In this guide, we will build an event-driven architecture using AWS EventBridge and AWS Lambda.
You will learn how to create an EventBridge rule that automatically triggers a Lambda function. As an example, we will use a cron expression to fetch S3 object details
At the end of this blog, you will have learned
- Create an EventBridge Rule
- Create a AWS Lambda function
- Trigger the Lambda function using the EventBridge Rule
Before we move to the setup, you need to know what the AWS Lambda service and the AWS EventBridge service are.
What is AWS EventBridge?
AWS EventBridge is a fully managed serverless event bus that lets you create custom events like cron expressions or capture events from AWS services and external applications.
These events can then be routed to targets like Lambda, SQS, or SNS
For example, if an EC2 instance goes down, EventBridge can automatically capture the event and send an email to the respective team.
It also helps in,
- Generating reports
- Periodical backups or cleanup
- Running maintenance tasks
What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a serverless service where we can directly run our code without managing the servers.
To run our code, we can manually trigger the function or use any automatic trigger, such as an event from another service.
If you are new to AWS Lambda, check out our simple blog to deploy serverless framwork on AWS Lambda.
Now, we can see the overview of the setup workflow.
EventBridge + Lambda Workflow
The following is the workflow diagram of the integration of AWS EventBridge and Lambda.
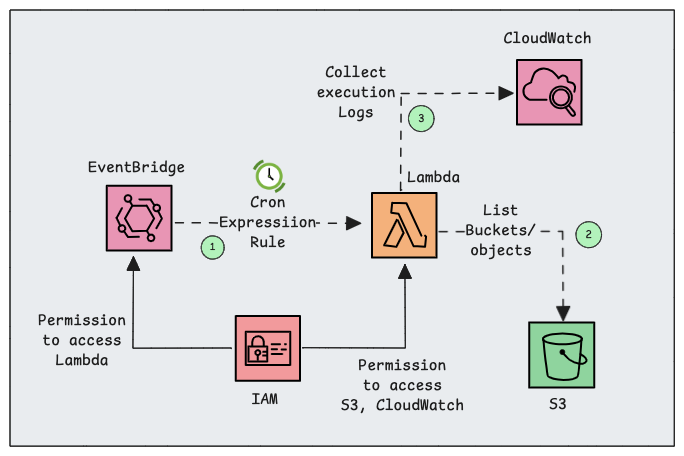
Here is how the workflow looks.
- The EventBridge Rule is created to trigger the Lambda function on a periodic interval.
- An EventBridge Rule is attached to an IAM Role to access the Lambda.
- Once the event is triggered, the Lambda function will activate and run the script.
