This blog covers the essential steps to secure your Docker images against potential vulnerabilities using Trivy Container Scanner.
What is Trivy?
Trivy is an open-source security scanner that scans for vulnerabilities in containers and other artifacts. It has an internal database called trivy-db which contains information about different vulnerabilities.
It is created and maintained by AquaSecurity
Trivy not only scan for vulnerability but also give suggestion to solve the issues and links to the vulnerable data for more information.
Trivy can access a wide range of vulnerability information from different vulnerability databases and uses vulnerability data from those vulnerability databases to detect security issues. Some of the vulnerability databases are National Vulnerability Database (NVD), Red Hat Security Data, and Alpine SecDB.
While scanning Trivy compares the directory or container image’s software packages and libraries with the information in the vulnerability database and if a match is found that means the package or library in the container image has a vulnerability. Then Trivy reports these vulnerabilities along with other details such as severity level, affected versions, and repair suggestions.
Trivy updates its database every 6 hours. When you start the scan, trivy updates the databases automatically so that you don’t have to keep track of database updates.
Another important feature of Trivy is generating SBOM. It provides a detailed inventory of all the components used in software, including open-source and third-party libraries.
Install Trivy
Let’s see how to install Trivy on Ubuntu, follow the below steps to install Trivy.
For other platform, please visit the official installation page.
Step 1: First, install the required dependencies for Trivy using the command given below:
sudo apt-get install wget apt-transport-https gnupg lsb-releaseStep 2: Download the public key and Trivy repository using the commands given below:
wget -qO - https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb/public.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/trivy.gpg > /dev/null
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/trivy.gpg] https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb $(lsb_release -sc) main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/trivy.listStep 3: Update the repository using the update command.
sudo apt update -yStep 4: Install Trivy using the command:
sudo apt install trivyTo verify the installation and understand all the available option, run the following trivy help command.
trivy -hYou should get an output a shown below.
trivy -h
Scanner for vulnerabilities in container images, file systems, and Git repositories, as well as for configuration issues and hard-coded secrets
Usage:
trivy [global flags] command [flags] target
trivy [command]
Examples:
# Scan a container image
$ trivy image python:3.4-alpine
# Scan a container image from a tar archive
$ trivy image --input ruby-3.1.tar
# Scan local filesystem
$ trivy fs .
# Run in server mode
$ trivy server
Scanning Commands
aws [EXPERIMENTAL] Scan AWS account
config Scan config files for misconfigurations
filesystem Scan local filesystem
image Scan a container image
kubernetes [EXPERIMENTAL] Scan kubernetes cluster
repository Scan a remote repository
rootfs Scan rootfs
sbom Scan SBOM for vulnerabilities
vm [EXPERIMENTAL] Scan a virtual machine image
Management Commands
module Manage modules
plugin Manage plugins
Utility Commands
completion Generate the autocompletion script for the specified shell
convert Convert Trivy JSON report into a different format
help Help about any command
server Server mode
version Print the version
Flags:
--cache-dir string cache directory (default "/Users/bibinwilson/Library/Caches/trivy")
-c, --config string config path (default "trivy.yaml")
-d, --debug debug mode
-f, --format string version format (json)
--generate-default-config write the default config to trivy-default.yaml
-h, --help help for trivy
--insecure allow insecure server connections
-q, --quiet suppress progress bar and log output
--timeout duration timeout (default 5m0s)
-v, --version show version
Use "trivy [command] --help" for more information about a command.
Using Trivy To Scan for Vulnerability
Whenever you run the Trivy command to scan for vulnerabilities it will download the relevant database first and compare it with the vulnerabilities listed in the database.
Trivy shows the risk of vulnerability as critical, high, medium, and low.
- Critical – This is the most severe vulnerability which needs to be fixed as soon as possible because it can allow administrative control over the system.
- High – It could cause data leakage.
- Medium – It could make the system unavailable for users.
- Low – This can be solved during regular maintenance.
