This kubernetes tutorial explains how to create kubernetes jobs and cronjobs, along with its basics, use cases, and a few tips and tricks.
Here is what you will learn from this tutorial.
Table of Contents
- What is a Kubernetes Job?
- Kubernetes Jobs & CronJobs Use Cases
- How to Create a Kubernetes Job
- Multiple Job Pods and Parallelism
- Generate Random Name for Kubernetes Job
- How to Create a Kubernetes CronJob
- Run a Kubernetes CronJob Manually
- Few Key Kubernetes Job Parameters
- Monitoring Kubernetes Jobs & Cronjobs
What is a Kubernetes Job?
Kubernetes jobs and cronjobs are Kubernetes objects that are primarily meant for short-lived and batch workloads.
kubernetes job object basically deploys a pod but it runs for completion as opposed to objects like deployment, replicasets, replication controllers, and DaemonSets, which runs continuously.
Meaning, Jobs run until the tasks specified in the job are completed and if the pods give an exit code 0, the job will exit. The task could be a shell script execution, an API call, or a java python execution that does a data transformation and upload it to cloud storage.
Whereas in normal Kubernetes deployments, irrespective of the exit codes, the deployment object will create new pods when it terminates or throws an error to keep the deployment’s desired state.
During a Job run, if the node hosting the pod fails, the job pod will get automatically rescheduled to another node.
Kubernetes Jobs & CronJobs Use Cases
The best use case for Kubernetes jobs are,
- Batch processing: Let’s say you want to run a batch task once a day or during a specific schedule. It could be something like reading files from storage or a database and feed them to a service to process the files.
- Operations/ad-hoc tasks: Let’s say you want to run a script/code which runs a database cleanup activity or to even backup a kubernetes cluster itself.
In one of the projects I have worked on, we have used Kubernetes jobs extensively for ETL workloads.
How to Create a Kubernetes Job
In this example, I will use an Ubuntu container that runs a shell script that has a for-loop that echoes a message based on the argument you pass to the container. The argument should be a number that decides the number of times the loop runs to echo the message.
You Might Like: CKA, CKAD & CKS Exam Coupon Codes
For example, if you pass 100 as an argument, the shell script will echo the message 100 times and the container will exit.
You can view the Dockerfile and the shell script from here ->
Let’s get started with a job with a simple setup.
Step 1: Create a job.yaml file with our custom Docker image with 100 as a command argument. The value 100 will be passed to the docker ENTRYPOINT script as an argument.
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: kubernetes-job-example
labels:
jobgroup: jobexample
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: kubejob
labels:
jobgroup: jobexample
spec:
containers:
- name: c
image: devopscube/kubernetes-job-demo:latest
args: ["100"]
restartPolicy: OnFailureStep 2: Let’s create a job using kubectl with the job.yaml file. The job gets deployed in the default namespace.
kubectl apply -f job.yamlStep 3: Check the status of the job using kubectl.
kubectl get jobsStep 4: Now, list of pods using kubectl.