- Lambda function is attached with the IAM Role to access specific AWS services (e.g., S3, CloudWatch)
- During the execution, metrics and logs will be stored in CloudWatch so that we can monitor them.
Now, we can start the setup.
Setup Prerequisites
To achieve this setup, we need the following requirements.
- AWS Account - Required permission to create and manage services
- AWS CLI, [Local Workstation]
Now, we can start the setup by creating a Lambda Function.
Creating a Lambda Function
To begin the setup, you need to open the Lambda service and, from the home page, click the Create a function button to create a function.
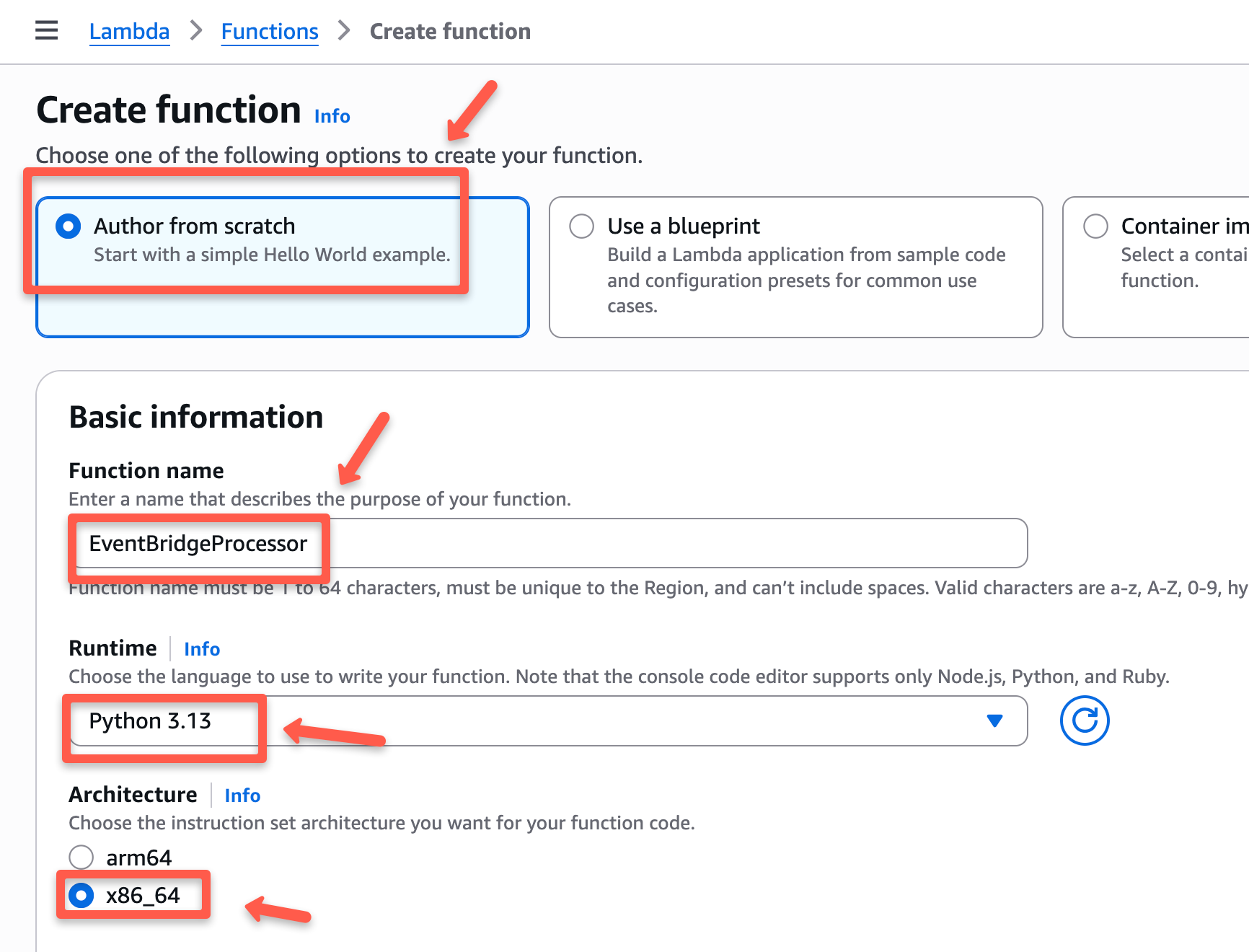
On the function creation page, select the option of Author from scratch to create your own function, give a name to the function, and select a runtime where you are comfortable to write scripts.
For this, I am choosing the Python 3.13 runtime, and I am keeping the rest of the configuration as the default.
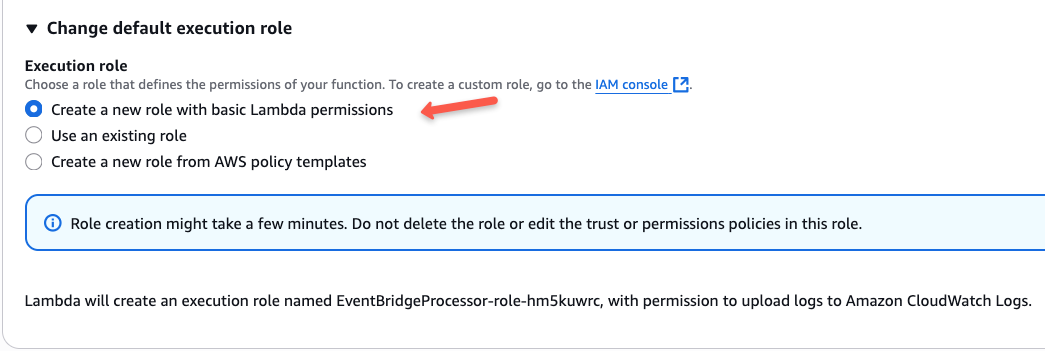
When scrolling down, you can see a section to create an IAM Role for your Lambda function.
This IAM Role defines the permissions of which AWS services that the Lambda can access.
For example, if I write a script for Lambda to list S3 buckets, it needs the required permission to access the S3.
So in the execution role section, I am selecting "Create a new role with basic Lambda permissions" to create a Role.
But if you already have an existing role with the necessary permissions, you can use that as well.
On the same page, you can also configure networking and Encryption using KMS. You can configure them if required.
The basic IAM Role will have permission to CloudWatch to write the Lambda logs, but we need to add the S3 permission on this Role.
Once the role creation is completed, open the created IAM Role and add the S3 permission.
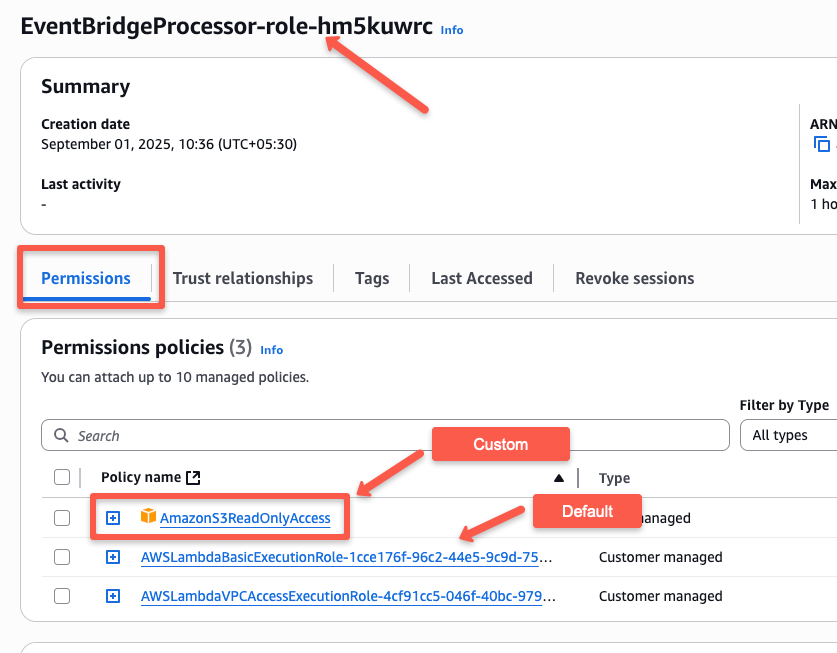
Now, we have our IAM Role ready for the Lambda function with required permission.
