In this blog, we will look into GitHub Actions workflow to automate adding a cluster to ArgoCD.
This workflow removes the repeated process of adding new clusters each time, saving time and reducing the possibility of human error.
We have used an AWS EKS cluster for this setup.
By the end of this blog, you will understand:
- Workflow to automate adding clusters to ArgoCD.
- Understanding of how the workflow works.
- And how to troubleshoot if the cluster is not added correctly.
Runner Configuration
We used an AWS EC2 instance as a runner for GitHub Actions.
For this workflow to work, the GitHub actions runner should have IAM permissions to get the EKS cluster context.
If you are using dynamic docker based or pod based runners, you need to make sure it has permissions to get the cluster contexts.
Workflow Diagram
The diagram below shows the workflow for automating the addition of clusters to ArgoCD.
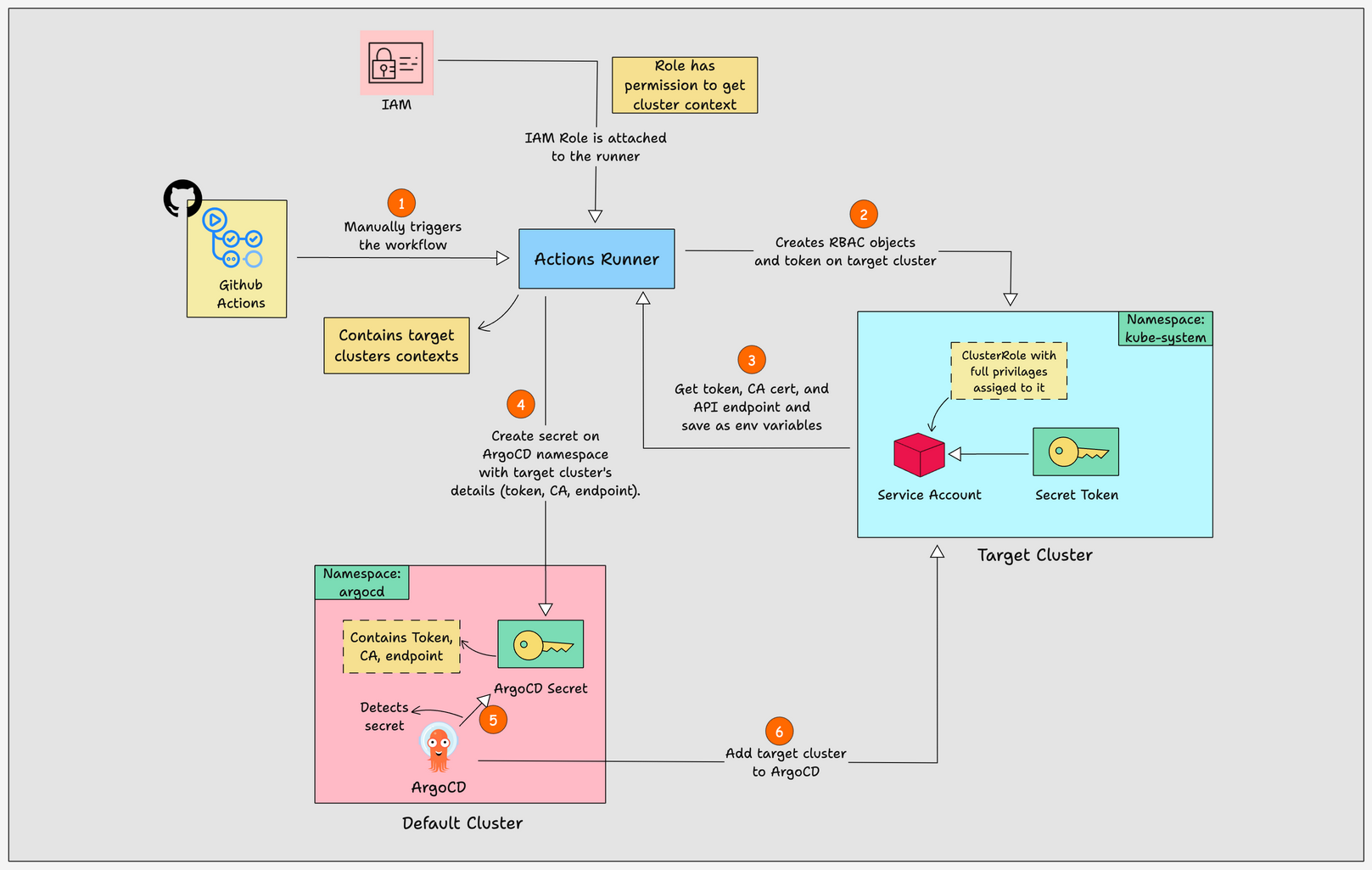
Explanation:
- The workflow starts by deploying an EKS cluster using a GitHub Actions workflow.