We can use Trivy to scan the following targets:
- Container images
- Filesystem
- Remote Git repositories
There are also experimental features to scan Kubernetes & AWS configurations.
Trivy uses different commands to scan targets that are mentioned above.
The following image shows the high level components and container scanning workflow.
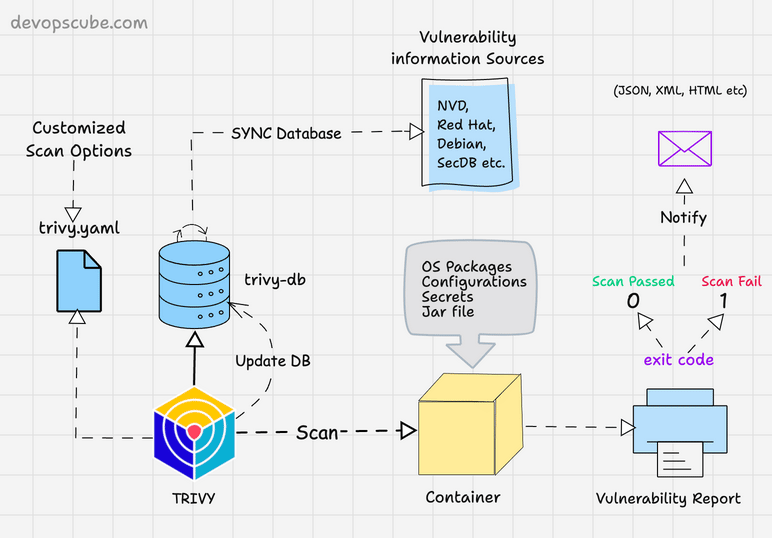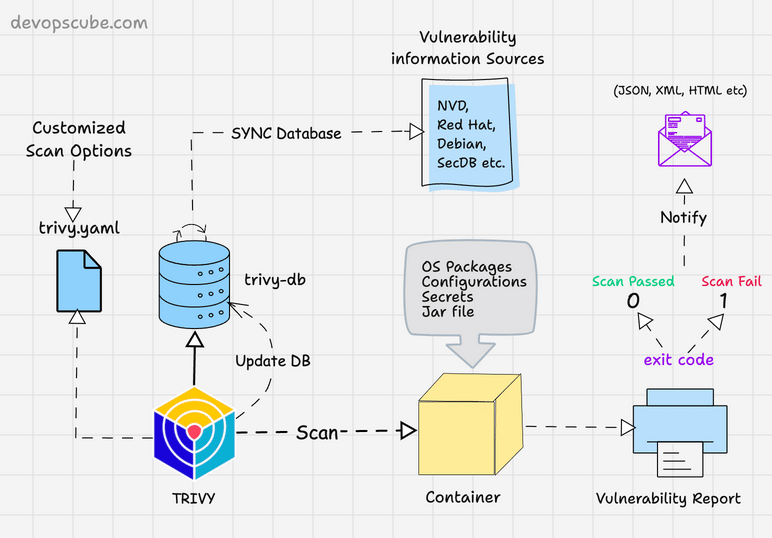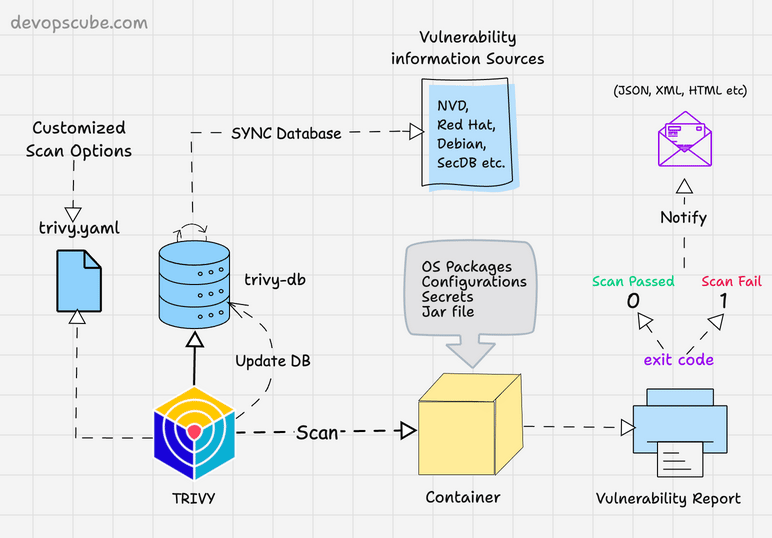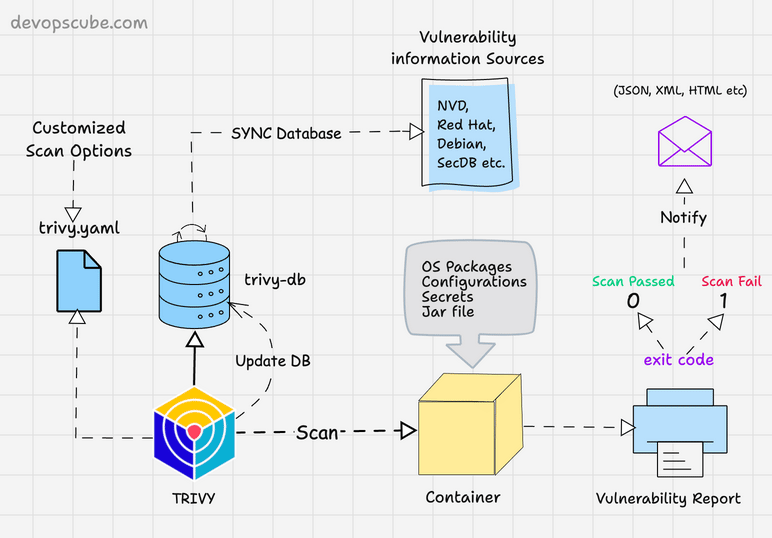
Scan Container Images With Trivy