Once the function is created, you will reach a page similar to the following one.
Now, we need to configure the Function code.
For demo, I am adding a Boto3 script to list the S3 buckets and their object details.
import boto3
# This script lists all S3 buckets and their objects using the Boto3 library in Python.
s3 = boto3.client('s3')
list_buckets = s3.list_buckets()
bucket_names = [bucket['Name'] for bucket in list_buckets['Buckets']]
for bucket in bucket_names:
print(bucket)
def list_objects_in_bucket():
list_objects = s3.list_objects(
Bucket = source_bucket
)
if 'Contents' in list_objects:
for obj in list_objects['Contents']:
print(f"Object: {obj['Key']}, Last Modified: {obj['LastModified']}, Size: {obj['Size']} bytes")
else:
print("No objects found in the bucket.")
for source_bucket in bucket_names:
print(f"Source Bucket: {source_bucket}")
list_objects_in_bucket()
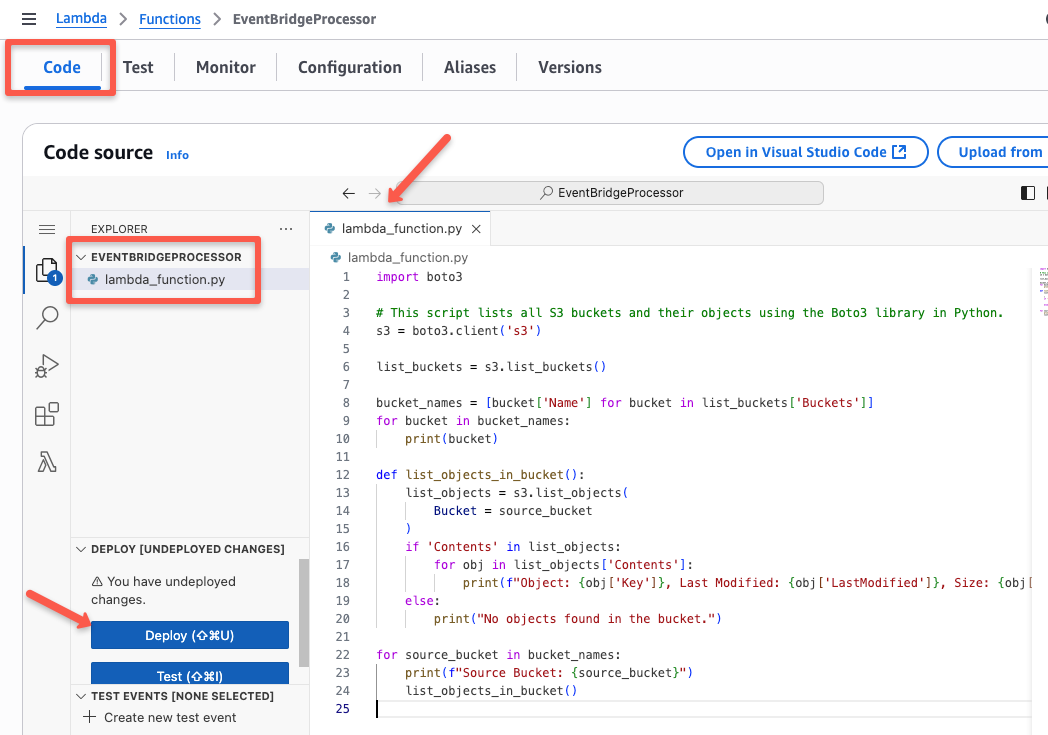
Now, we need to create an event to trigger this lambda function automatically.
Configuring AWS EventBridge Rule
We are now selecting one specific configuration in EventBridge.
We will create a Rule with a scheduling expression to define how often it should run.
In our case, the Rule will periodically (e.g., every 5 min) trigger the Lambda function that we created in the previous step.
Open the EventBridge service from the console, select the rules section, and click Create rule to configure a rule.
