This post walks you through the steps to install Helm on different platforms and shows you how to verify the installation using Helm charts.
By the end of this guide, you will have learned:
- The prerequisites and permissions required for using Helm
- How to install Helm using different methods
- How to add a chart repository and search for Helm charts
- How to deploy a sample Helm chart to validate your setup
Helm Prerequisites
You should have the following before getting started with the helm setup.
- A running Kubernetes cluster.
- The Kubernetes cluster API endpoint should be reachable from the machine you are running helm.
- You should be able to authenticate to the cluster using kubectl, and your user should have cluster-admin permissions
Many Helm charts require elevated permissions to install components like RBAC resources, CustomResourceDefinitions (CRDs), or cluster-wide resources.
Cluster-admin permissions ensure Helm can perform all necessary operations without permission conflicts
Method 1: Install Helm Using Bash Script
I recommend this method if you are setting up a test environment in your local workstation or a server. For project requirements, please follow the binary installation of the specific version that is explained in the next section.
Step 1: Download the latest Helm installation script.
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/scripts/get-helm-3Step 2: Add execute permissions to the downloaded script.
chmod +x get_helm.shStep 3: Execute the installation script. This script will automatically find the right binary for your system.
./get_helm.shStep 4: Validate helm installation by executing the helm command.
helmMethod 2: Install Helm 3 From Binary
This method is recommended for project requirements where you can have a specific version of Helm installed across all the environments.
For example, if you are using Jenkins for Helm deployments, ensure the Jenkins agent where the Helm command runs has kubectl configured with admin permissions.
Step 1: Head over to the Github helm release page and copy the Linux amd64 link for the required version.
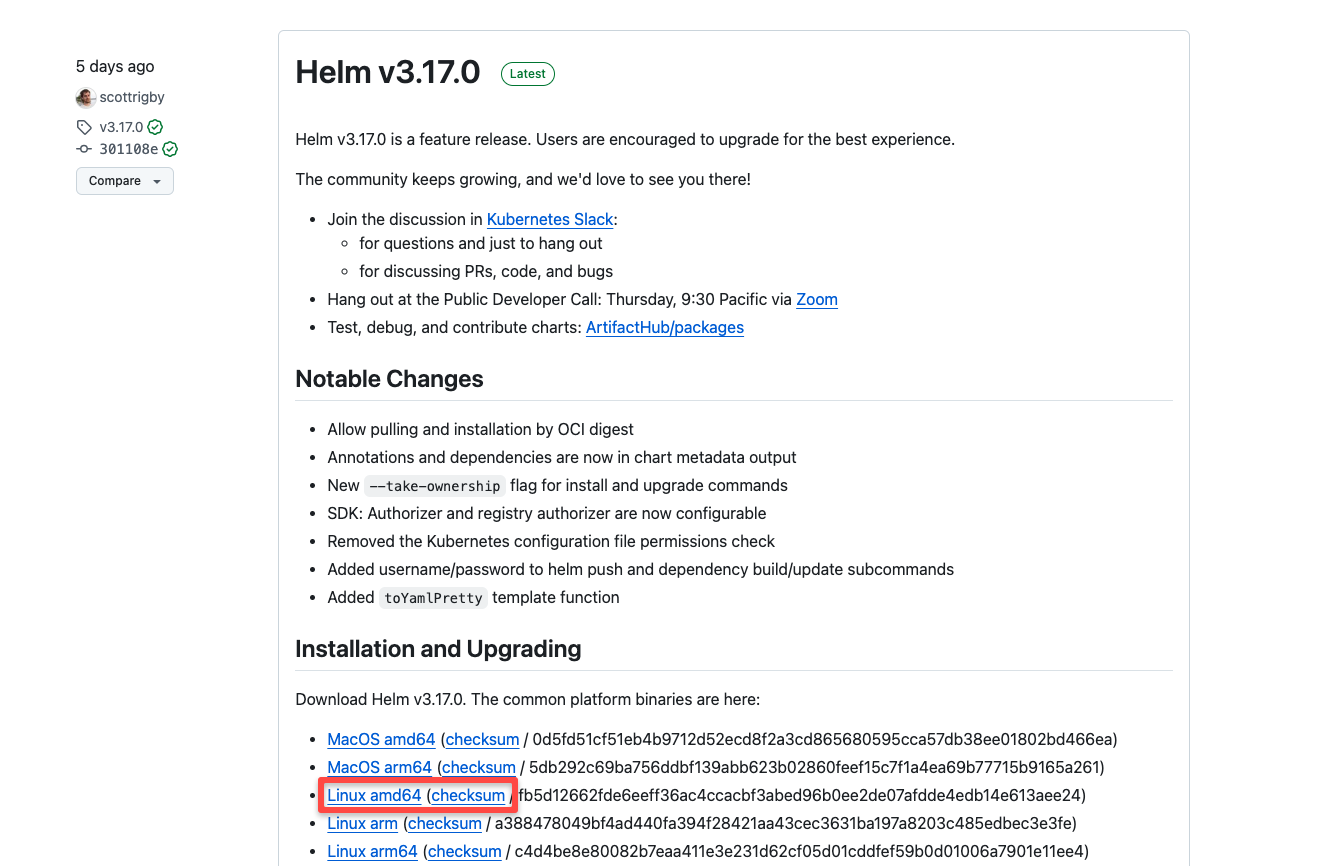
Step 2: Download the binary using wget.
