In this blog, you will learn how to configure ingress TLS certificates for Kubernetes Ingress resources.
This blog is based on an actual demo done using demo.mlopshub.com public DNS and its self-signed certificate. If you do not have a domain name, you can use the workstation host file for DNS resolution or the curl resolve command.
Prerequisites and Assumptions
For this blog, the assumption is you have a working ingress controller setup, and you want to configure TLS for your ingress resource.
This blog is part of the Kubernetes Ingress series. If you do not have an ingress controllers setup or want to understand Kubernetes ingress concepts in detail, please go through the following blogs first.
- Kubernetes Ingress Tutorial - Covers all Ingress concepts
- Setup Nginx Kubernetes Ingress controller - Detailed guide on ingress controller
Obtaining Kubernetes Ingress SSL/TLS Certificates
The basic requirement for ingress TLS is a TLS/SSL certificate. You can obtain these certificates in the following ways.
- Self-Signed Certificates: TLS certificate created and signed by our own Certificage Authority. It is great optionfor development environments where you can share the rootCA with the team so that browsers can trust the certificate. Check out create self-signed certificate blog to create your own certificates.
- Purchase an SSL Certificate: You need to buy an SSL certificate from a well-known certificate authority trusted by browsers & operating systems for production use cases. Check out the top SSL Providers for more information.
- Use Letsencrpt Certificate: Letsencrypt is a non-profit trusted certificate authority that provides free TLS certificates.
Every SSL certificate comes with an expiry date. So you need to rotate the certificate before it expires. For example, Letsecrypt certificates expire every three months. I will talk about automated certificate rotation towards the end of the article.
Also, if you are working on an internal application, most organizations have their own PKI infrastructure for providing SSL certificates for internal applications. You can request the network/security team to provide the certificates.
How Does Ingress TLS/SSL Work?
Adding TLS to ingress is pretty simple. All you have to do is,
- Create a Kubernetes secret with
server.crtcertificate and server.key private key file. - Add the TLS block to the ingress resource with the exact hostname used to generate cert that matches the TLS certificate.
SSL is handled by the ingress controller, not the ingress resource. Meaning, when you add TLS certificates to the ingress resource as a kubernetes secret, the ingress controller access it and makes it part of its configuration.
For example, in the Nginx controller, the SSL certificates are dynamically handled by the following block in nginx.conf
ssl_certificate_by_lua_block {
certificate.call()
}The following diagram shows the high-level ingress TLS workflow.

Configure Ingress TLS/SSL Certificates
Let's look a the steps in configuring TLS in ingress.
Deploy a Test Application
Let's begin by deploying a sample application. We will use this application to test our ingress TLS.
Create a dev namespace.
kubectl create ns devSave the following YAML as hello-app.yaml. It has a deployment and service object.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-app
namespace: dev
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: "gcr.io/google-samples/hello-app:2.0"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-service
namespace: dev
labels:
app: hello
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: hello
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
Deploy the test application.
kubectl apply -f hello-app.yaml Create a Kubernetes TLS Secret
server.crt and server.key SSL files from a Certificate authority or your organization or self-signed.The SSL certificate should be added as a Kubernetes secret. It will be then referred to the ingress resources TLS block.
Let's create a Kubernetes secret of type TLS with the server.crt and server.key files (SSL certificates). We are creating the secret in the dev namespace where we have a hello app deployment.
Execute the following kubectl command from the directory where you have the server.crt and key files or provide the absolute path of the files . hello-app-tls is an arbitrary name.
kubectl create secret tls hello-app-tls \
--namespace dev \
--key server.key \
--cert server.crtFollowing is the equivalent YAML file where you have to add the crt and key file contents.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: hello-app-tls
namespace: dev
type: kubernetes.io/tls
data:
server.crt: |
<crt contents here>
server.key: |
<private key contents here>Add TLS block to Ingress Object
The ingress resource with TLS has to be created in the same namespace where you have the application deployed. So we create the example ingress TLS resource in dev namespace.
Save the following YAML as ingress.yaml. Replace demo.mlopshub.com with your hostname.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: hello-app-ingress
namespace: dev
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- hosts:
- demo.mlopshub.com
secretName: hello-app-tls
rules:
- host: "demo.mlopshub.com"
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/"
backend:
service:
name: hello-service
port:
number: 80As you can see, I have added the TLS block with the hostname (demo.mlopshub.com) and tls secret we created in the previous step. I have created the self-signed TLS certificate with emo.mlopshub.com domain.
tls:
- hosts:
- demo.mlopshub.com
secretName: hello-app-tlsThe host in the TLS block and rules block should match.
🎉 Congratulations you have deployed Ingress with TLS.
Validate Ingress TLS
You can validate the Ingress TLS using the curl command as well as the browser.
From the CLI, run the curl command as given below with your domain name.
curl https://demo.mlopshub.com -kvIn the output, under server certificate, you can validate the certificate details as shown below.

From the browser, access the domain and click the Lock icon to view the certificate details. If you have a valid certificate, you will see the information as shown below.
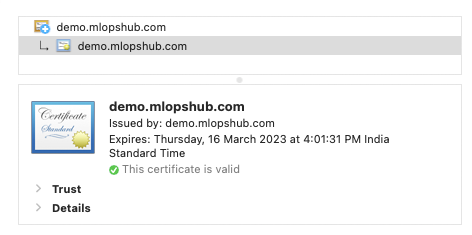
If you don't have a valid certificate or if the ingress TLS configuration is wrong, you will see "Your connection is not private" security warning and if you check the certificate details, you will see the certificate name as "Kubernetes Ingress Controller Fake Certificate".

Kubernetes Ingress Controller Fake Certificate is the default SSL certificate that comes with the Nginx ingress controller. If you check the nginx.conf of the Nginx controller, you will see the configured default certificates as shown below.

Ingress SSL Termination
By default, SSL gets terminated in ingress the controller
So all the traffic from the controller to the pod will be without TLS (decrypted traffic)
If you want full SSL, you can add the supported annotation by the ingress controller you are using. For example, In the Nginx ingress controller, to allow SSL traffic till the application, you can use the nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTPS" annotation. For this, your application should have SSL configured.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have learned to configure ingress TLS certificates with kubernetes ingress TLS example
Also, you can configure more TLS parameters using annotations. The annotations differ between different ingress controllers.
Also, if you are learning Kubernetes, you can check out my Kubernetes tutorials for beginners.
Drop a comment if you need any clarification or tips to share.