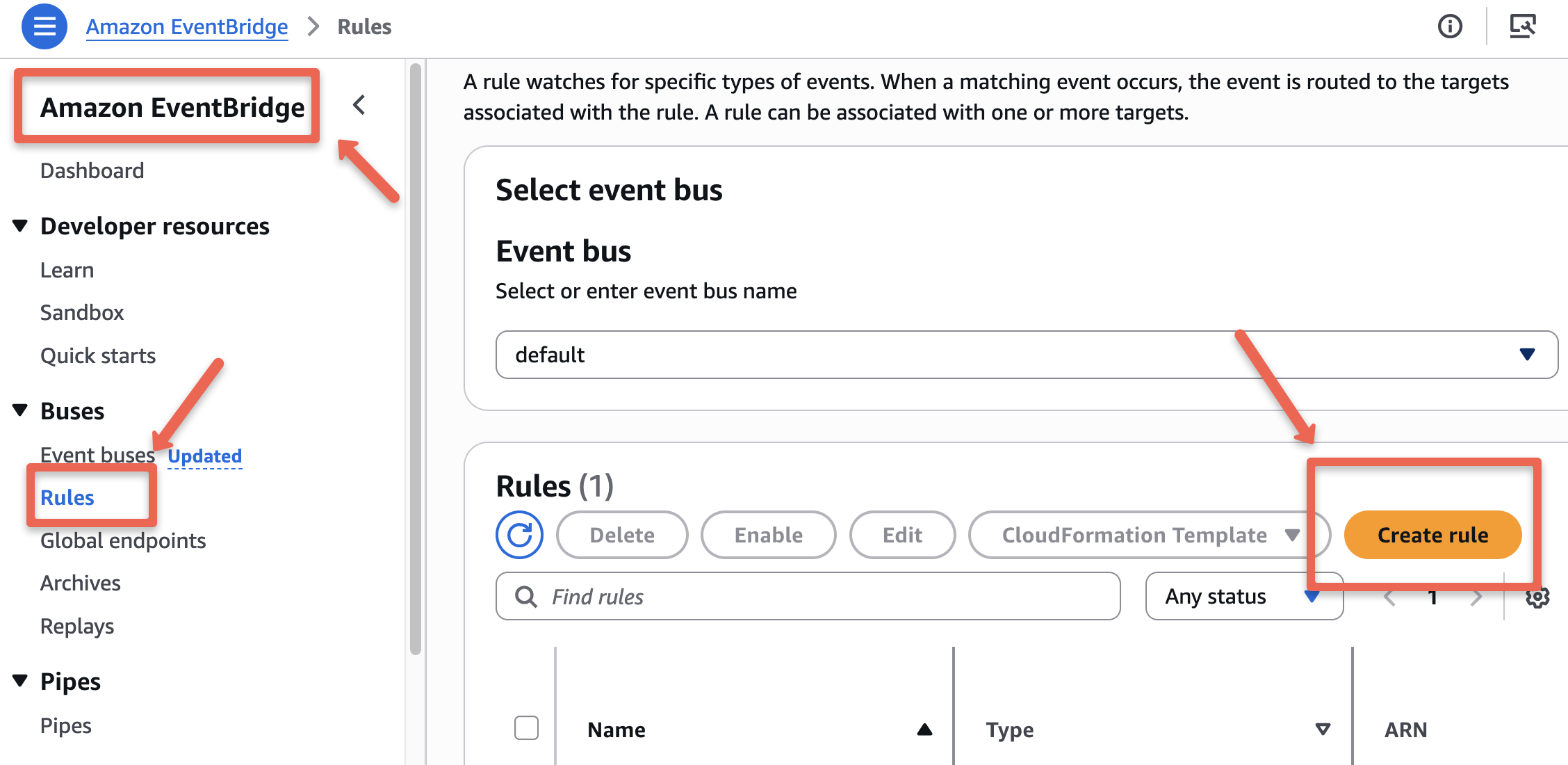
On the first page, give a name to the rule and select the rule type as Schedule
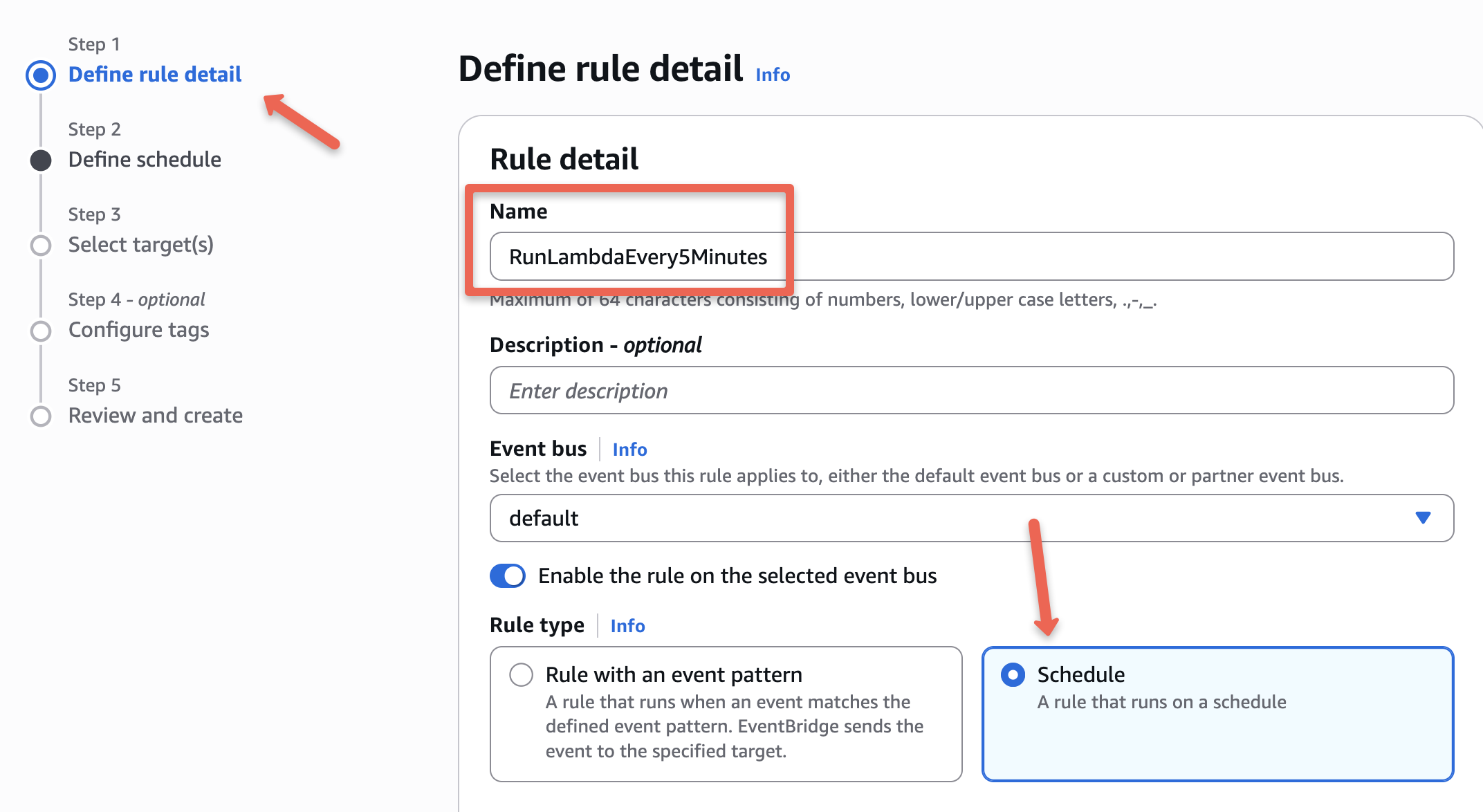
On the next page, you will see two schedule patterns, which are "One time schedule" and "Recurring schedule".
