If you are tired of writing long AWS CLI commands, Amazon Q Developer CLI can save you a lot of time. It is an AI-powered CLI tool that turns plain English into working AWS commands.
In this blog, you will get a complete guide to Amazon Q CLI with practical examples on how to use it and save time while working with AWS services.
By the end of this blog, you will know how to:
- Install Q CLI
- Authenticate Q CLI
- Use Q CLI with real examples
- Follow best practices
- Understand the pricing of Q CLI
What is Amazon Q Developer CLI?
Amazon Q CLI is an AI-powered command line interface that helps developers and Devops engineers perform tasks on AWS backed by Claude LLM.
With Q CLI, you can query on the terminal in plain English, and the Q CLI will convert them into AWS CLI commands and execute them.
You can even find and fix errors, analyze logs, and deploy fixes without switching tools
Overall it can boost the productivity of Devops engineers working with AWS services.
Amazon Q CLI is essentially the command-line version of Amazon Q Developer.
Before we move on to the Q CLI installation, let's have a look at how it works.
Amazon Q CLI Workflow
The following workflow diagram explains how, when a user makes a query, it reaches AWS, and the user gets the output.
Before explaining the workflow, you need to know two things: authentication and the backend LLM of the Q CLI.
- The Q CLI fetches the AWS Credentials, which are currently present in the local system for the AWS CLI authentication.
- The Q CLI is backed by Claude 4.0 to structure the output to the user.
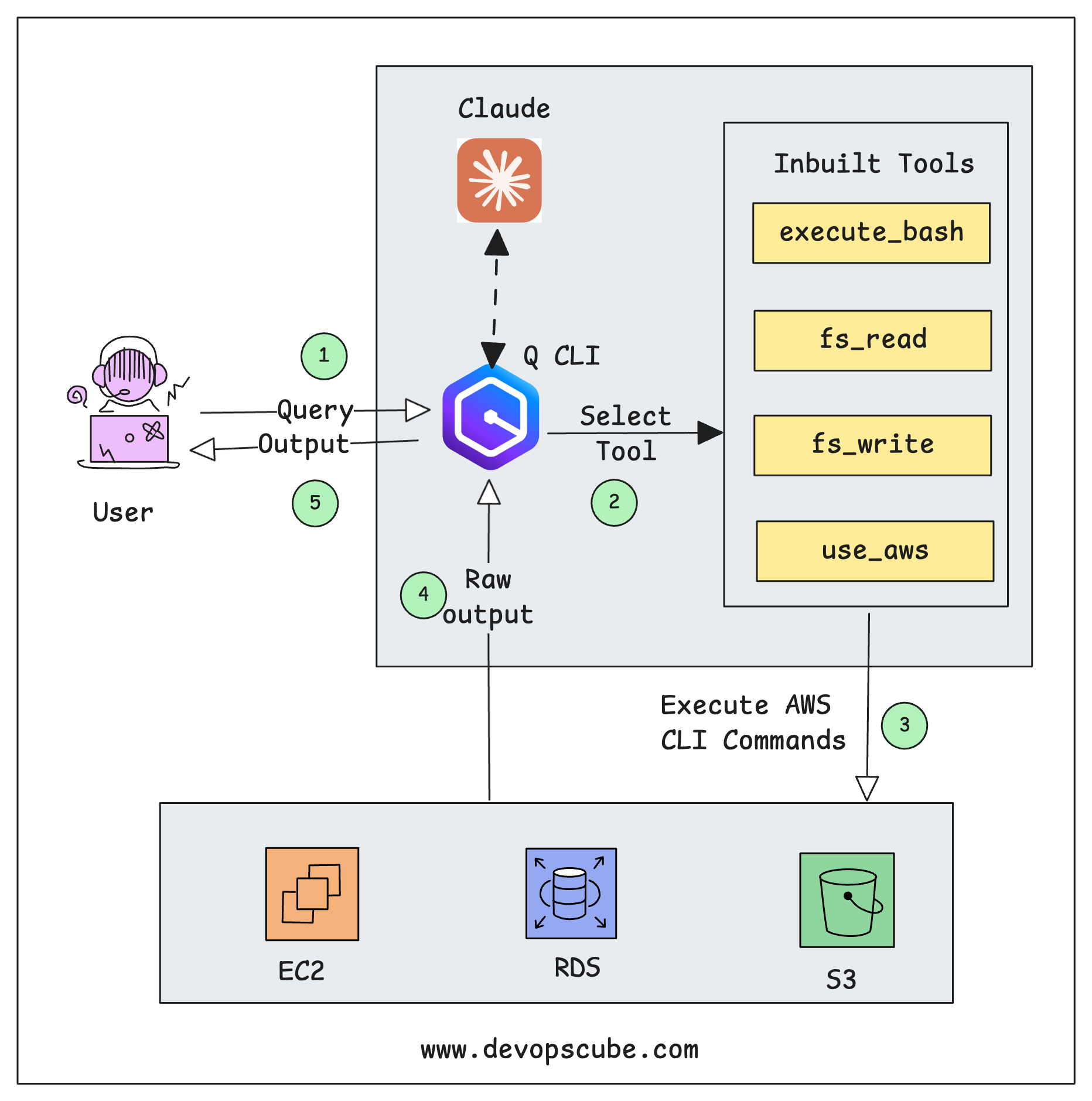
Here is how it works.