- In the next step, the workflow updated the current context to the newly created EKS cluster.
- With that context, it creates RBAC objects ( service account, clusterrole, clusterrolebinding) and a token that would be required for ArgoCD to connect to the new cluster.
- Then the new clusters Token, CA data, and cluster API endpoints are saved as environment variables in the runner.
- Next, the runner changes the cluster context to the cluster where ArgoCD is installed.
- Then it creates a secret in the argocd namespace, with the Token, CA data, and cluster API endpoints of the target cluster.
- Once the secret is created, ArgoCD automatically detects the secret because of the
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: clusterannotation in the secret. - And finally, ArgoCD uses the secret to add the target cluster.
Prerequisites
You should have the following prerequisites for this setup.
- At least two Kubernetes Cluster
- ArgoCD installed on the cluster (assume the cluster is dev)
- GitHub Actions runner configured
How to Automate Adding Clusters to ArgoCD?
First, fork this GitHub repository and configure your actions on it.
The files we will use for this automation are given in the structure below.
.
├── README.md
├── .github
│ └── workflows
│ └── add-cluster.yaml
└── multi-cluster-configurations
├── target-cluster-rbac.yaml
└── traget-cluster-token.yamlThe workflow we will use to automate adding clusters is given below.
name: Pipeline to Add Cluster to ArgoCD
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
environment:
description: 'Environment to add (stage or prod)'
required: true
type: choice
options:
- stage
- prod
jobs:
add-cluster:
runs-on: infra
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Update kubeconfig file of Target Cluster
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ github.event.inputs.environment }}-cluster"
echo "CLUSTER_NAME=$CLUSTER_NAME" >> $GITHUB_ENV
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name $CLUSTER_NAME --region us-east-1
- name: RBAC and Token creation on Target Cluster
run: |
kubectl apply -f ./multi-cluster-configurations/target-cluster-rbac.yaml
kubectl apply -f ./multi-cluster-configurations/target-cluster-token.yaml
- name: Save Token and CA Data to Environment Variables
run: |
TARGET_TOKEN=$(kubectl get -n kube-system secret/argocd-manager-token -o jsonpath='{.data.token}' | base64 --decode)
TARGET_CA_DATA=$(kubectl get -n kube-system secret/argocd-manager-token -o jsonpath='{.data.ca\.crt}')
TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT=$(aws eks describe-cluster --name $CLUSTER_NAME --query "cluster.endpoint" --output text | sed 's~https://~~')
echo "TARGET_TOKEN=$TARGET_TOKEN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "TARGET_CA_DATA=$TARGET_CA_DATA" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT=$TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Update kubeconfig file to Dev Cluster
run: |
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name dev-cluster --region us-east-1
- name: Add Target Cluster to ArgoCD
run: |
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -n argocd -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: ${{ github.event.inputs.environment }}-cluster-secret
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: cluster
type: Opaque
stringData:
name: ${{ github.event.inputs.environment }}-cluster
server: https://$TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT
config: |
{
"bearerToken": "$TARGET_TOKEN",
"tlsClientConfig": {
"serverName": "$TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT",
"caData": "$TARGET_CA_DATA"
}
}
EOFExplanation:
Let me explain each block to show you what it does.
name: Pipeline to Add Cluster to ArgoCD
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
environment:
description: 'Environment to add (stage or prod)'
required: true
type: choice
options:
- stage
- prodThis contains the name of the pipeline, and the workflow can be triggered only manually.
jobs:
add-cluster:
runs-on: infra
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3Here we have specified the runner's label and the first step, which clones every file and folder in the repo to the Actions workspace.
- name: Update kubeconfig file of Target Cluster
run: |
CLUSTER_NAME="${{ github.event.inputs.environment }}-cluster"
echo "CLUSTER_NAME=$CLUSTER_NAME" >> $GITHUB_ENV
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name $CLUSTER_NAME --region $REGIONThis is the second step, which saves the cluster's name as an environment variable and substitutes it in the kubeconfig update command to update the cluster's context.
The ${{ github.event.inputs.environment }} gets the values from the option we select in the first block, which is either stage or prod.
Our cluster names are stage-cluster and prod-cluster. You can change the options in the first block according to your cluster names.