We select the recurring schedule to configure the cron expression.
Unlike the regular cronjob, EventBridge cron expression has an additional field to add the year.
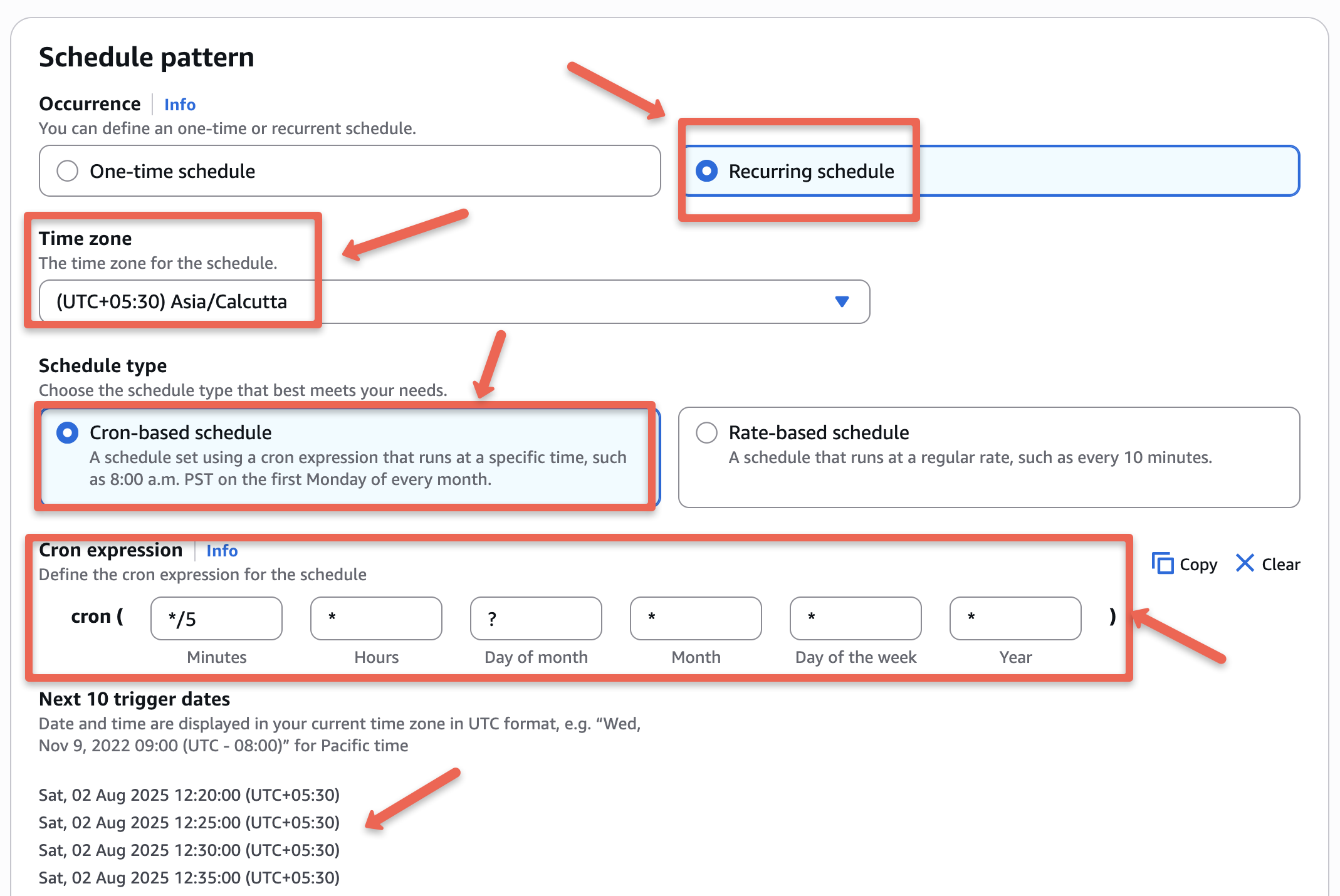
Also, choose the flexible time window option to "Off", but if you want, set when the EventBridge rule should start.