- When a user makes a query to AWS (like listing the S3 buckets) via the Q CLI, it passes your request to a Claude model.
- Claude figures out the right AWS CLI command.
- The Q CLI then selects the appropriate inbuilt tool (
use_aws) to execute the commands from local to AWS. - The raw result comes back.
- Now, Claude helps turn that into a clean, easy to read reply as terminal output.
Now, lets look at how it works in practice.
Setup Prerequisites
To install the Q CLI, we need the following requirements.
- Ubuntu machine - (v24.04)
- AWS CLI - (v2.0 +) - Should be configured with credentials to access the AWS services.
- Python - (v3.10 +)
- AWS Builder ID
Once the prerequisites are ready, we can start the installation.
Installing Amazon Q CLI
Follow the steps below to install the Q CLI on a CLI based Ubuntu 24.04 machine.
Step 1: Check the GLIBC Version
Check the glibc version to ensure the Q CLI library comptibility.
ldd --versionIf the version is 2.34 or higher, follow the below steps.
Step 2: Download the Q CLI Package
To download the package, use the following command.
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf "https://desktop-release.q.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/latest/q-x86_64-linux.zip" -o "q.zip"Step 3: Unzip the Package
Use the following command to extract the packages.
unzip q.zipStep 4: Installation of Q CLI
To install the package by running the following script.
./q/install.shDuring the script execution, an authentication message will pop up.
Step 5: Authentication of Q CLI
The script execution will prompt to select yes and will ask to select Builder ID or Pro License for authentication.
Selecting Builder ID will generate a code and a URL to authenticate from the browser.
Paste the URL into a browser where you're already logged in with your Builder ID to complete authentication.
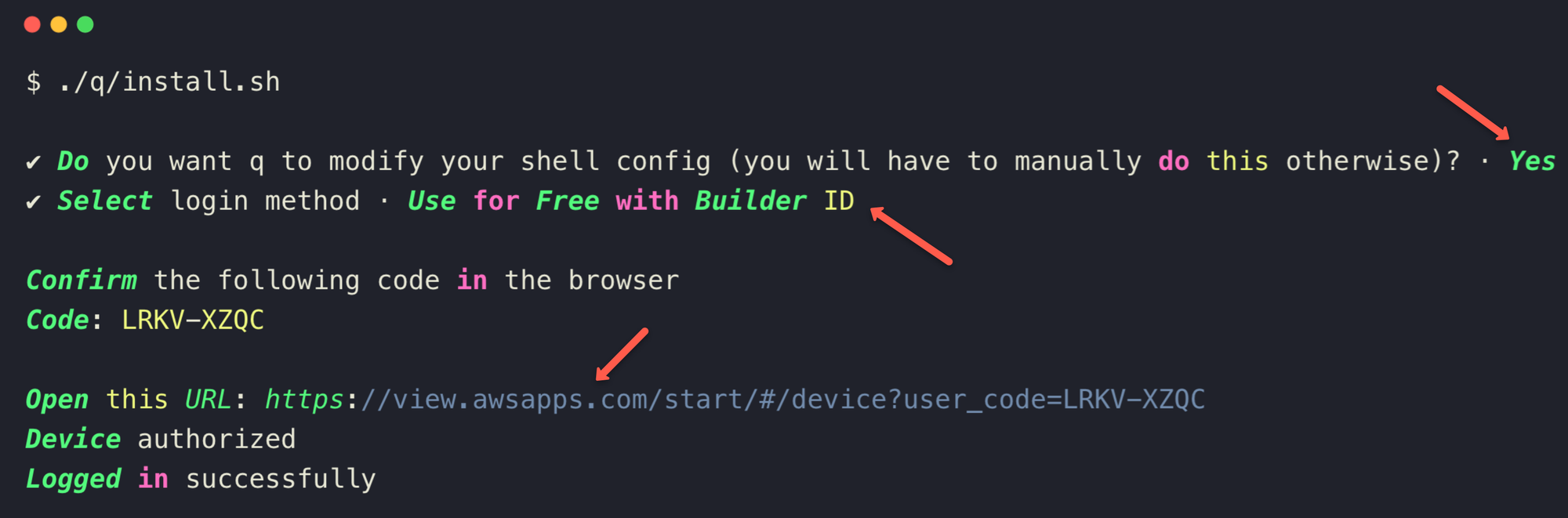
If the authentication is completed, you will see a successful message.
On the next step, we need to configure the path to execute the Q CLI commands from the terminal.
Step 6: Adding Q Executable to the PATH
To add the q/bin to the PATH, use the following command