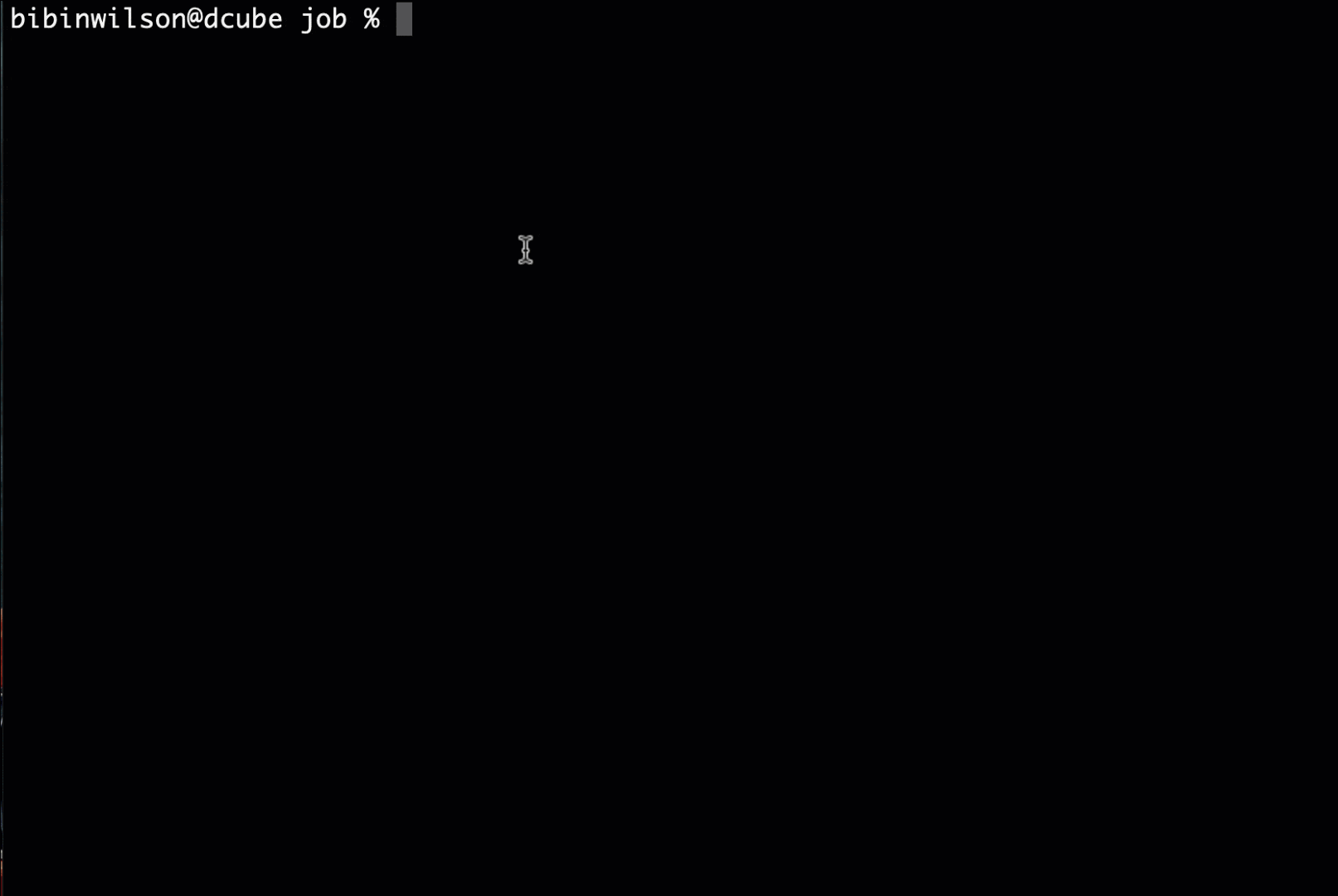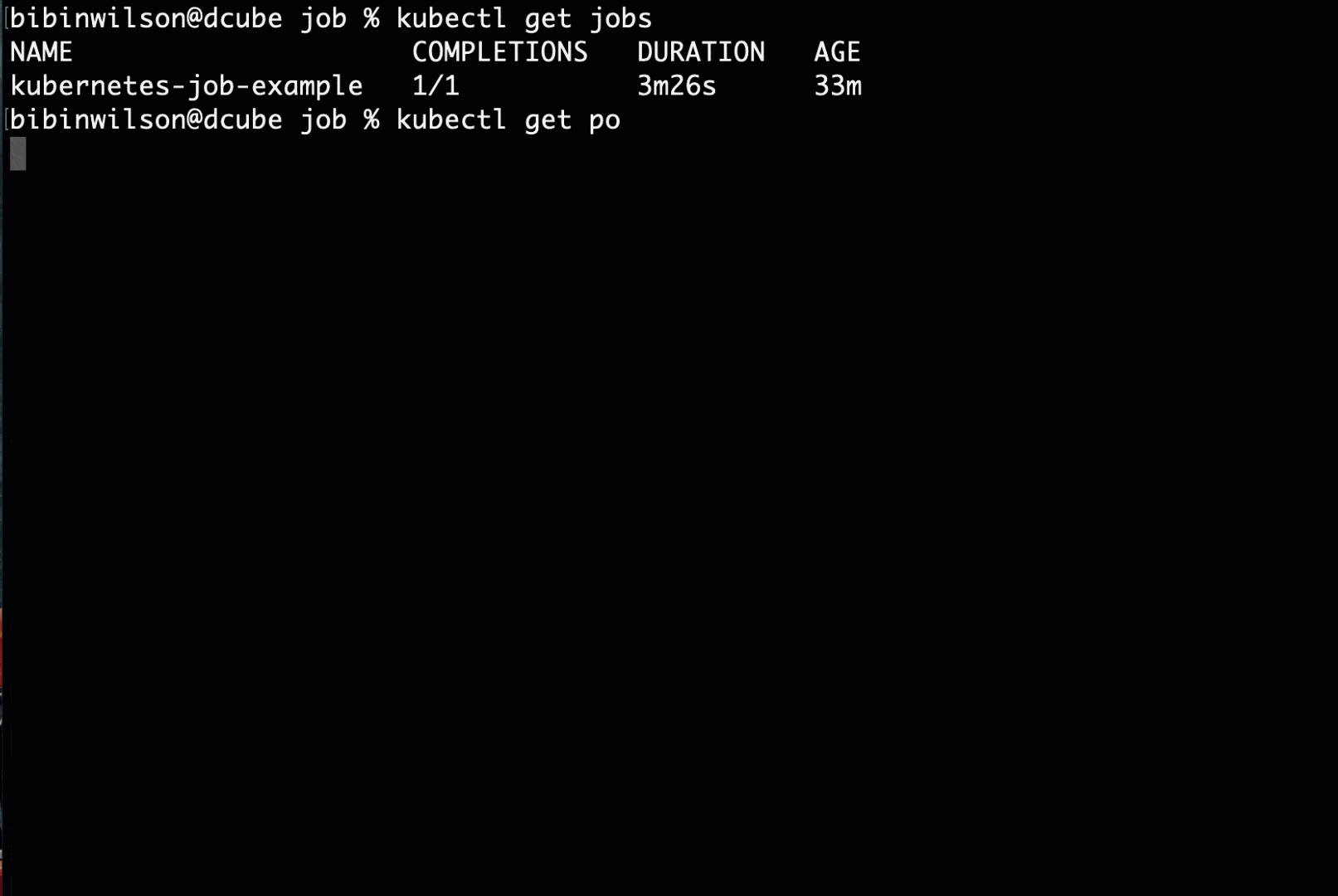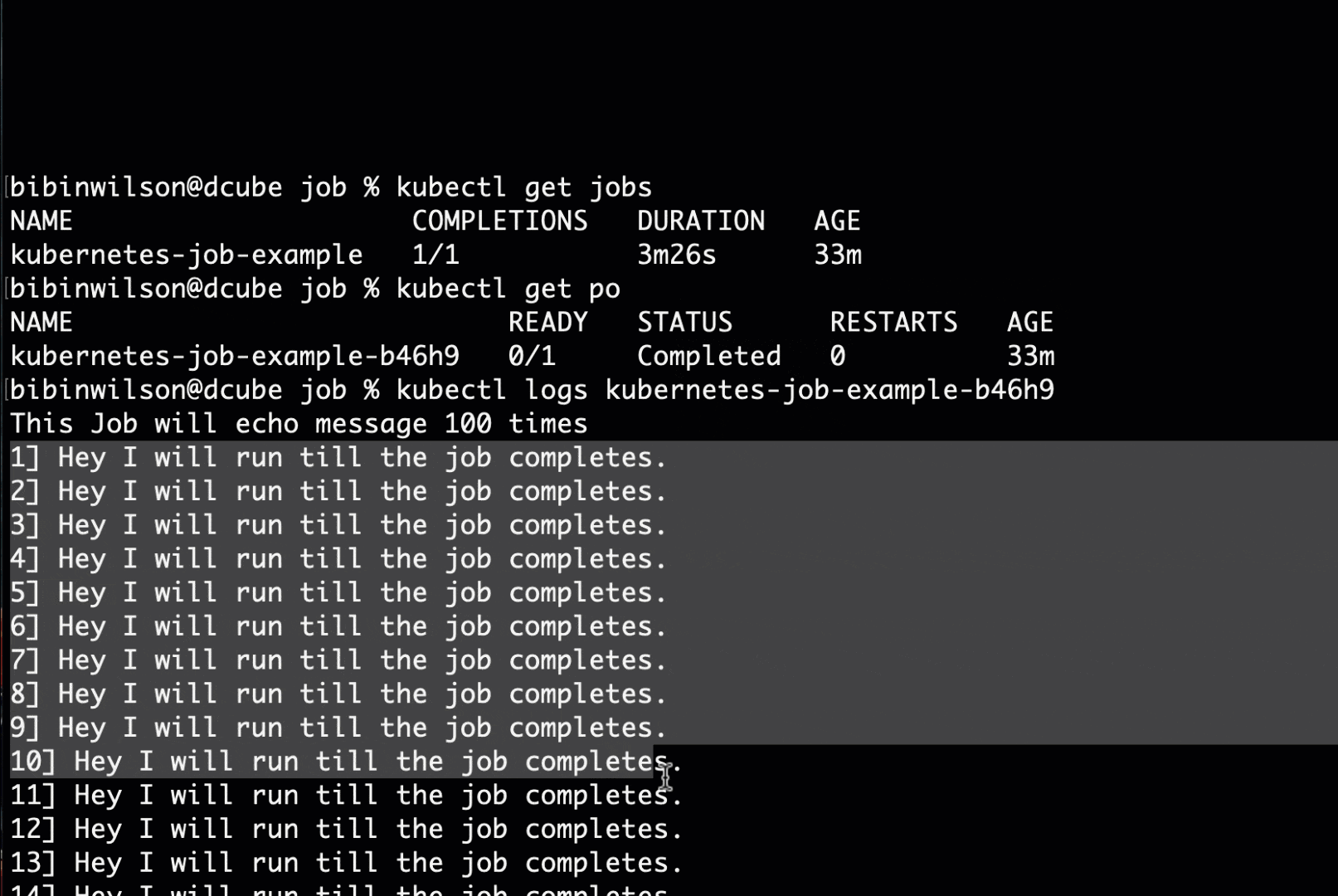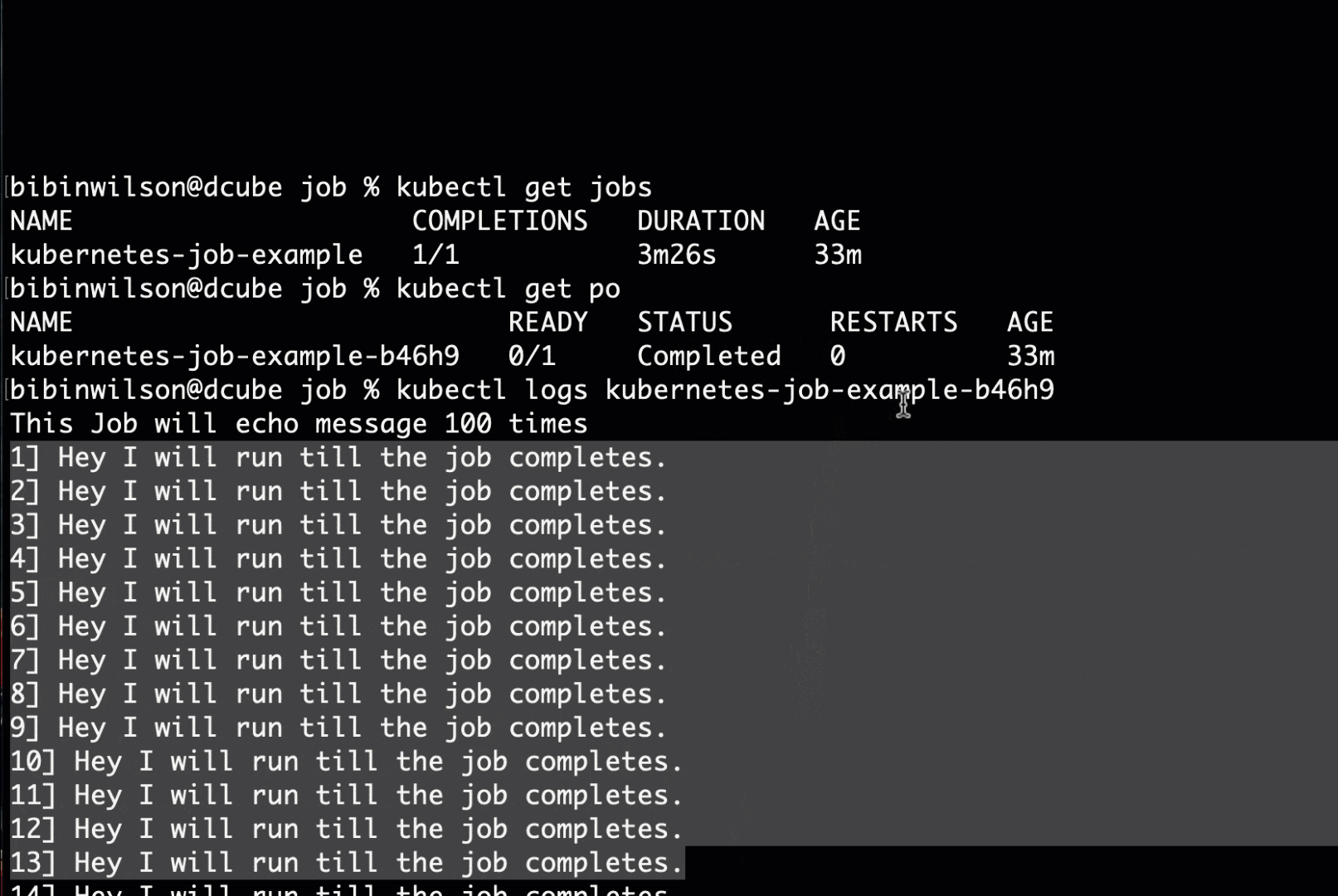
kubectl get poStep 5: You can get the job pod logs using kubectl. Replace the pod name with the pod name you see in the output.
kubectl logs kubernetes-job-example-bc7s9 -fYou should see an output as shown below.
Multiple Job Pods and Parallelism
When a job is deployed you can make it run on multiple pods with parallelism.
For example, in a job if you want to run 6 pods and run 2 pods in parallel, you need to add the following two parameters to your job manifest.
completions: 6
parallelism: 2The job will run 2 pods in parallell for 3 times to achieve 6 completions.
Here is the manifest file with those parameters.
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: kubernetes-parallel-job
labels:
jobgroup: jobexample
spec:
completions: 6
parallelism: 2
template:
metadata:
name: kubernetes-parallel-job
labels:
jobgroup: jobexample
spec:
containers:
- name: c
image: devopscube/kubernetes-job-demo:latest
args: ["100"]
restartPolicy: OnFailureOne use case for parallel pod processing is a batch operation on a message queue. Let’s say you have a message queue with thousands of messages to be processed at a certain time a day.
You can run the message processing code as a job with parallelism for faster processing. Even though all the pods used the same message processing code, each pod would be processing a different message from the queue.
Generate Random Name for Kubernetes Job
You cannot have a single job manifest file and create multiple jobs from it. Kubernetes will throw an error stating that a job with the same name exists.
