving tool. Every now and then, a new version comes up with improvements and features. It is the duty of the administrator to take care of version upgrades.
| Kubeadm Upgrade Task | Kubernetes Version Upgrade Use Kubeadm |
Implement etcd Backup and Restore
You need to learn and practice etcd backup and restore using the etcdctl utility.
Etcd is a key-value store of the cluster. All the cluster configuration and information regarding pods, services, etc. are stored here in key-value format
| Reference Task | etcd Backup & Restore Operations |
Workloads & Scheduling [ 15% ]
Learn About Static Pod
Static pod in Kubernetes is a concept of deploying pod on specific nodes using Kubelet. These pods are not directly managed by the API server. These are primarily used for cluster bootstrapping purposes to bring up the cluster components that run as a pod.
| Static Pod Task | Create a Static Pod |
Understand Deployments and How to Perform Rolling Update and rollbacks
Kubernetes Deployment ensures a minimum number of application replicas are running at all times. In case a replica goes down, the Kubernetes API ensures that a new one is created within minutes.
Imperative commands: These are commands which let you create Kubernetes objects via a CLI. Meaning they remove the need to write the whole YAML. Knowing imperative commands can help you save time in the exam. I highly recommend them!
Kubectl commands:
Here is the imperative command to create deployment YAML using dry-run flag.
k create deploy web-deployment \
--image=nginx \
--dry-run=client -o yaml > deployment.yamlk create deploy <name> --image=<name> //create deployment
k create deploy <name> --image=<name> -- sleep 300 //with command arguments
k scale deploy <name> --replicas=4 //scale up or down
| Reference | Kubernetes Deployment Concepts |
Sometimes, you may want to rollback a Deployment; for example, when the Deployment is not stable, such as a crash loopback error, you can roll back the Deployment
Kubectl commands:
kubectl set image deployment <name of deployment> <name of container>=<new image name> // update image
kubectl rollout status deployment <name of deployment> //see status
kubectl rollout history deployment <name of deployment> //see history
| Reference | Kubernetes Rolling Update |
Use Config Maps and Secrets to Configure applications
Kubernetes Configmaps are useful to store non-critical data in key-value pair format. They can also be used to inject env vars into pods.
| Reference | Kubernetes Configmap Concepts |
Kubectl Commands for Configmaps:
kubectl create cm <name of configmap> --from-file=hello.txt
kubectl create cm <name of configmap> --from-literal=key1=value1 Secrets are useful to store sensitive data in key-value pair format. They can also be used to inject env vars into pods.
| Reference | Kubernetes Secrets Concepts |
Kubectl commands for secrets:
kubectl create secrets <name of secret> --from-file=hello.txt
kubectl create secrets <name of secret> --from-literal=key1=value1 Know How to Scale Applications
Kubernetes provides different ways to scale applications. You can use deployment objects and increase the number of replicas of your application.
Horizontal Pod Autoscalers (HPAs) can also be used to increase the number of replicas based on application metrics.
Understand the Primitives Used to Create Robust, Self-healing, Application Deployments
This section is mostly conceptual, for any self-healing application you should use deployments or stateful sets so that whenever pods go down, Kubernetes recreates them instantly.
Deployments also give you the option to keep track of all the changes you make. You can also roll back to a previous state very easily.
kubectl set image deployment <name of deployment> <name of container>=<new image name> // update image
kubectl rollout status deployment <name of deployment> //see status
kubectl rollout history deployment <name of deployment> //see history
Understand How Resource Limits Can Affect Pod Scheduling
Cluster management also involves the management of workloads, as an admin – you should ensure that each pod is able to get resources based on its needs.
In Kubernetes, you can assign each pod a minimum and maximum amount of CPU and memory usage.
| Reference 01 | Manage Container Resources |
| Reference 02 | Pods with resource requests |
Awareness of manifest management and common templating tools
This section expects you to be familiar with tools like kustomization, helm, etc.
| Kubernetes Manifests | Managing Kubernetes Objects |
| Kustomization | Manage objects with Kustomize |
Init Containers
Learn about init containers. You might be asked to create an init container to perform specific actions or files required for the main container inside the pod.
Official Task: Configure Pod Initialization
Services & Networking [ 20% ]
Understand host networking configuration on the cluster nodes
Kube-proxy is the component required on each worker node for the pods to communicate with each other. Networking between nodes involves Kube proxy participation as well.
Kubelet is how a worker node is in-network with the master node. All these concepts are required for understanding networking inside kubernetes.
| Reference | Kubernetes Networking |
Understand the Connectivity Between Pods
Kubernetes Pods communicate with each other using services. Kube proxy is the component that makes this possible.
| Reference | Understand Kube Proxy |
Understand ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer service types and endpoints
Understanding each service type along with their use cases is very important. Special attention should be paid to understanding how pods can be added under a service.
| Reference | Kubernetes Service Explained |
Know how to use Ingress controllers and Ingress resources
Ingress resources are how external entities are assigned access to internal cluster services. Ingress controllers are load balancers that make it possible.
| Reference 01 | Kubernetes Ingress |
| Reference 02 | Kubernetes Ingress Controller |
| Blog | Ingress Tutorial for Beginners |
| SSL BLOG | Ingress TLS/SSL Setup |
Know How to Configure and Use CoreDNS
CoreDNS is a flexible, extensible DNS server that can serve as the Kubernetes cluster DNS. Like Kubernetes, the CoreDNS project is hosted by the CNCF.