To get started, you need to have trivy intalled on you system or the CI agent node where you want to implement the Docker image scanning.
You can find the installation steps at official Trivy installation page.
Scanning Docker Images using Trivy is very easy. You just need to run the following trivy command with the image name you want to scan.
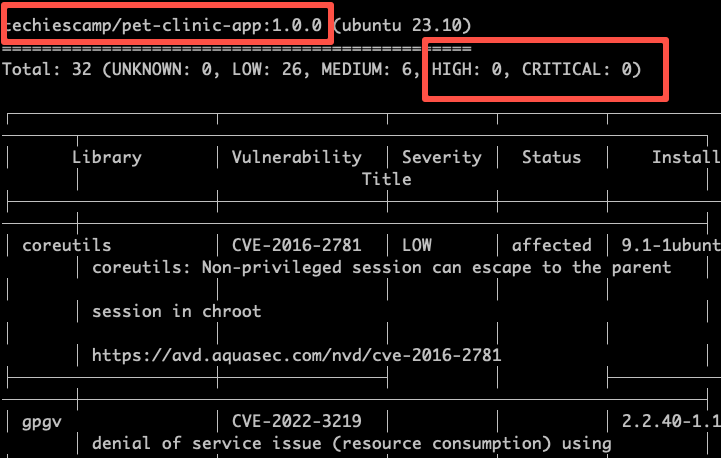
trivy image <image-name>For example, I have a image named techiescamp/pet-clinic-app in my workstation. It is a docker image with java spring boot application.