For example, if your cluster's names are stage-web-app-cluster and prod-web-app-cluster, then modify the options like:
options:
- stage-web-app
- prod-web-appThe cluster at the end will be added from the command CLUSTER_NAME="${{ github.event.inputs.environment }}-cluster.
Also, update the region where your cluster is created.
- name: RBAC and Token creation on Target Cluster
run: |
kubectl apply -f ./multi-cluster-configurations/target-cluster-rbac.yaml
kubectl apply -f ./multi-cluster-configurations/target-cluster-token.yaml This step created the RBAC objects (service account, clusterrole, clusterrole binding) and bearer token on the target cluster.
I have updated the files to create RBAC objects and a token in the GitHub repo.
- name: Save Token and CA Data to Environment Variables
run: |
TARGET_TOKEN=$(kubectl get -n kube-system secret/argocd-manager-token -o jsonpath='{.data.token}' | base64 --decode)
TARGET_CA_DATA=$(kubectl get -n kube-system secret/argocd-manager-token -o jsonpath='{.data.ca\.crt}')
TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT=$(aws eks describe-cluster --name $CLUSTER_NAME --query "cluster.endpoint" --output text | sed 's~https://~~')
echo "TARGET_TOKEN=$TARGET_TOKEN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "TARGET_CA_DATA=$TARGET_CA_DATA" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT=$TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT" >> $GITHUB_ENVThis step will get and save the token and clusters CA certificate as environment variables.
Also, it saves the cluster endpoint in $TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT a variable using the AWS command specified in it
If you are using other cloud clusters, change the command accordingly.
You can see I have used the SED command at the end of the cluster endpoint command to remove it https:// from the endpoint while saving it as a variable.
You will understand why I removed https:// it before saving the cluster endpoint in the final step.
- name: Update kubeconfig file to Dev Cluster
run: |
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name dev-cluster --region us-east-1This command updates the kubeconfig file to use the cluster dev-cluster, where ArgoCD is installed.
Update the cluster name and region, in the above step.
- name: Add Target Cluster to ArgoCD
run: |
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -n argocd -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: ${{ github.event.inputs.environment }}-cluster-secret
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: cluster
type: Opaque
stringData:
name: ${{ github.event.inputs.environment }}-cluster
server: https://$TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT
config: |
{
"bearerToken": "$TARGET_TOKEN",
"tlsClientConfig": {
"serverName": "$TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT",
"caData": "$TARGET_CA_DATA"
}
}
EOFThis is the final step, which creates a secret on the argocd namespace with the token, CA certificate, and Cluster endpoint.
This secret is the configuration for ArgoCD to connect with a new cluster.
It uses the cluster endpoint to connect, a token, and CA data for authentication and secure connection.
You can see it $TARGET_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT is used in two places in the above command.
One with https:// and another without it, this is the reason I saved the cluster endpoint without https:// using the SED command
Trigger the Workflow
Now, it's time to trigger the workflow.
Since we have only configured a manual trigger, you have to go to Actions, select the workflow name, click the Run workflow toggle button, select the environment, and click the Run workflow button as shown below.
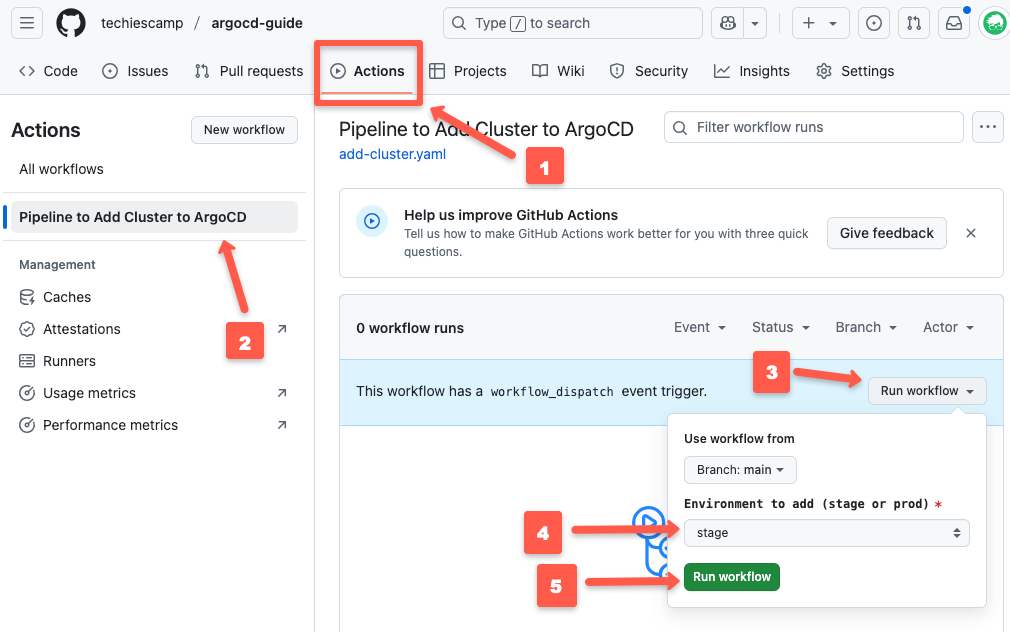
Once you have triggered the workflow, you will see it start as shown below.
