If you want to know what is service discovery and how it works, this guide is for you. I have explained service discovery, its patterns, and its tools with practical examples.
What is Service Discovery?
Service discovery is a method of identifying and accessing devices and services automatically on a network. It is a common pattern followed in distributed systems and microservice architectures. Because servers in such an environment may be short-lived and relying on static IP addresses to connect with these systems is not reliable and may lead to system failures and errors.
What Does Service Discovery really mean?
Let's understand service discovery with a real-world example.
Let's say you have an application that's deployed on multiple servers and a database cluster consisting of six servers. The application needs to connect to the database in order to store and retrieve data.
In order to make this connection, the application needs to know the network locations (IP address and port number) of the database cluster. One way to do this is to hardcode the IP address and port number in the application properties. However, this approach has a few drawbacks:
- It's not scalable: If the database cluster is fully automated, the IP address of the database servers could change during patching or failover scenarios. Or more servers could be added to the cluster to scale the cluster. In this case, you'll need to update the application properties on every server in the application cluster.
- It's error-prone: If you mistype the IP address or port number, the application won't be able to connect to the database.
- It's not flexible: If you need to add or remove database nodes with different IP addresses, you'll need to update the application code.
- You could use a DNS endpoint for the servers. However, if the IP changes, you need to manually update the IP address of the DNS.
Therefore, an efficient mechanism is needed for the application to access healthy database servers at all times.
Here you can use a service discovery approach. A service discovery system is a tool that allows servers/services to register themselves and discover other services.
In our example, the database cluster nodes would register themselves with the service discovery system (service registry), and the application servers would use the service discovery system (service registry) to find the IP addresses of the database servers.
Now let's look at what is a service registry. The key component of service discovery.
Service Registry
It is a centralized service registry that maintains information about available services. In most cases, it is a key-value store database. The following image shows the dashboard of a service registry of a service discovery tool called consul.
Here is how it works in our example.
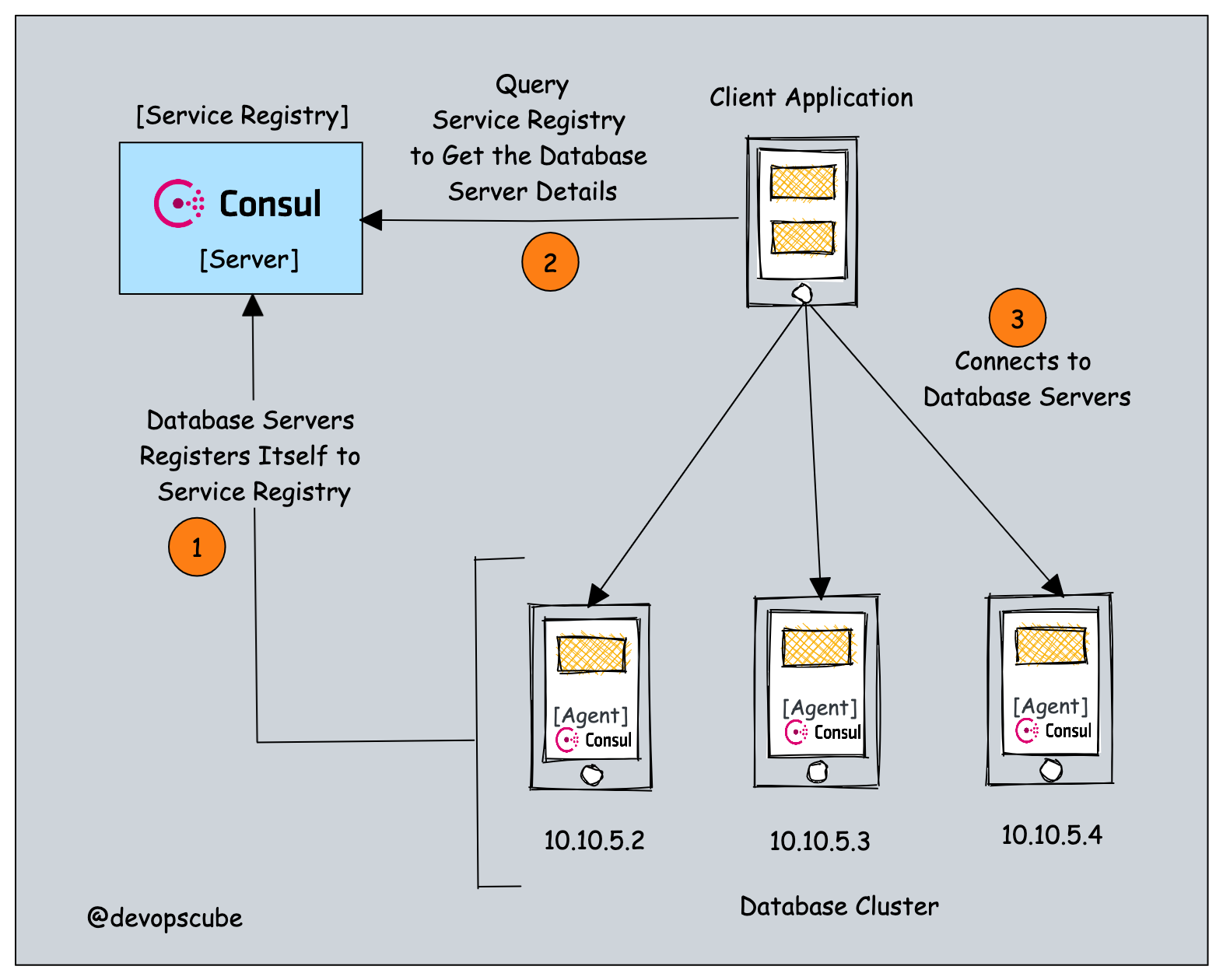