Choose an appropriate container network interface plugin
CNI stands for Container Networking Interface and its goal is to create a generic plugin-based networking solution for containers.
There are a lot of solutions such as Flannel, Calico, etc. This section explores some of them.
| Reference | Kubernetes Network Plugins |
Storage [ 10% ]
Understand Storage Classes, Persistent Volumes, Persistent Volume Claims
StorageClasses: StorageClass provides a way to describe the “classes” of storage available.
PersistentVolume: It is a piece of storage in the cluster that has been provisioned by an administrator or dynamically provisioned using StorageClasses. They are created over StorageClasses.
PersistentVolumeClaim: It is a request for storage by a user. They are created over PersistentVolumes.
| Reference | Kubernetes Persistent Volumes |
Understand Volume Mode, Access Modes, and Reclaim Policies for volumes
Volume modes: Kubernetes supports two types of volume modes: Filesystem & Block.
Access modes: Kubernetes supports three types of access modes: ReadWriteOnce, ReadOnlyMany & ReadWriteMany.
Reclaim Policy: Kubernetes supports three policies: Retain, Recycle & Delete
Know How to Configure Applications With Persistent Storage
Application pods can use persistent storage by mounting a PVC.
Troubleshooting [ 30% ]
Evaluate Cluster and Node Logging & Managing Logs
Application logs can help in understanding the activities and status of the application. The logs are particularly useful for debugging problems and monitoring cluster activity.
Going through logs of kubernetes control plane components like etcd, the scheduler can also be very helpful.
There are certain flags in kubectl commands which can help speed up your debugging cases, they are given below.
Kubectl Command To Check Logs:
kubectl logs deployment/<name of deployment>
kubectl logs deployment/<name of deployment> --tail=10
kubectl logs deployment/<name of deployment> --tail=10 -f
| Reference | Kubernetes Logging |
Understand How to Monitor Applications
Monitoring applications can be done by storing logs and studying the application’s metrics.
Tools like Prometheus & Grafana are popular as they make the management of metrics very easy.
Very often, sidecar containers are used as metrics exporters of the main application container.
Troubleshoot Application Failure
Administrators are also required to help users debug applications that are deployed into Kubernetes and not behaving correctly.
Troubleshoot Cluster Component Failure
Cluster components need to be debugged and perform troubleshooting for failures when users are sure that their application has everything perfectly set up.
Troubleshoot Networking
There can be scenarios where things are going wrong on the network end such as some incorrect configuration in ingress resources etc.
CKA Mock Exams
Once you learn all the CKA exam concepts, the final step is to give the mock exams.
When you purchase the subscription, you will get free access to https://killer.sh/cka exam simulator. You get access to two free mock exams. You can make use of the simulator to give the CKA practice exam.
Also, you can use the following Mock exam to practice for the CKA exam before appearing for the exam.
Some Unofficial Useful CKA Resources
- Understand kubernetes SSL certificates
- Simulator for hands-on practice
- Vim shortcuts. This will help you save time on exams.
- Hands-on CKA practical question bank on Github
- Tips to Create Kubernetes YAML Quickly
CKA Exam DOs
Following are the things you should do for CKA Certification.
- Get the CKA Candidate Handbook and read all the instructions carefully.
- Start the pre-exam process 30 minutes before the scheduled time. The process includes PSI browser setup, exam environment verification, etc. Overall the pre-exam process takes anywhere between 10-15 minutes.
- While giving CKA practice exams, try to wrap up 15 minutes before the deadline – it will give you additional time to revise the solutions.
- Give a couple of practice exams, identify your weak topics, and spend more time on those.
- If any particular question will take more than 6-7 mins to solve, flag/mark it to solve for later and come back once you solve the rest.
- Ensure you have very good and stable internet connectivity while appearing for the exam. For some reason, if you lose the connectivity you will have to go through the verification process again. That will give you less time to solve the CKA tasks.
- On exam day, try to keep an alternative internet source handy in case of Wi-Fi internet goes down. We don’t want all our handwork to be wasted, do we?
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
CKA is a challenging exam. So it is very important to avoid mistakes people often make so you can avoid them.
Here are some of the common mistakes and tips on how to avoid them.
- Do not rush through questions. Read each question carefully and understand it before you start answering them.
- Do not spend too much time on one question. Move on to the next question and come back later after solving other questions.
- After finishing each question, take a moment and double-check the answers. For example, the file path where you have redirected the output.
- Under exam pressure, there are high chances you might even forget the basic commands. So practice all the basic commands repeatedly and make them stick to your memory.