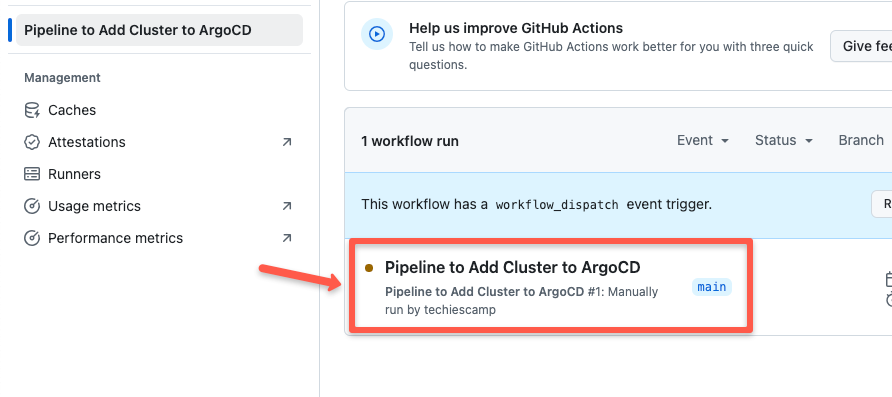
If everything runs without any issues, you can see the workflow build as shown below.
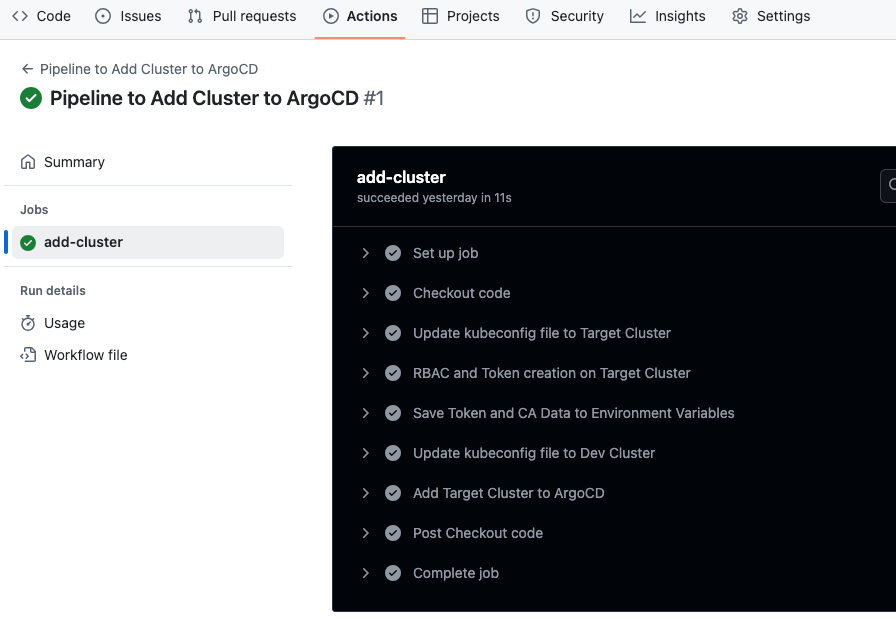
Now, log in to your ArgoCD UI and go to Settings, the final step for workflows.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
The only issue you may face in this workflow is that the runner cannot access the target cluster.
If you face this issue, check the following:
- Check if the target clusters are created and running
- Check if the runner has permissions to access the cluster.
- Check if the target clusters' kubeconfig contexts are added to the runner.
- Check if the runner has permissions to access the cluster.
- Check that the region and cluster names on the workflow are correct.
Conclusion
That's all for the automation workflow. With this, you don't need to add new clusters to ArgoCD repeatedly.
In this guide, you have learned about the workflow for automating cluster additions to ArgoCD, how the workflow works, and how to troubleshoot if a cluster is not added correctly.
If you want to try the manual setup, follow this blog.