There are additional configurations, such as timeframes, that you can configure if required. For now, we are keeping the rest of the configurations as default values.
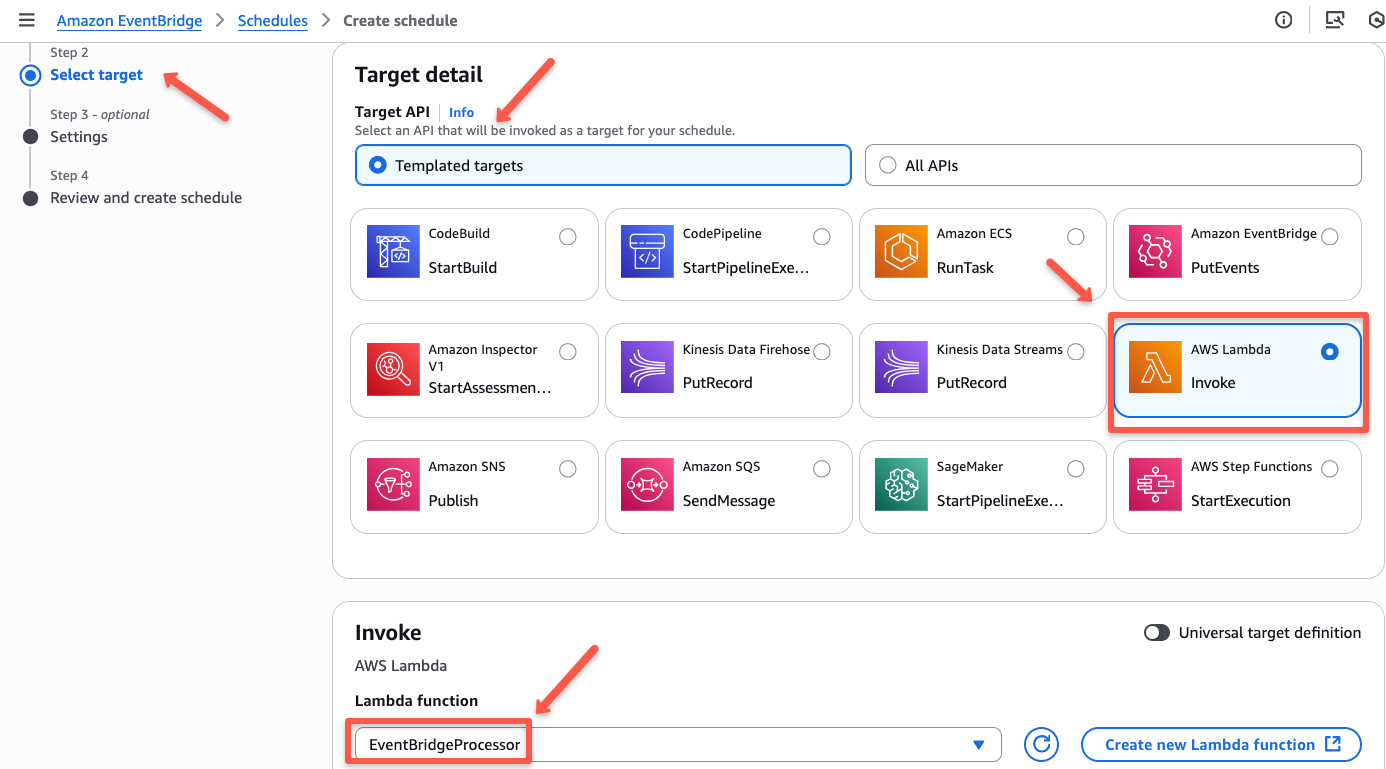
On the next page, you need to select the target. In our case, it is Lambda. Once you select Lambda, you will get a list to select the Lambda function.
On the next page, you can configure the settings, such as scheduling state, after completion action, retry policy, encryption, and permissions. You can customize them if required.