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/q/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc && source ~/.bashrc
The installation part is completely done, so we need to validate the installation.
Step 7: Verifying the Q CLI Installation
We can check the version of the Q CLI over the terminal to ensure that the installation is properly done.
$ q version
q 1.12.4At present, the latest version of the Q CLI is 1.12.4.
Q CLI & AWS Authentication
Q CLI can be logged in with Builder ID or Q Developer Pro License.
Builder ID can be used for free basic usage but for the full access you need to subscribe for the AWS Q Developer service which will cost $19 monthly.
For a pro license, type
/subscribe inside the Q CLI, which will route you to your currently logged-in AWS account, where you can subscribe for a Pro License.Q CLI by default fetches the current AWS credentials from ~/.aws/credentials and ~/.aws/config. But if you are managing multiple AWS profiles, tell the Q CLI which profile to use to execute.
Now, we can see some examples of how we use the Q CLI in our day to day workflow.
Real-World Q CLI Examples You Can Try
By default, the Q CLI will not be active, so we need to invoke the Q CLI by using the following command.
q chatThis will open the Q interactive terminal where we can query something to perform some tasks on AWS.
The output ensures that the Q CLI is ready to accept queries.
But, we can switch the model version to 3.7 or 3.5 if required by type and enter
/model on the Q CLI.Querying AWS Resources With Q CLI Prompts
Querying is nothing but asking something by chat instead of using the direct AWS CLI commands.
Check current AWS identity
Use the following prompt to get your current identity.
Prompt: Show me the current AWS account and IAM role I'm using.
You will get an output like the following.
> Show me the current AWS account and IAM role I'm using
.
.
.
.
● Completed in 1.362s
> Here's your current AWS identity information:
• **AWS Account ID**: 45674567456
• **User Type**: Root user
• **ARN**: arn:aws:iam::45674567456:rootList s3 Buckets
Let's ask with a small one, like listing the available S3 buckets in the account.