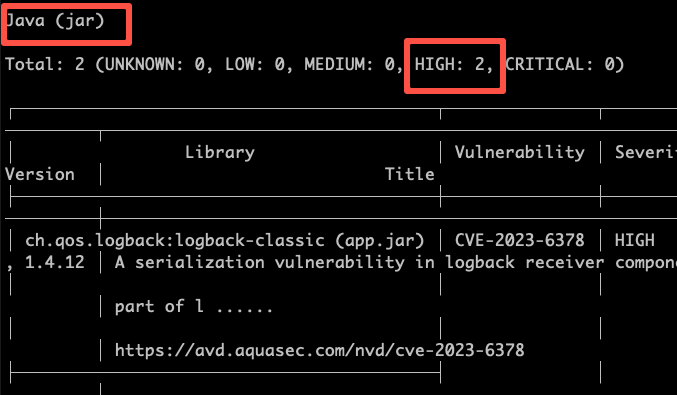
I can scan the image using the following command. Trivy scans for both vulnerabilities in the image as as the java jar that is part of the image. The results of the scan will be displayed in a human-readable format.
trivy image techiescamp/pet-clinic-app:1.0.0The scan result shows that there are not high or critical vulnerabilties in the image.
Also it shows 2 high vulnerabilities for the jar inside the Docker image.
Trivy can be used in multiple ways. Here are a few examples of advanced usage:
Scan for severity
Trivy can scan for vulnerabilities of a specific severity. To do this, use the --severity <severity> flag to specify the vulnerability severity that you need to scan.
trivy image --severity CRITICAL techiescamp/pet-clinic-app:1.0.0Output as JSON
Trivy can also give output in JSON format. To do this, use the --format json flag, it will display the scanned results in JSON format.
trivy image --format json techiescamp/pet-clinic-app:1.0.0Ignore fixed vulnerabilities
There are vulnerabilities that cannot be fixed even if the packages are updated (unpatched/unfixed). Trivy can scan images ignoring those vulnerabilities. To do this, use the --ignore-unfixed flag.
trivy image --ignore-unfixed java:0.1Scan Docker tar Images
There are situations you might have the Docker images in tar format. In this case, you can use trivy to scan the image in tar format.
For example,
trivy image --input petclinic-app.tarTrivy Scan in Docker Image Build Pipeline
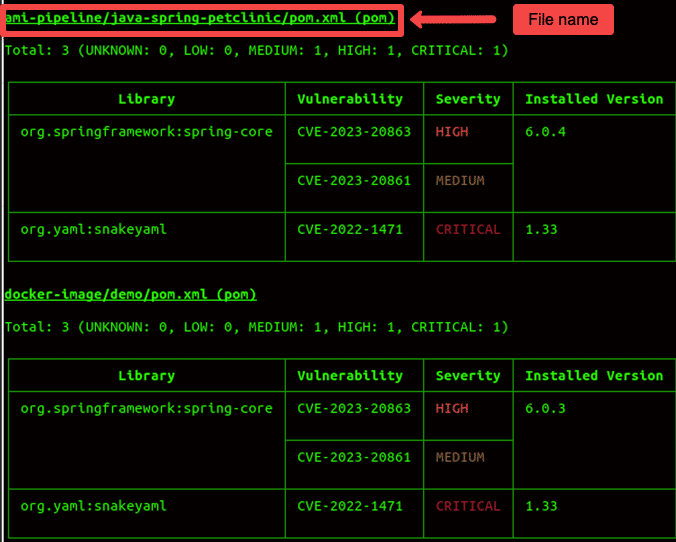
Trivy plays a key role in CI/CD pipeline in terms docker image builds. Organizations use trivy to scan for vulnerabilities in CI/CD pipeline to ensure a seecure image is getting deployed in production.
When using in CI/CD piepline, the the pipeline job should fail if there is any vulnerability in the image. The severity depends on the organizations security compliance. For example, some organization may have strict guidelines to fail the build for both HIGH and CRITICAL severities.
Now, the best way to fail the build is using exit codes.
To do this, use the --severity and --exit-code 1 flag with the trivy command as shown below. It will make Trivy exit with a non-zero exit code if any vulnerabilities are found for the given severities
trivy image --severity HIGH,CRITICAL --exit-code 1 techiescamp/pet-clinic-app:1.0.0Also, you can send the vulnerability report as a build failure notification to developers and DevOps engineers.