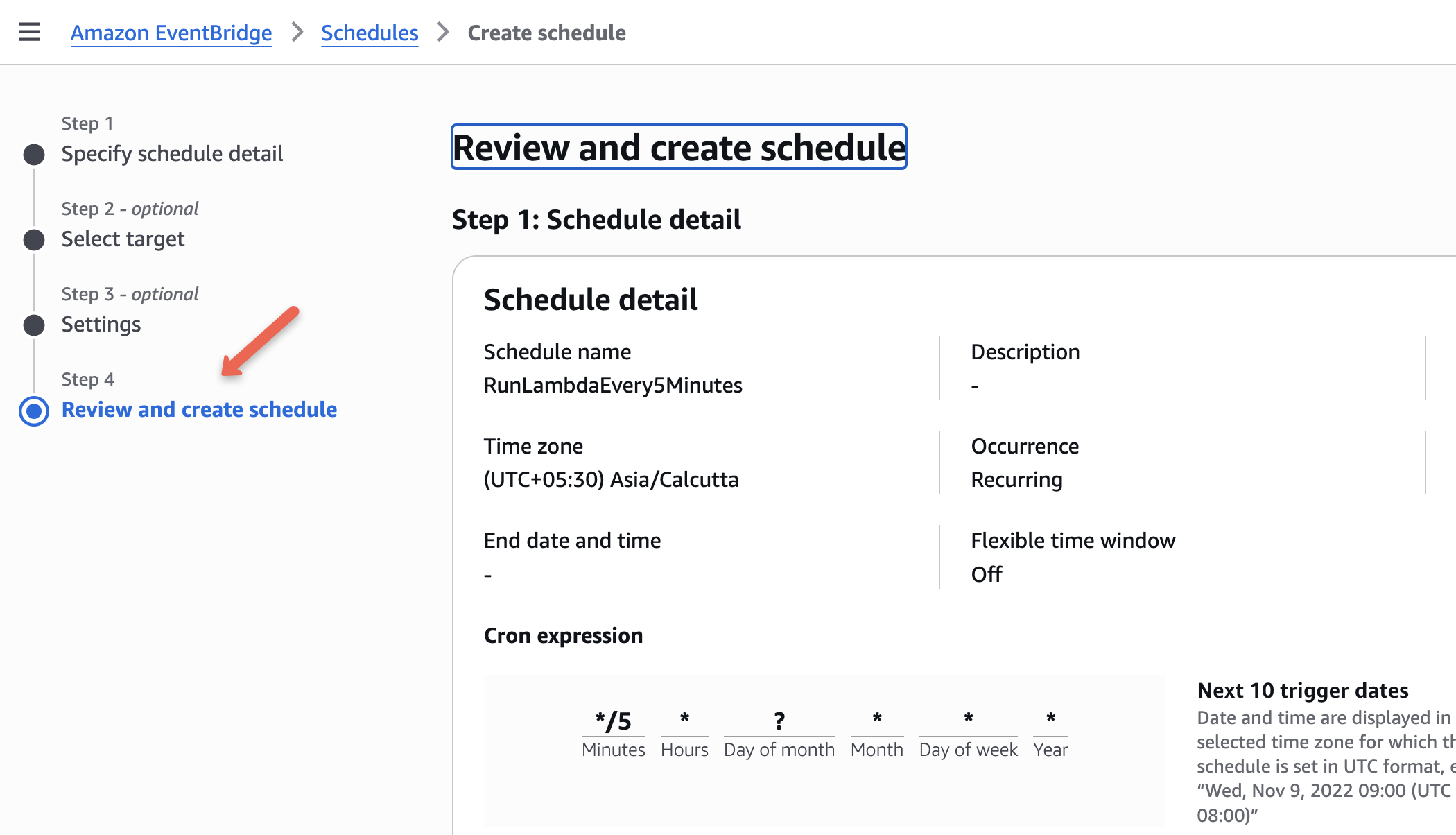
On the last page, you can review all the configurations that you have given, and then schedule the rule.
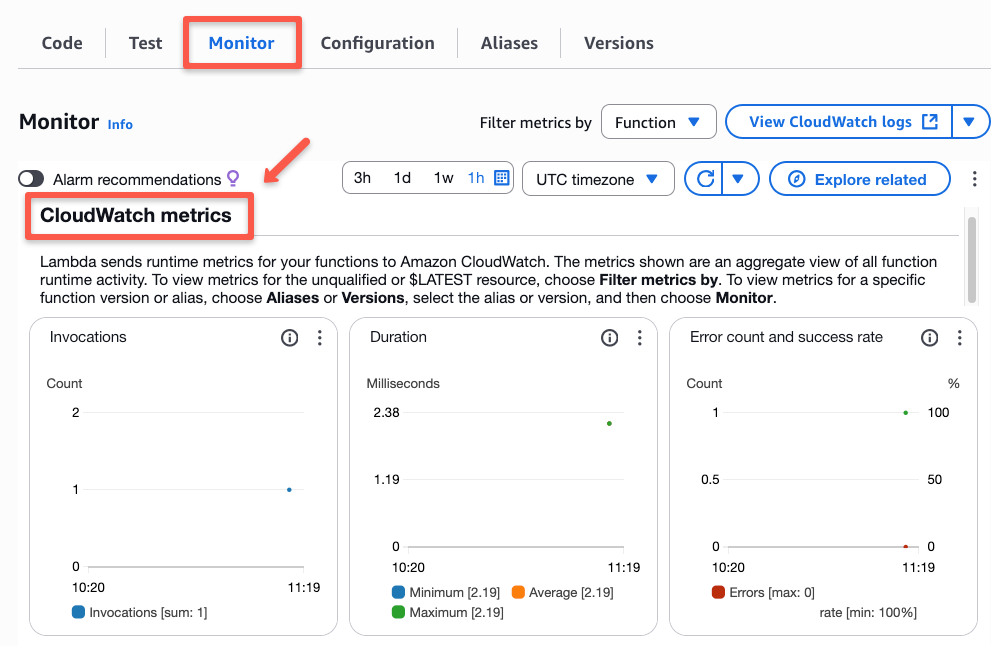
Testing the Setup
Let's wait a few minutes to trigger the first event. Once the event is triggered, the metrics and logs will be stored in CloudWatch.