wget -O helm.tar.gz https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.13.0-rc.1-linux-amd64.tar.gzStep 3: Untar the downloaded file.
tar -zxvf helm.tar.gzStep 4: Move the helm executable to the bin directory.
sudo mv linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helmStep 5: Validate by executing the helm command.
helmMethod 3: Install Helm From Package Managers
For Mac,
brew install helmTo install Helm on Ubuntu, use the following commands.
curl https://baltocdn.com/helm/signing.asc | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/helm.gpg > /dev/null
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https --yes
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/helm.gpg] https://baltocdn.com/helm/stable/debian/ all main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/helm-stable-debian.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install helmFor Windows,
# For Scoop
scoop install helm
#For Chocolatey
choco install kubernetes-helmAdd Chart Repository
Now we have installed helm, the next step is to add the chart repository.
The Bitnami Helm repo contains many stable helm charts developed and maintained by the community.
Now, add the chart repo for installing the stable charts.
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnamiNow, you can search the available chart using the search command.
For example, if you want to set up ArgoCD on Kubernetes, you can search for ArgoCD chart using the following command.
$ helm search repo argo
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
bitnami/argo-cd 9.0.12 3.0.4 Argo CD is a continuous delivery tool for Kuber...
bitnami/argo-workflows 12.0.0 3.6.7 Argo Workflows is meant to orchestrate Kubernet...When it comes to cloud AWS ECR supports Helm charts as OCI artifacts.
Google Artifact Registry support Helm charts
Azure Container Registry also support Helm charts
Alternatively, you can search for stable community charts via artifacthub.com where you can find many community-contributed helm charts.
Install & Validate Helm Chart
To validate the helm setup let's set up the Nginx ingress controller using the helm chart available in Artifacthub.
Step 1: First add the nginx-ingress helm repo.
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginxStep 2: Update the chart repo.
helm repo updateStep 3: Let's install a stable Nginx chart and test the setup. The ingress controller gets deployed in the default namespace.
helm install ingress-controller ingress-nginx/ingress-nginxHere ingress-controller is the custom release name. You can give the name of your preference.
Step 4: Now, check the status of the ingress helm deployment using the following command. It should show the status of the deployment.
helm lsAlternatively, you can use the kubectl command to check the ingress deployment in the default namespace.
kubectl get deploymentsStep 4: Now, to remove the deployment after validation, all you have to do is uninstall the deployment using its release name.
helm uninstall ingress-controllerUpgrade Helm Executable
If you are using a older version of helm and if you want to upgrade it to the latest version, you can use the following steps as per the OS type.
For MAC,
brew update
brew upgrade helmFor Linux,
The following script will fetch the latest version and upgrade it.
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3 | bashFor Windows,
choco upgrade kubernetes-helmAfter the upgrade, check the version using the following command.
helm versionConclusion
In this post, we have seen how to install Helm, install chart repo, and validate the installation using a sample Helm deployment.
When you use helm for project use cases, it is recommended you create your own helm charts with approved container images from the security team.
If you use community helm charts in project environments, ensure you replace the community docker images with custom-built images.
Next, look at the comprehensive beginner's guide on how to create a Helm chart. It covers the helm chart development and its best practices using step-by-step guides.