To circumvent this problem, you can add the generateName name parameter to the metadata.
For example,
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: kube-job-
labels:
jobgroup: jobexampleIn the above example, every time you run the manifest, a job will get created with kube-job- as a prefix followed by a random string.
How to Create a Kubernetes CronJob
What if you want to run a batch job on specific schedules, for example, every 2 hours. You can create a Kubernetes cronjob with a cron expression. The job will automatically kick in as per the schedule you mention in the job.
Here is how we specify a cron schedule. You can use the crontab generator to generate your own schedule.
schedule: "0,15,30,45 * * * *"The following image shows the kubernetes cronjob scheduling syntax.
If we were to run our previous job as a cronjob every 15 minutes, it looks like the manifest given below.
Create a file named cron-job.yaml and copy the following manifest.
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: kubernetes-cron-job
spec:
schedule: "0,15,30,45 * * * *"
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cron-batch-job
spec:
restartPolicy: OnFailure
containers:
- name: kube-cron-job
image: devopscube/kubernetes-job-demo:latest
args: ["100"]Let’s deploy the cronjob using kubectl.
kubectl create -f cron-job.yamlList the cronjobs
kubectl get cronjobsTo check Cronjob logs, you can list down the cronjob pod and get the logs from the pods in running state or from the finished pods.
Run a Kubernetes CronJob Manually
There are situations where you might want to execute the cronjob in an ad-hoc manner. You can do this by creating a job from an existing cronjob.
For example, if you want a cronjob to be triggered manually, here is what we should do.
kubectl create job --from=cronjob/kubernetes-cron-job manual-cron-job--from=cronjob/kubernetes-cron-job will copy the cronjob template and creates a job named manual-cron-job
Few Key Kubernetes Job Parameters
There are a few more key parameters you can use with kubernetes jobs/cronjobs based on your needs. Let’s have a look at each.
- failedJobHistoryLimit & successfulJobsHistoryLimit: Deletes the failed and successful job history based on the retention number you provide. This is super useful to trim down all failed entries when you try to list the jobs. For example,
failedJobHistoryLimit: 5 successfulJobsHistoryLimit: 10
- backoffLimit: Total number of retries if your pod fails.
- activeDeadlineSeconds: You can use this parameter if you want to specify a hard limit on how the time the cronjob runs. For example, if you want to run your cronjob only for one minute, you can set this to 60.
Monitoring Kubernetes Jobs & Cronjobs
Kube state metrics provide a few metrics to monitor kubernetes Jobs and cronjobs. It does not come with the cluster by default. You need to set up Kube state metrics separately.
See cronjob metrics document for the supported metrics.
You can make use of these metrics using the Prometheus monitoring stack and visualize it using Grafana.
There is a Grafana template available for the Cronjob monitoring dashboard. See, Cron and Batch monitoring template
If you want to monitor custom metrics generated by Jobs or Cronjobs, you need to use the Prometheus push gateway to get all the metrics on Prometheus.








4 comments
Just one question here , when you create job with parallel 2 does it means; two pods will run same job eg like in your case you are printing a string 100 times. So it could be the case where one pod prints string x times and other prints y times. where x+y =100?
or both will print 100 times so string is printed total 100 times
Hi Kunal,
Good question!
Both will print 100 times.
To elaborate, a pod gets deployed from an image and the image with script/code is the same for all the deployed pods. for example, the script which prints 100 lines.
You might ask, how it helps.
Here is one use case. Let’s say you have a message queue with messages that need to be processed as a batch. In this case, your job pod will have the code to process available messages.
So you can run 10 pods in parallel to process the messages fast. Even though the code running in 10 pods is the same, 10 pods will process 10 different messages at a time.
Hope I have cleared your doubts.
I have updated this in the post as well.
I think your job.yaml file is not proper. There’s a syntax error
“`
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job metadata:
name: kubernetes-job-example
“`
Thanks for the update. We have corrected the YAML.