In this comprehensive ingress guide, you will learn how to setup Nginx ingress controller on Kubernetes and configure ingress using DNS.
If you want to understand how Kubernetes ingress works, read my Kubernetes Ingress Tutorial. for beginners. I have explained all the core ingress concepts including how an ingress object works with an ingress controller.
There are two Nginx ingress controllers.
We will be using the Kubernetes community Nginx controller.
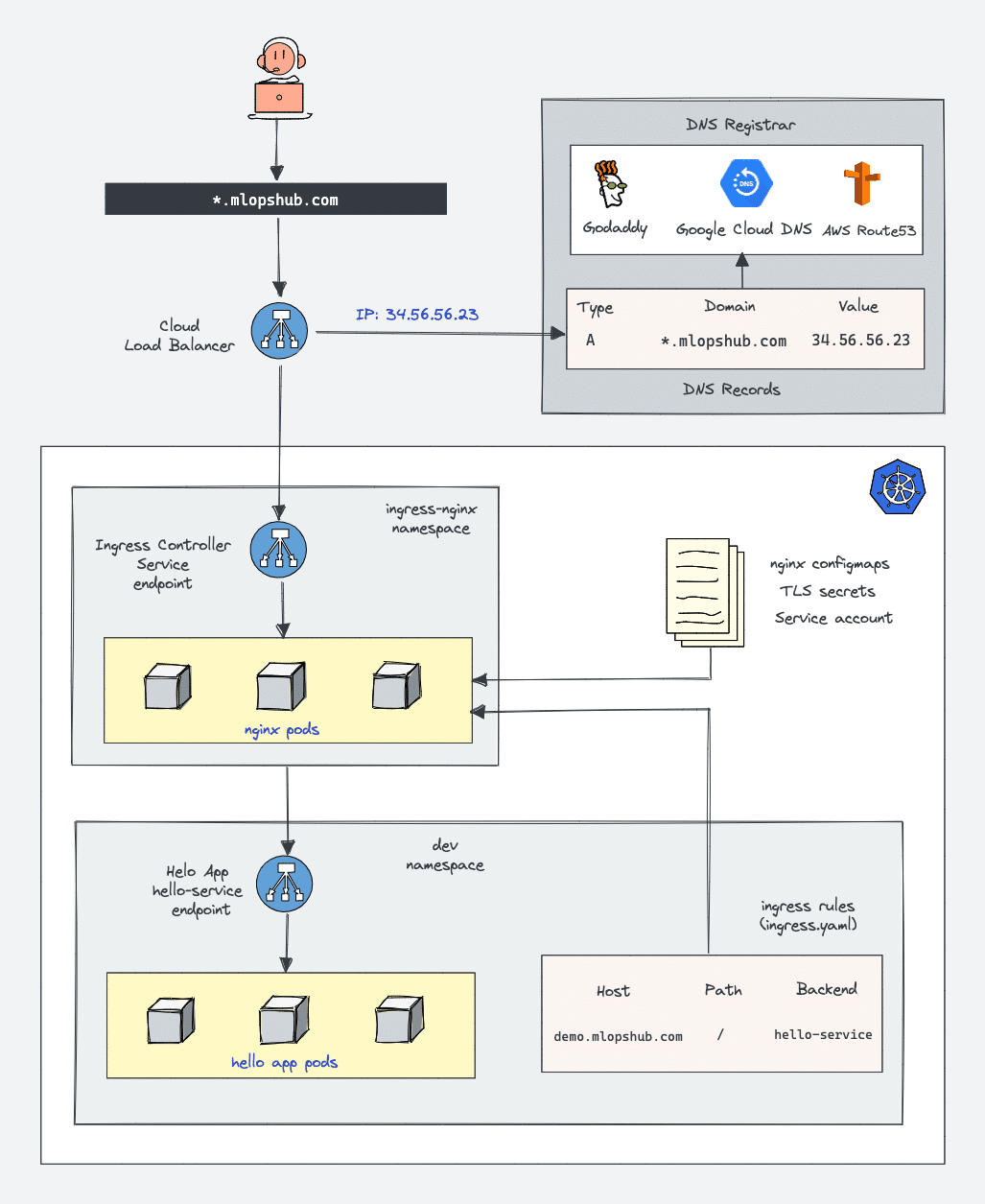
Ingress & Nginx Ingress Controller Architecture
Here is a high-level architecture of Kubernetes ingress using the Nginx ingress controller. In this guide, we will learn to build the setup in the architecture.