A recommended approach is to use a Trivy config file to set the defaults for a scan. You can use this file to accomodate your scanning requirements specific to your project needs.
Here is an example of trivy.yaml file
timeout: 10m
format: json
dependency-tree: true
list-all-pkgs: true
exit-code: 1
output: result.json
severity:
- HIGH
- CRITICAL
scan:
skip-dirs:
- /lib64
- /lib
- /usr/lib
- /usr/include
security-checks:
- vuln
- secret
vulnerability:
type:
- os
- library
ignore-unfixed: true
db:
skip-update: falseHere is the syntax to use the config file
trivy image --config path/to/trivy.yaml your-image-name:tagGenerate a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM)
An SBOM is a complete list of all components used in a software application, such as a library, framework, and module, including their versions.
It helps to identify potential vulnerabilities, manage licenses, and maintain software more effectively.
For example, vulnerabilities like Log4j (CVE-2021-44228) affected many organization. With SBOM organizations can quickly search across its entire software ecosystem to locate which applications or services use Log4j and take remediation measures.
Trivy can generate SBOM CycloneDX and SPDX formats.
Use the below command to generate SBOM in either CycloneDX or SPDX format.
trivy image --format spdx-json --output result.json techiescamp/pet-clinic-app:1.0.0
trivy image --format cyclonedx --output result.json techiescamp/pet-clinic-app:1.0.0Trivy also has the ability to scan for vulnerabilities using the SBOM file, use the following command to scan for vulnerabilities using an SBOM file
trivy sbom result.jsonScan Filesystem
The command used to scan the filesystem is given below:
trivy fs <path of the directory>For example, if the path of the directory is Documents/jenkins-pipeline/ then the command will be:
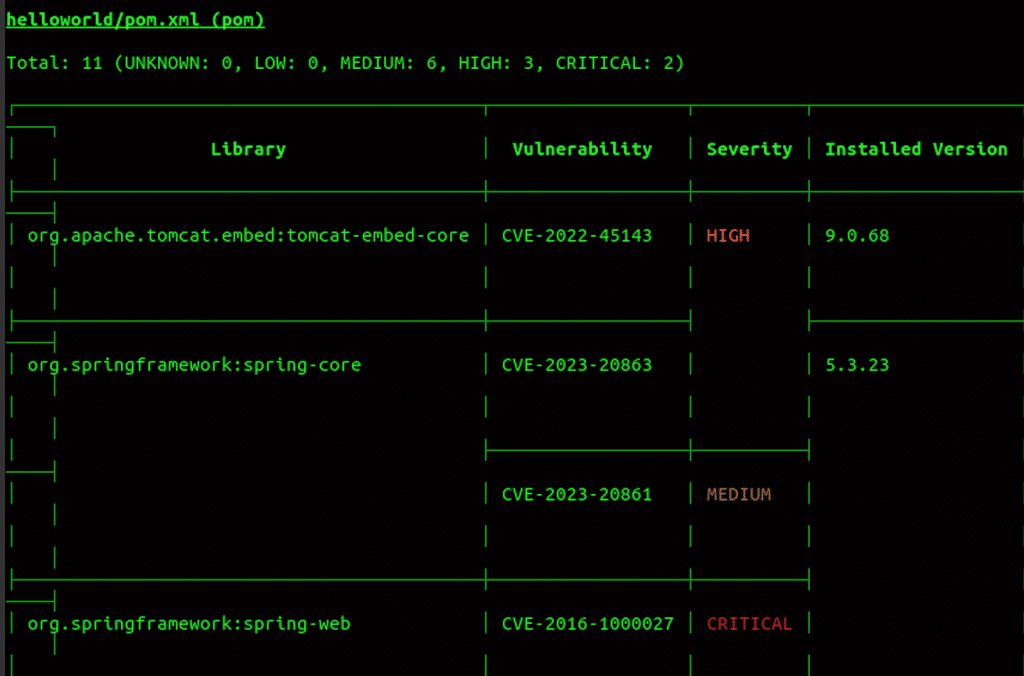
trivy fs Documents/jenkins-pipeline/It will scan the directory and shows the vulnerability in the directory as shown below.