To see the logs, scroll down the page where you can see the execution logs.
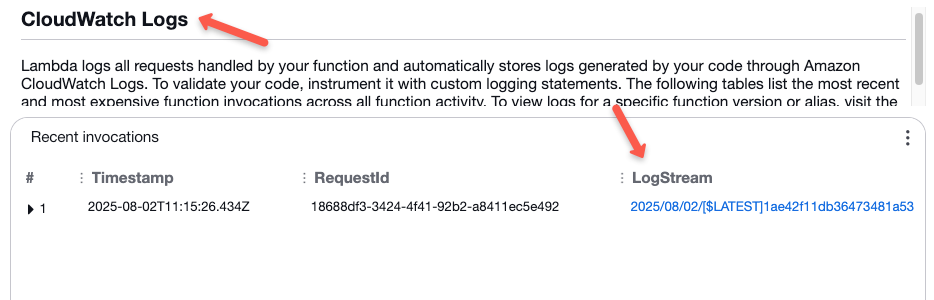
Clicking the log stream will show you the execution steps.
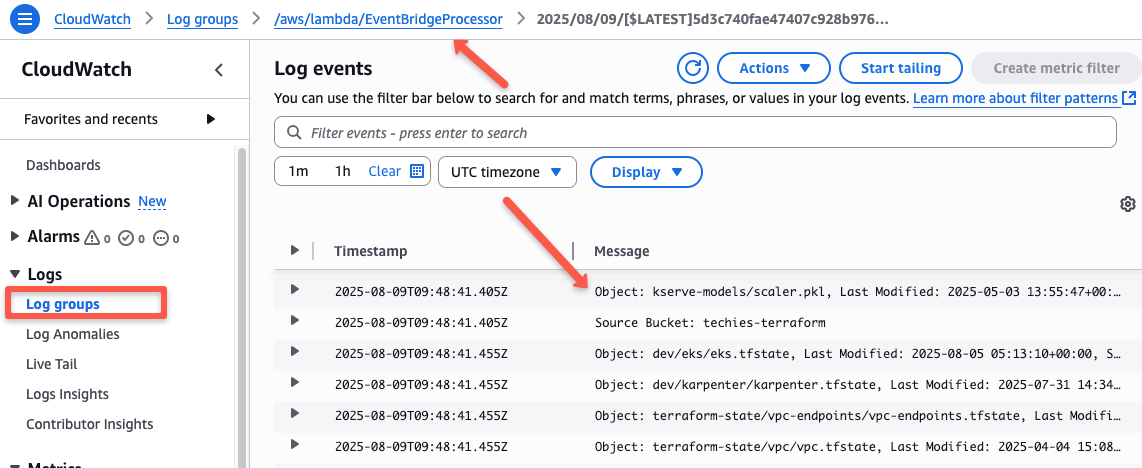
This ensures that the EventBridge Rule is triggering the Lambda function. You can extend this with your use cases like, send this report as an email using SES.
Cleanup the Setup
Now, we can start the cleanup process
Let's start by disabling the event and deleting the rule from the EventBridge
Disabling the event will not trigger the lambda function, so if we need it again, we can enable it again.
Now, we can delete the event rule.
Once the EventBridge Rule is deleted, we can delete the Lambda function.
Now, we have cleaned up the entire setup.
DevOps Use cases
Following are some of the key DevOps use cases for EventBridge in enterprise environments.
- Organizations with many AWS accounts (for dev, test, prod etc) send audit logs (e.g. IAM changes, ECR image deletions) from all accounts into a central EventBridge event bus. Then filter the events to to catch suspicious events and send alerts
- You can also ingest events coming from SaaS providers (like monitoring tools, CRMs) and integrate them into internal workflows. For example, receive alerts from Datadog, PagerDuty, then trigger internal remediation.
- When a file is uploaded to an S3 bucket, it can trigger ETL or Lambda function to process data.
- If a database record changes (e.g. DynamoDB stream), trigger downstream services.
Conclusion
The event driven workflow is quite vast, so depending on your use cases, you can configure them with other services.
Both the services are serverless so you will pay for what you use. The pricing of the AWS EventBridge and Lambda depends on the events, requests, and the duration of the execution.