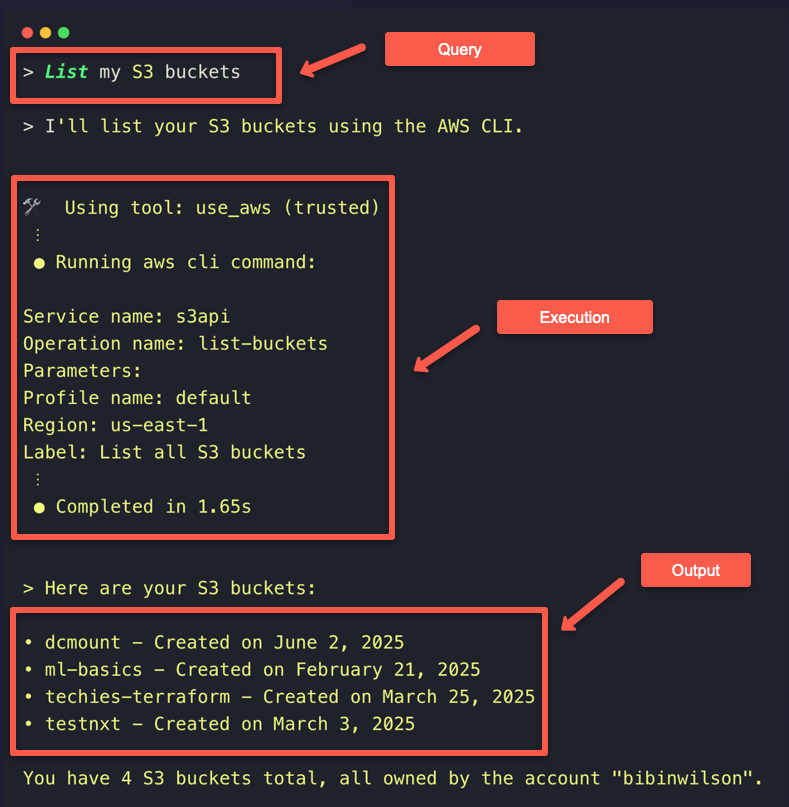
Here, we can see on the execution of Using tool: use_aws, means the Q CLI converted our query to an AWS CLI command and executed it, then the raw output is structured by Q CLI so that we are seeing the output as bullet points.
List Instances With Specific Instance Profile
Let's assume, we have a couple of EC2 instances in the us-west-2 region but some of them are using the admin instance profiles, so we need to list them out.
> Show me all EC2 instances in us-west-2 that are using the instance profile of "admin-role".
> I'll check for EC2 instances in the us-west-2 region that are using the "admin-role" instance profile.
🛠️ Using tool: use_aws (trusted)
⋮
● Running aws cli command:
Service name: ec2
Operation name: describe-instances
Parameters:
- query: "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{InstanceId:InstanceId,InstanceType:InstanceType,State:State.Name,IamInstanceProfile:IamInstanceProfile.Arn,LaunchTime:LaunchTime,Tags:Tags[?Key=='Name'].Value|[0]}"
- filters: [{"Name":"iam-instance-profile.arn","Values":["*admin-role*"]}]
Profile name: default
Region: us-west-2
Label: List EC2 instances with admin-role instance profile in us-west-2
⋮
● Completed in 1.174s
> Found 1 EC2 instance in us-west-2 using the "admin-role" instance profile:
• Instance ID: i-0654f6ecd273c51ec
• Name: Q CLI
• Instance Type: t3.micro
• State: running
• Instance Profile: admin-role
• Launch Time: July 14, 2025 at 05:47:59 UTC
This instance is currently running and was launched earlier today. It's using the exact "admin-role" instance profile you were looking for.
> The output clearly shows which instance is using that particular instance profile, but if you manually type the command, it would have been quite long and you probably wont remember all those parameters every time.
List EKS Clusters
Here is an example where I listed the running EKS clusters in my account.
> how many eks clusters are running in my account.
> I'll check how many EKS clusters are running in your AWS account.
🛠️ Using tool: use_aws (trusted)
⋮
● Running aws cli command:
Service name: eks
Operation name: list-clusters
Parameters:
Region: us-east-1
Label: List all EKS clusters in the account
⋮
● Completed in 1.971s
> You have 0 EKS clusters running in the us-east-1 region. This is how the Q CLI saves our time complex tasks on AWS with a few simple prompts.
But you might be thinking, how can the Q CLI can execute commands on AWS and read and write to the local machine?
Well, the Q CLI itself has inbuilt functions called tools to perform the operations on the local machine as well as AWS.
Amazon Q CLI Inbuilt Tools
The Q CLI tools are functions to perform some specific operations.
Here are the available inbuilt tools of the Q CLI.
execute_bash- To execute the Bash shell commands (e.g., ls, cat, pwd)fs_read- To read the local file system, like directories and files.fs_write- To write or modify the files on the local machine.report_issue- To report the issue to the Q like an error or bug in the Q CLI.use_aws- To use the locally installed AWS CLI to interact with the AWS services.