(Note: Click the image to view in high resolution)
Prerequisites
- A Kubernetes cluster
- kubectl utility installed and authenticated to kubernetes cluster.
- Admin access to kubernetes cluster.
- A valid domain to point to ingress controller Load Balancer IP. (Optional)
If you are trying this setup on Google Cloud, assign admin permissions to your account to enable cluster roles.
ACCOUNT=$(gcloud info --format='value(config.account)')
kubectl create clusterrolebinding owner-cluster-admin-binding \
--clusterrole cluster-admin \
--user $ACCOUNTNginx Ingress Controller Kubernetes Manifests
All the kubernetes manifests used in this tutorial are hosted on the Github repository.
Clone it and you can deploy the YAML files directly as you follow along the guide. These manifests are taken from the official Nginx community repo.
git clone https://github.com/techiescamp/nginx-ingress-controllerFirst, we will understand all the associated Kubernetes objects by deploying Nginx controllers using YAML manifests. Once we have the understanding, we will deploy it using the Helm chart.
If you want to deploy all the objects on one go, open the cloned repo in termal.
cd in in to the manifest folder and execute the following command. It will deploy all the manifests explained in this blog.
kubectl apply -f .Deploy Nginx Ingress Controller With Manifests
We need to deploy the following Kubernetes objects to have a working Nginx controller.
ingress-nginxnamespace- Service account/Roles/ClusterRoles for Nginx admission controller
- Validating webhook Configuration
- Jobs to create/update Webhook CA bundles
- Service account/Roles/ClusterRoles of Nginx controller deployment
- Nginx controller configmap
- Services for nginx controller & admission controller
- Ingress controller deployment
Need for Admission Controller & Validating Webhook
Kubernetes Admission Controller is a small piece of code to validate or update Kubernetes objects before creating them. In this case, it's an admission controller to validate the ingress objects. The Admission Controller code is part of the Nginx controller that listens on the port 8443.
Why do need the admission controller for ingress?
Without an admission controller, you can deploy ingress object that might contain wrong configurations. A wrong configuration can break all the ingress rules associated with the ingress controller.
With the admission controller in place, if you deploy a ingress object with wrong configurations, it will throw an error. This way you can ensure that the ingress object you create has the correct configurations and doesn't break routing rules.
Here is how admission controllers work for Nginx.
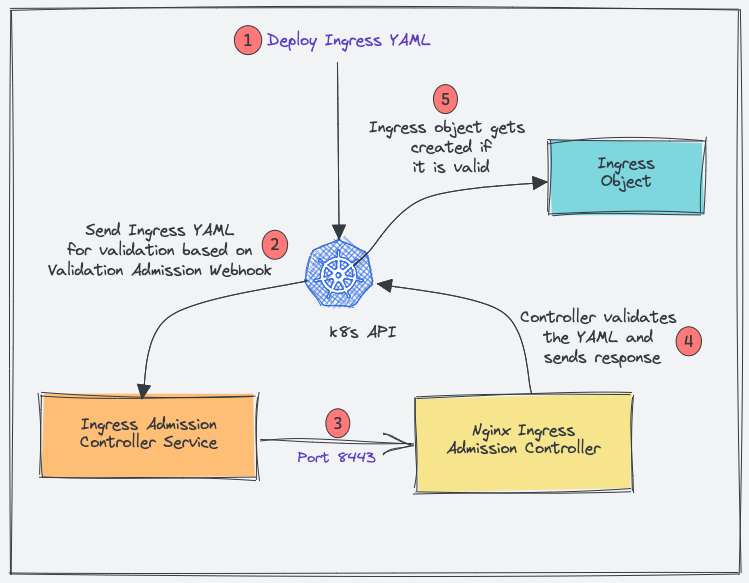
- When you deploy an ingress YAML, the Validation admission intercepts the request.
- Kubernetes API then sends the ingress object to the validation admission controller service endpoint based on admission webhook endpoints.
- Service sends the request to the Nginx deployment on port 8443 for validating the ingress object.