- When the database server comes up, its registers itself as an available service with the service registry. It provides its IP address, port number, and health check URLs of the application(Ex: MySQL application running on 3306). It happens via a code library or a service discovery agent running on the database nodes.
- The application server needs to connect to the database, so it uses a service discovery library/agent to connect to the service registry via API/DNS calls and queries for the available database server IPs.
- Since the database server has already registered itself, the application servers would be able to retrieve the IP and port information from the service registry and use it in its configuration to retrieve and store data.
The following gif shows an example of the self-registered node/service in the consul service registry.

What Happens if a Registered Server Fails?
If a database server fails, the service registry identifies it as such since it has a health check associated with each node. The service registry then marks the node as unhealthy. The agent running in the application server continuously monitors for changes in the service registry and thus identifies the node failure. As a result, the application servers remove the unhealthy database IP from their configurations. All of these changes occur within seconds.
What Happens if a New Server is Registered?
The workflow is the same. The new database server registers itself. The application server identifies it via the service registry and adds it to its configuration.
Types of Service Discovery
There are two types of service discovery patterns. Let's have a look at it.
1. Client-Side Service Discovery Pattern
In the client-side discovery pattern, the client, for example, an application is responsible for interacting with the service registry to get the service details.
For example, the client queries the service registry to get information about the available backend services.
In this model, the client has to implement the service discovery query logic in the application framework. For example, if an application server wants to get the available database server details, the application should implement the query using the service discovery client library to query the service registry.
2. Server Side Service Discovery Pattern
In the server-side discovery pattern, the request goes to a load balancer (server) and the load balancer connects to the service registry to get the IP addresses of the healthy backend servers.
Here the server component implements the agent or library to query the service registry. One classic example of this model is Nginx load balancing using service discovery. Here the clients (service consumers) directly talk to the Nginx load balancer and the load balancer queries the service registry to get the list of backend servers to route the traffic.
The following image shows service side service discovery using consul.
