It is very important to have Jenkins backup with its data and configurations. It includes job configs, builds logs, plugins, plugin configuration, etc.
Jenkins requires regular patching and plugin updates. During these processes, there is a risk of configuration issues, which could potentially lead to a Jenkins crash.
This may lead to a disruption in Jenkins service, so it is very important to back up Jenkins data periodically.
This article will cover the following three ways to back up Jenkins data and configurations.
- Using Think Backup Plugin
- Backup using Disk Snapshots
- Manual Backup
Jenkins Backup Using Thin Backup Plugin
Jenkins Thin Backup is a popular plugin for backing up Jenkins. It backs up all the data based on your schedule and handles backup retention as well.
The following are the core features of this plugin.
- Full backup
- Differential backup
- File exclusions from Backup
- Backup build results
- Cleanup of differential backups
- Archive old backups to ZIP format
Let’s get started with the setup.
Step 1: Install the Think Backup plugin.
1. Go to Manage Jenkins –> Manage Plugins
2. Click the Available tab and search for “Thin backup”
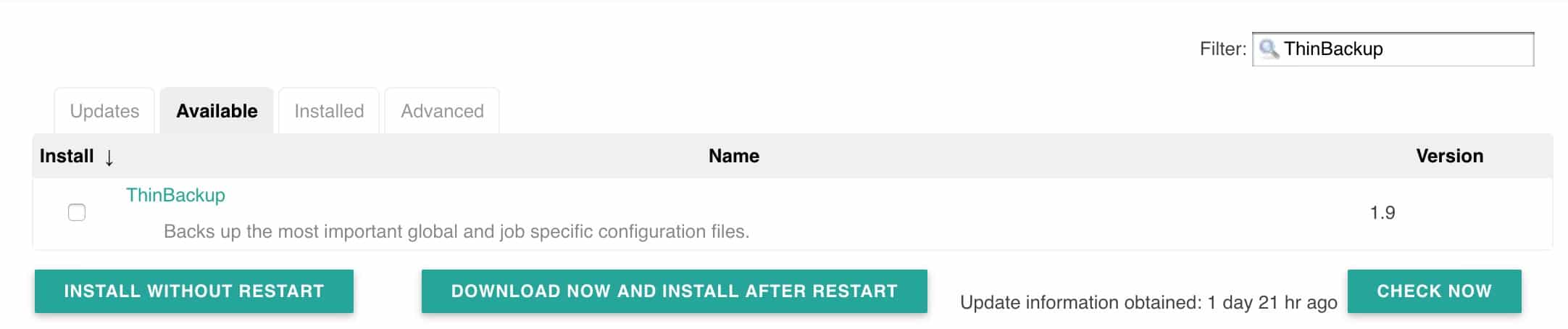
3. Install the plugin and restart Jenkins.
Step 2: Thinbackup Plugin Configuration
Once the plugin is installed, follow the steps given below to configure the backup settings.
1. Go to Manage Jenkins — > ThinBackup
2. Click the settings option.
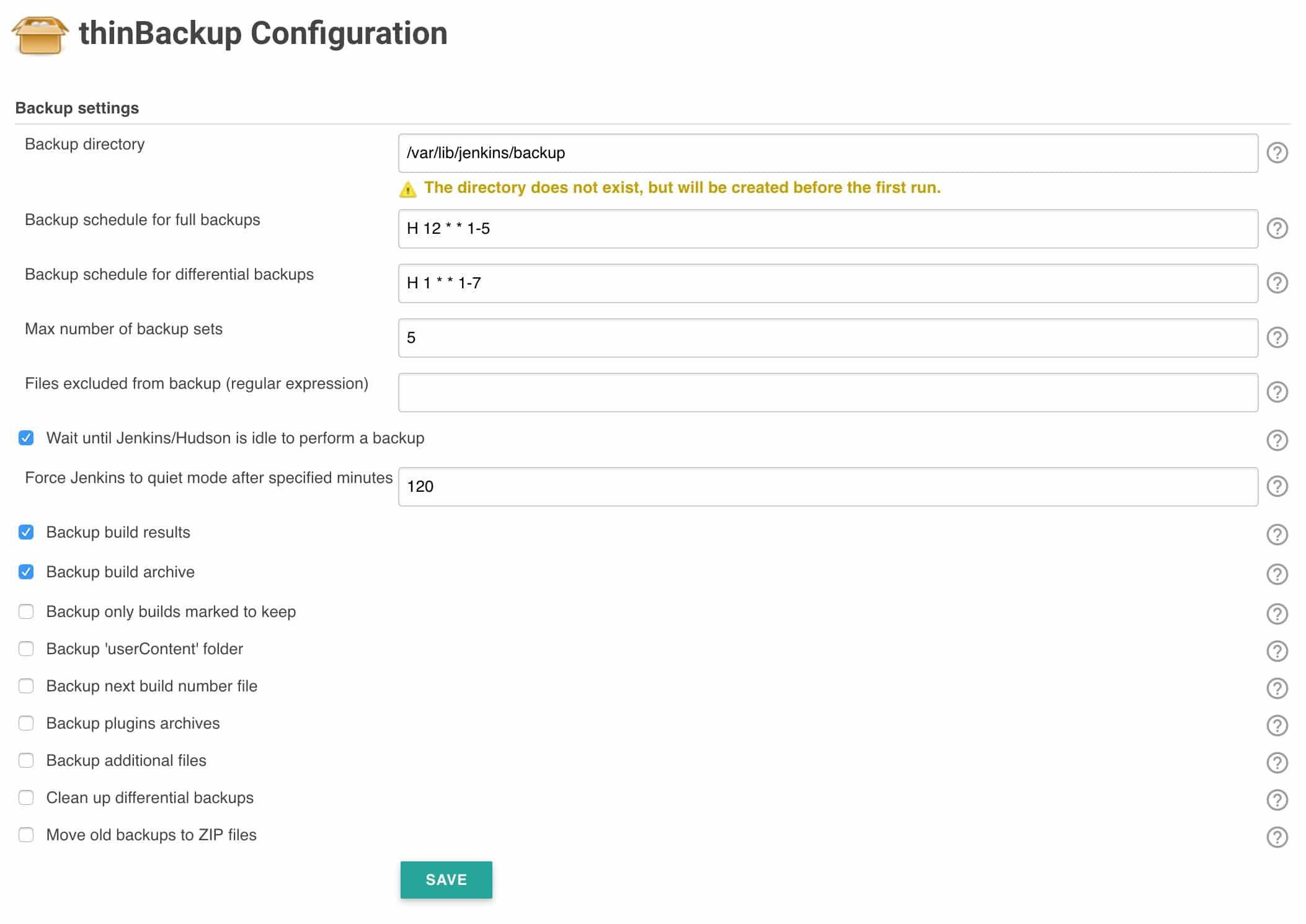
3. Enter the backup options shown below and save them. All the options are self-explanatory. The backup directory you specify should be writable by the user running the Jenkins service. The plugin saves the backup to the backup directory you specify.