- The admission controller then sends a response to the k8s API.
- If it is a valid response, the API will create the ingress object.
Now let's get started by creating Kubernetes objects for the ingress controller.
Create a Namespace
We will deploy all the Nginx controller objects in the ingress-nginx namespace.
Let's create the namespace.
kubectl create ns ingress-nginxCreate Admission Controller Roles & Service Account
We need a Role and ClusterRole with required permissions and bind to ingress-nginx-admission service account.
Create a file named admission-service-account.yaml and copy the following contents.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
annotations:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission
namespace: ingress-nginx
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- secrets
verbs:
- get
- create
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission
namespace: ingress-nginx
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: ingress-nginx-admission
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: ingress-nginx-admission
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission
rules:
- apiGroups:
- admissionregistration.k8s.io
resources:
- validatingwebhookconfigurations
verbs:
- get
- update
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: ingress-nginx-admission
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: ingress-nginx-admission
namespace: ingress-nginxDeploy the manifest.
kubectl apply -f admission-service-account.yaml Create Validating Webhook Configuration
Create a file named validating-webhook.yaml and copy the following contents.
---
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission
webhooks:
- admissionReviewVersions:
- v1
clientConfig:
service:
name: ingress-nginx-controller-admission
namespace: ingress-nginx
path: /networking/v1/ingresses
failurePolicy: Fail
matchPolicy: Equivalent
name: validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io
rules:
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
apiVersions:
- v1
operations:
- CREATE
- UPDATE
resources:
- ingresses
sideEffects: NoneCreate the ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
kubectl apply -f validating-webhook.yamlDeploy Jobs To Update Webhook Certificates
The ValidatingWebhookConfiguration works only over HTTPS. So it needs a CA bundle.
We use kube-webhook-certgen to generate a CA cert bundle with the first job. The generated CA certs are stored in a secret named ingress-nginx-admission
The second job patches the ValidatingWebhookConfiguration object with the CA bundle.
Create a file named jobs.yaml and copy the following contents.
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission-create
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission-create
spec:
containers:
- args:
- create
- --host=ingress-nginx-controller-admission,ingress-nginx-controller-admission.$(POD_NAMESPACE).svc
- --namespace=$(POD_NAMESPACE)
- --secret-name=ingress-nginx-admission
env:
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
image: registry.k8s.io/ingress-nginx/kube-webhook-certgen:v20231011-8b53cabe0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: create
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
restartPolicy: OnFailure
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 2000
serviceAccountName: ingress-nginx-admission
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission-patch
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-admission-patch
spec:
containers:
- args:
- patch
- --webhook-name=ingress-nginx-admission
- --namespace=$(POD_NAMESPACE)
- --patch-mutating=false
- --secret-name=ingress-nginx-admission
- --patch-failure-policy=Fail
env:
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
image: registry.k8s.io/ingress-nginx/kube-webhook-certgen:v20231011-8b53cabe0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: patch
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
restartPolicy: OnFailure
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 2000
serviceAccountName: ingress-nginx-admissionCreate the jobs
kubectl apply -f jobs.yamlVerify the job completion using the following command.
kubectl get jobs -n ingress-nginxOnce the jobs are executed, you can describe the ValidatingWebhookConfigurationand, you will see the patched bundle.