- You need to stay calm during the exam. If you are not able to solve a question, don’t panic. Move on to the next one. Nervousness will lead to careless errors.
- Even if you are someone working on Kubernetes daily, it is very important to get plenty of hands-on practice for the exam. Test your skills repeatedly using labs and real-world scenarios.
- Most people don’t even use an alias. So no need to overwhelm yourself with an
aliasfor everything. - Don’t schedule the exam on the last day of the expiration. The idea is to give it in a pressure-free environment.
CKA Exam Day Checklist
Let’s look at what you need to prepare and what you should expect when taking the exam. The last thing you want is to feel stressed out because you forgot something important for the exam. This checklist helps you keep track of all the things you need for the exam and be prepared to focus only on the exam aspects.
First Ensure you have completed the exam preparation checklist in the Linux Foundation exam portal.
The following are the key items that should be part of your CKA exam checklist.
- Ensure you have a stable internet connection. It is recommended to have an alternative connection ready.
- Ensure you have the computer camera working.
- Double-check that you have all the necessary system requirements. Run the System check as recommended by the Linux Foundation.
- Have a clutter-free desk and room because the examiner checks for the surroundings through the camera. Linux Foundation has strict rules on the CKA exam environment.
- Ensure you have a comfortable seating setup as the exam takes 2 hrs to complete.
- Have your ID ready for verification.
- Keep some water nearby to keep you hydrated and energized.
This video shows the PSI Online Proctoring Experience. It shows all the process involved in the certification including ID verification, web cam verification etc.
Can I use an Extended Monitor For the CKA Exam?
Yes. An extended monitor connected to a single computer is supported provided you have the camera attached to it. Also, you should be able to show around the room using the attached camera.
You can use only one screen at a time. If you want to use the extended screen of a laptop, you need to close the laptop and use only the extended screen with an active webcam.
Also, extended monitor is a great option becuase you will get a lot of real-estate to work on the tasks.
For example, the following image shows the exam UI. As you can see, with the good wide monitor you will can adjust the terminal and browser as per your preference.
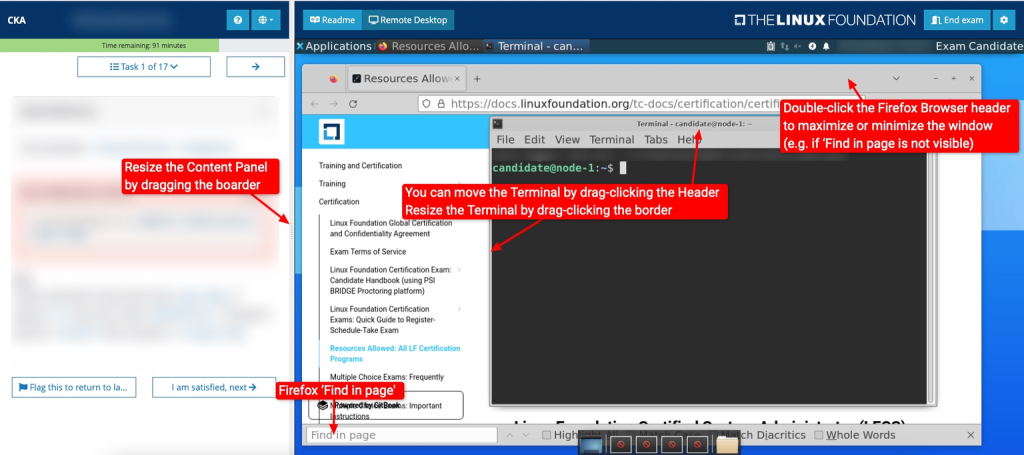
CKA Preparation Courses
Investing in a course will help you understand all the concepts for the exam in an easier manner. If you are a beginner, we strongly suggest you invest some time and money in a course of your choice.
We have the following recommendation.
- CKA preparation course by Mumshad: His course has a lot of quizzes and hands-on labs.
CKA Exam Updates
The new PSI environment for the CKA exam is being rolled out. Few users reported geting the the new PSI environment for the exam.
In the old environment you will have to execute the context for each task. In the new exam environment you will have to SSH in to different nodes to perform each tasks.
CKA Exam FAQs
Is there any coupon code for the CKA Exam?
Yes. You can use code DCUBE20 at kube.promo/devops to redeem a 20% discount on CKA exam registration
Conclusion
This CKA exam study guide will help you understand cluster components and their management in a much better way and help in your career progression.
If you’re aiming to become a DevOps engineer, having a CKA certification is a great asset. Its importance is growing every year. So give your best and prepare well!
This guide has given you all the resources, tips, and methods to help you prepare. we will keep updating it with new tools and resources. Best of luck with your preparations..
Also, check out Kubernetes beginners tutorials to learn more about Kubernetes. If you want a structured roadmap, check out the Kubernetes learning path.
If you are interested in DevOps certifications, check out our comprehensive guide on the best devops certifications.




1 comment
kubectl create secret generic ….