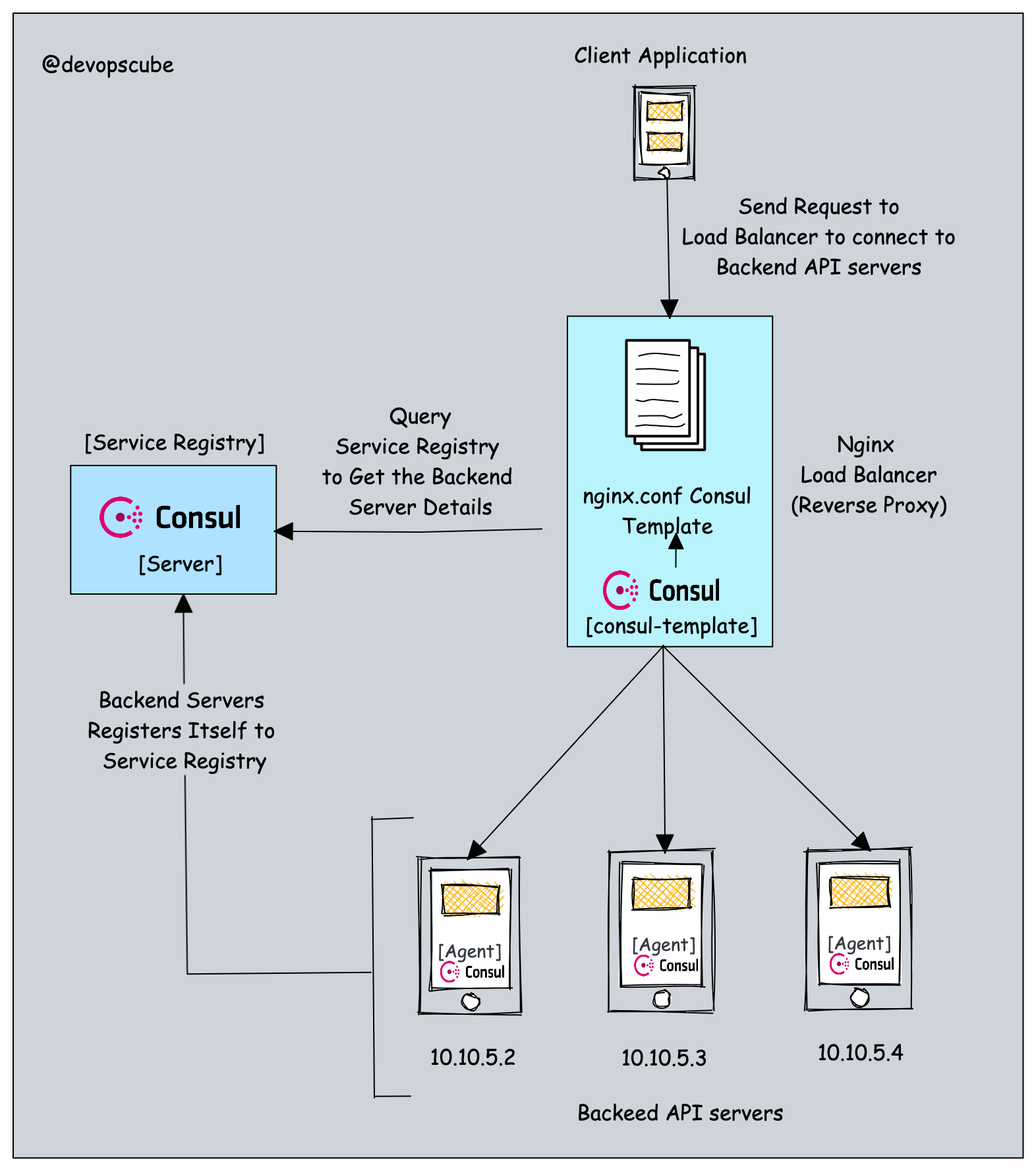
If you are aware kubernetes, the ingress controller implements the service side service discovery.
Service Discovery Tools
To implement the concept of a service registry you need specific tools. Following are the two common open-source service discovery tools.
- Hashicorp Consul
- etcd (primarily used for Kubernetes service discovery)
You can use HTTP REST API, DNS, and gRPC protocol with these service discovery tools.
Service Discovery Hands-On
If you want to get your hands on service discovery concepts, you can try setting up Nginx reverse proxy configuration using consul.
I have published a detailed hands-on guide for the same. Check out the Service Discovery Example Using Consul
Conclusion
Service discovery is a must-know concept for developers and devops engineers. Most of the distributed systems and microservices architectures implement service discovery.
One class example is Kubernetes. It relies heavily on service discovery using etcd datastore.

![What is Service Discovery? [Explained With Examples]](/content/images/size/w100/2025/03/service-doscovery-explained-1.png)