kubectl describe ValidatingWebhookConfiguration ingress-nginx-admission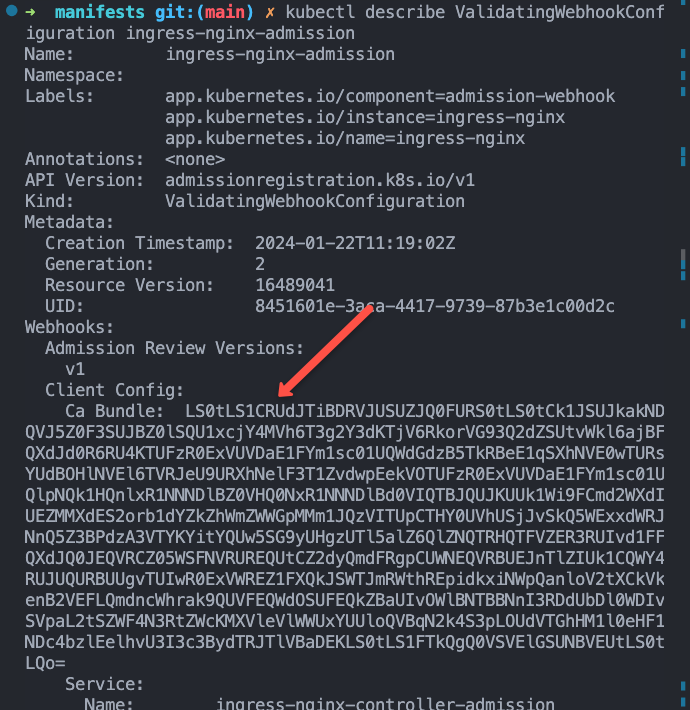
Create Ingress Controller Roles & Service Account
Create a file named ingress-service-account.yaml and copy the following contents.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- pods
- secrets
- endpoints
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses/status
verbs:
- update
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingressclasses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resourceNames:
- ingress-controller-leader
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- create
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: ingress-nginx
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- nodes
- pods
- secrets
- namespaces
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses/status
verbs:
- update
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingressclasses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: ingress-nginx
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginxDeploy the manifest.
kubectl apply -f ingress-service-account.yamlCreate Configmap
With this configmap, you can customize the Nginx settings. For example, you can set custom headers and most of the Nginx settings.
Please refer to the official community documentation for all the supported configurations.
Create a file named configmap.yaml and copy the following contents.
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
allow-snippet-annotations: "true"
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-controller
namespace: ingress-nginxCreate the configmap.
kubectl apply -f configmap.yamlCreate Ingress Controller & Admission Controller Services
Create a file named services.yaml and copy the following contents.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
ipFamilies:
- IPv4
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
ports:
- appProtocol: http
name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: http
- appProtocol: https
name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: https
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
type: LoadBalancer
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-controller-admission
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
ports:
- appProtocol: https
name: https-webhook
port: 443
targetPort: webhook
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
type: ClusterIPCreate the services.
kubectl apply -f services.yamlingress-nginx-controller service creates a Loadbalancer in the respective cloud platform you are deploying.
You can get the load balancer IP/DNS using the following command.
kubectl --namespace ingress-nginx get services -o wide -w ingress-nginx-controllerCreate IngressClass
Create a file named ingressclass.yaml and copy the following contents.
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: IngressClass
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: admission-webhook
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: nginx
spec:
controller: k8s.io/ingress-nginxDeploy the ingress class.
kubectl apply -f ingressclass.yamlIt will create a ingress class named nginx. We have to use this ingress class name in Ingress objects we create.
Create Ingress Controller Deployment
Create a file named deployment.yaml and copy the following contents.
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
name: ingress-nginx-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
minReadySeconds: 0
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
spec:
containers:
- args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --publish-service=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/ingress-nginx-controller
- --election-id=ingress-controller-leader
- --controller-class=k8s.io/ingress-nginx
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/ingress-nginx-controller
- --validating-webhook=:8443
- --validating-webhook-certificate=/usr/local/certificates/cert
- --validating-webhook-key=/usr/local/certificates/key
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: LD_PRELOAD
value: /usr/local/lib/libmimalloc.so
image: registry.k8s.io/ingress-nginx/controller:v1.9.5
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
lifecycle:
preStop:
exec:
command:
- /wait-shutdown
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 5
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
name: controller
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: http
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 443
name: https
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 8443
name: webhook
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 90Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: true
capabilities:
add:
- NET_BIND_SERVICE
drop:
- ALL
runAsUser: 101
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/local/certificates/
name: webhook-cert
readOnly: true
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
serviceAccountName: ingress-nginx
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 300
volumes:
- name: webhook-cert
secret:
secretName: ingress-nginx-admissionCreate the deployment.
kubectl apply -f deployment.yamlTo ensure that deployment is working, check the pod status.
kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginxValidate Ingress Controller Deployment
You can validate the ingress controller deployment using the LoadBlancer endpoint created by the service.
Nginx Ingress controller has a default backend. All the requests that doesn't have a entry in the ingress goes to this default backend.
We will validate out controller using the default backend.
Get your Loadbalancer endpoint the try to acess it. You should get a 404 error as shown below.