Scan Git Repository
The command used to scan the git repository is given below:
trivy repo <repo URL>If you are using a private repository, you need to provide your git token for authentication as given below.
export GITHUB_TOKEN=,git token>
trivy repo <repo URL>It will scan the repo and shows the vulnerability in the repo as shown below.
You can also check out the official Trivy scanner video guide to see Trivy in action.
What Does Trivy Scan In Container Images?
Following are the key elements in the Docker image that are scanned by Trivy.
- Trivy can scan for vulnerabilities in a variety of package managers, including apt, yum, apk, and npm. This means that Trivy can scan for vulnerabilities in images that use a variety of different software dependencies.
- Trivy can scan for vulnerabilities in both Linux and Windows images. This means that you can use Trivy to scan images that will be running on either Linux or Windows hosts.
- Trivy can scan for vulnerabilities in images that are stored in a variety of different formats, including Docker images, tar archives, and filesystems. This means that you can use Trivy to scan images that are stored in a variety of different locations.
- Trivy can scan for vulnerabilities in Docker images running in various environments, including plain Docker containers and Kubernetes pods. This means that you can use Trivy to scan images that are running in any environment that you use.
Benefits of Container Image Vulnerability Scanning With Trivy
The following graphs shows the total vulnerabilities from the CVE database. As you can see it keeps on increasing every year.
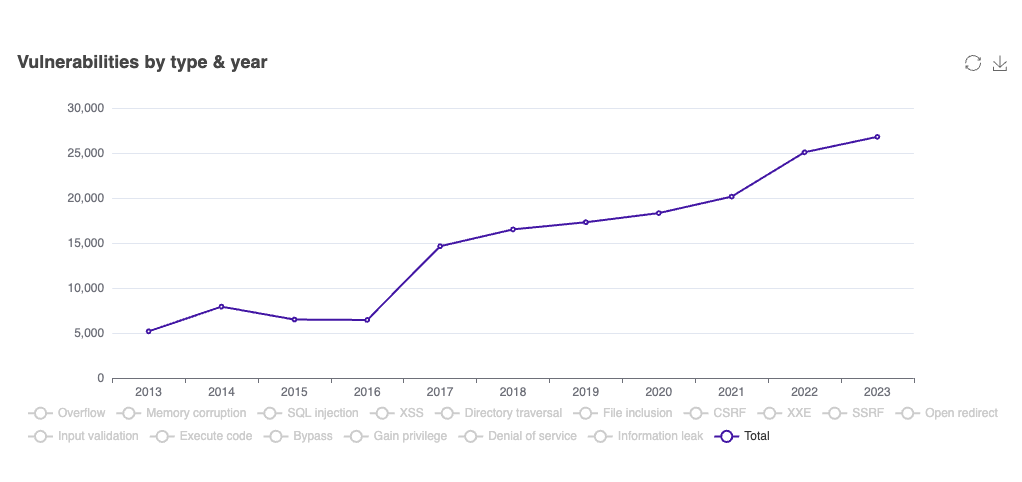
Considering the increase in vulnerabilities, there are many benefits of scanning Docker images with Trivy.
Some of the benefits include:
- Identifying vulnerabilities: Trivy can identify vulnerabilities in the packages used in your Docker images. This is particularly helpful in base image patching and application image builds.
- Improving security posture: By scanning your images for vulnerabilities, you can improve the security posture of your organization.
- Security Compliance: Many organizations are required to check their Docker images for vulnerabilities as part of the security compliance. You can achieve these standards with the help of Trivy.
Conclusion
Docker image vulnerability scanning is a must during development as well as during CI/CD process. This ensures you follow good DevSecOps principles and implement best practices to maintain robust security in your Docker based environments.
You can also use Hadolint in your CI/CD piepline before vulnerabilkity scan. It ensures you follow all the Dockerfile best practices.