4. Now, you can test if the backup works by clicking the Backup Now option. It will create a backup of Jenkins data in the backup directory you specified in the settings.
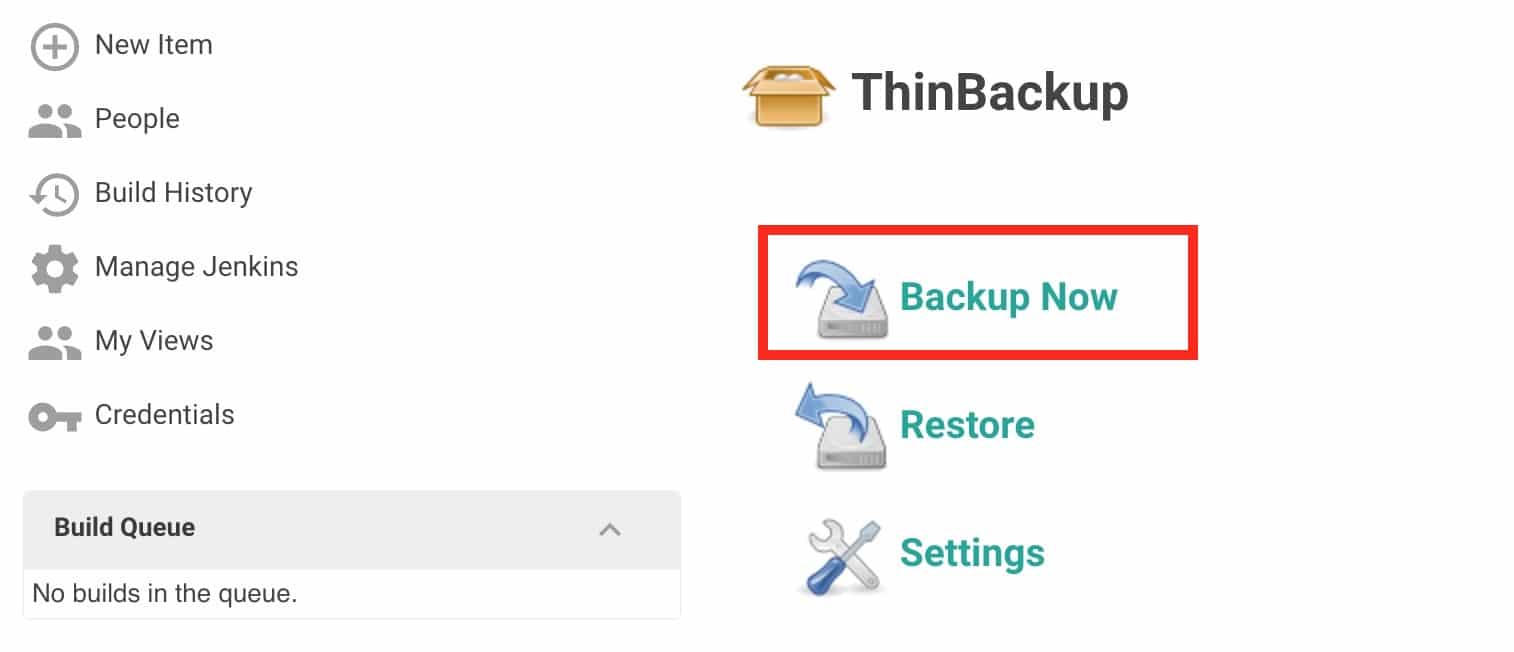
5. If you check the backup directory on the server, you can see the backup created. For every new backup, it attaches the timestamp to the folder name and keeps the old backup based on the retention policy you mentioned in the settings.
An example is shown below.
[devopscube@jenkins backup]$ pwd /var/lib/jenkins/backup [devopscube@jenkins backup]$ ls FULL-2017-08-20_05-42 FULL-2017-08-20_05-43 FULL-2017-08-20_05-44 [devopscube@jenkins backup]$
Step 3: Backing up the Jenkins Backup
Keeping the Jenkins backup in Jenkins itself is not a good idea. It is a single point of failure.
It is a must to move thin backups to cloud storage or any other backup location so that even if the Jenkins server crashes, you will have all the data.
If you are on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, you can upload the backup’s respective storage solution using a Linux CronJob
Jenkins Backup Using Disk Snapshots
As you know, Jenkins doesn’t have a database. All the configurations are stored as files in the /var/lib/jenkins folder.
All the modern private and public cloud platforms support the disk snapshot feature.
If your environment supports disk snapshots, here is what you can do during the initial Jenkins installation.
- Attach an external disk to your Jenkins server.
- Mount the disk to the server on a folder, say
/jenkins_data - If you have existing data, move all data from
/var/lib/jenkinsto/jenkins_datafolder first. - Symlink
/var/lib/jenkinsto/jenkins_data. - Restart Jenkins and check if Jenkins is using the newly mounted disk.
- Now, you can take a timely snapshot of the extra disk. This will serve as a point-in-time backup for your Jenkins.