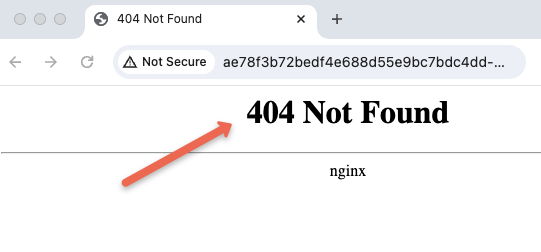
Now try to access the /heathz url using curl as given below. You should get a 200 response. Replace <LOAD-BALANCER-ENDPOINT> with your Loadbalancer endpoint.
curl http://<LOAD-BALANCER-ENDPOINT>/healthz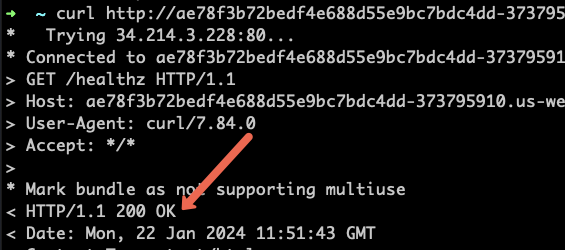
Nginx Ingress Controller Helm Deployment
If you are a Helm user, you can deploy the ingress controller using the community helm chart. ValidatingWebhookConfiguration is disabled by default in values.yaml.
Deploy the helm chart. It will create the namespace ingress-nginx if not present.
helm upgrade --install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx \
--repo https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx \
--namespace ingress-nginx --create-namespaceVerify the helm release.
helm list -n ingress-nginxTo clean up the resources, uninstall the release.
helm uninstall ingress-nginx -n ingress-nginxMap a Domain Name To Nginx Ingress Loadbalancer IP
The primary goal of Ingress is to receive external traffic to services running on Kubernetes. Ideally in projects, a DNS would be mapped to the ingress controller Loadbalancer IP.
This can be done via the respective DNS provider with the domain name you own.
Single DNS Mapping
You can map a single domain directly as an A record to the load balancer IP. Using this you can have only one domain for the ingress controller and multiple path-based traffic routing.
For example,
www.example.com --> Loadbalancer IPYou can also have path-based routing using this model.
Few examples,
http://www.example.com/app1
http://www.example.com/app2
http://www.example.com/app1/api
http://www.example.com/app2/apiWildcard DNS Mapping
If you map a wildcard DNS to the load balancer, you can have dynamic DNS endpoints through ingress.
Once you add the wildcard entry in the DNS records, you need to mention the required DNS in the ingress object and the Nginx ingress controller will take care of routing it to the required service endpoint.
For example, check the following two mappings.
*.example.com --> Loadbalancer IP
*.apps.example.com --> Loadbalancer IP This way you can have multiple dynamic subdomains through a single ingress controller and each DNS can have its own path-based routing.
Few examples,
#URL one
http://demo1.example.com/api
http://demo1.example.com/api/v1
http://demo1.example.com/api/v2
#app specific urls
http://grafana.apps.example.com
http://prometheus.apps.example.com
#URL two
http://demo2.apps.example.com/api
http://demo2.apps.example.com/api/v1
http://demo2.apps.example.com/api/v2
For demo purposes, I have mapped a wildcard DNS to the LoadBalancer IP. Based on your DNS provider, you can add the DNS record.
The following image shows the DNS records I used for this blog demo. I used EKS so instead of Loadnbalacer IP, I have a DNS of network load balancer endpoint which will be a CNAME. In the case of GKE, you will get an IP and in that case, you need to create an A record.
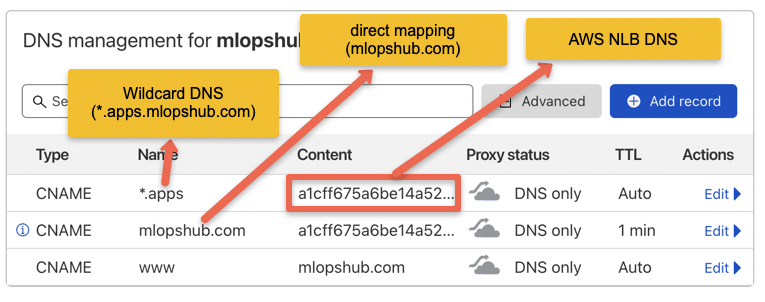
Deploy a Demo Application
For testing ingress, we will deploy a demo application and add a ClusterIp service to it. This application will be accessible only within the cluster without ingress.
Step 1: Create a namespace named dev
kubectl create namespace devStep 2: create a file named hello-app.yaml and copy the following contents.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-app
namespace: dev
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: "gcr.io/google-samples/hello-app:2.0"Step 3: Create the deployment using kubectl
kubectl create -f hello-app.yamlCheck the deployment status.
kubectl get deployments -n devStep 5: Create a file named hello-app-service.yaml and copy the following contents and save the file.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-service
namespace: dev
labels:
app: hello
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: hello
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCPStep 6: Create the service using kubectl.
kubectl create -f hello-app-service.yamlCreate Ingress Object for Application
Now let’s create an ingress object to access our hello app using a DNS. An ingress object is nothing but a set of routing rules.
If you are wondering how the ingress object is connected to the Nginx controller, the ingress controller pod connects to the Ingress API to check for rules and it updates its nginx.conf accordingly.
Since I have wildcard DNS mapped (*.apps.mlopshub.com) with the DNS provider, I will use demo.apps.mlopshub.com to point to the hello app service.
Step 1: Create a file named ingress.yaml
Step 2: Copy the following contents and save the file.
Replace demo.apps.mlopshub.com with your domain name. Also, we are creating this ingress object in the dev namespace becuase the hello app is running in the dev namespace.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress
namespace: dev
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: "demo.apps.mlopshub.com"
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/"
backend:
service:
name: hello-service
port:
number: 80Step 3: Describe created ingress object created to check the configurations.
kubectl describe ingress -n devNow if I try to access demo.apps.mlopshub.com domain, I will be able to access the hello app as shown below. (You should replace it with your domain name)
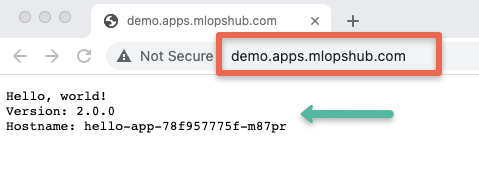
You might face https error in the browser. in that case you can use a curl command to verify ingress endpoint.
curl demo.apps.mlopshub.comTLS With Nginx Ingress
You can configure TLS certificates with each ingress object. The TLS gets terminated at the ingress controller level.
The following image shows the ingress TLS config. The TLS certificate needs to be added as a secret object.
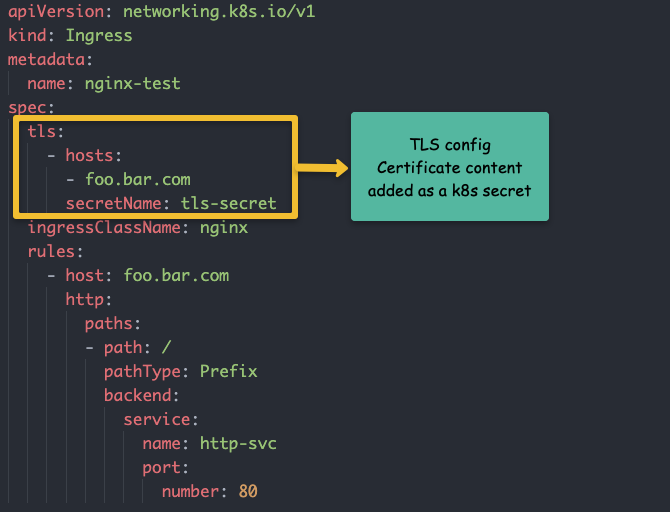
I have written a detailed article on Ingress TLS configuration.
👉 Take a look at the guide to configure ingress TLS on Kubernetes.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned how to set up the Nginx ingress controller.
It is very easy to get started. However, for project implementation ensure that you go through all Nginx configurations and tune them according to the requirements.
With the Nginx controller configmap, you can configure all the Nginx settings without redeploying the controller.
I hope you enjoyed this guide on Nginx ingress controller.
Let me know your thoughts and queries in the comment section.
Also, if you are learning Kubernetes, check out my comprehensive Kubernetes tutorials.