For some reason, if your Jenkins server crashes or data gets corrupted, create a new disk from the existing snapshot backup and replace it in the Jenkins server. Jenkins will have all the data from the snapshot point in time backup.
If you are on the AWS cloud, use the EBS snapshot automation feature to back up the Jenkins data disk.
Also, if you run Jenkins on Kubernetes, you can back up the persistent volume.
Also, we suggest you use the Thin backup plugin in conjunction with disk snapshots.
Jenkins Manual Backup
If you don’t have any option using Thinback or disk snapshot, you can go for manual backups.
First, stop Jenkins to ensure the data is not being written or modified during backup. You can stop Jenkins with the following command:
sudo systemctl stop jenkinsCreate a tar.gz archive of the Jenkins home directory to ensure all files are preserved
tar -czvf jenkins_backup.tar.gz /var/lib/jenkinsYou can also copy the directory to a backup location:
cp -r /var/lib/jenkins /path/to/backup/locationYou can also automate this process using Linux cron Job.


6 comments
Top content as always Bibin brother Thanks for sharing
Can I take differential backup of one jenkins server and use this backup to restore in another jenkins server using ThinBackup Plugin?
If yes what will be the challenges?
Can I use backup of one jenkins server and use this backup to restore in another jenkins server
If yes what will be the challenges
Hi Pallavi, remember me?
We can take a copy of /var/lib/jenkins. this is what thin backup does. use the same by replacing the files and permissions.
Yes, I use ThinBackup quite a lot. I think it should be shipped with Jenkins itself. Super handy.
Everyone using Jenkins will have this. It should be part of Future Jenkins releases!