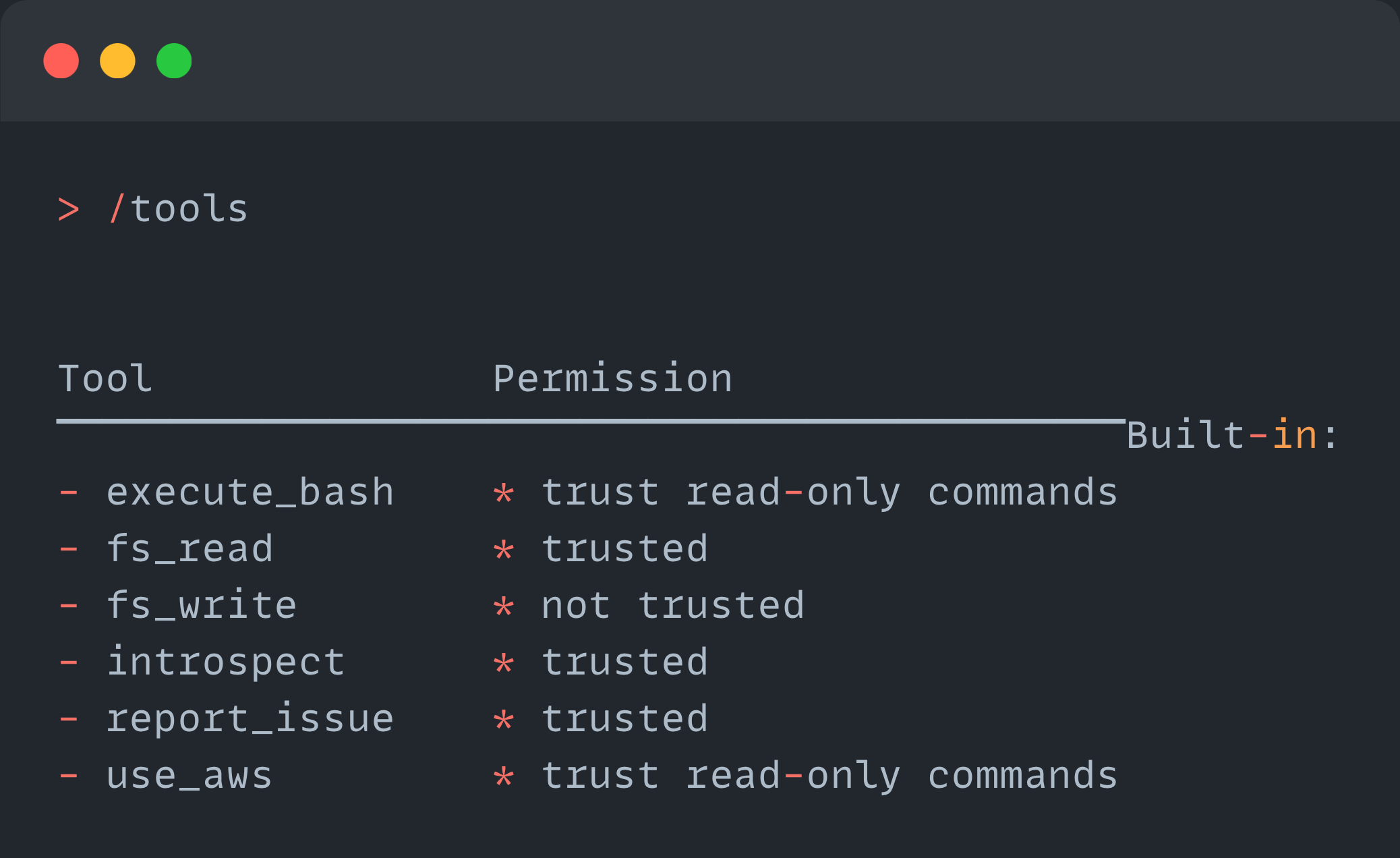
All these tools require permission to perform the action, so it will ask us if the permission is set as not trusted.
This is how the Q CLI performs operations using tools on both the local and the AWS.
In the next section, we can see some of the advantages of using the Q CLI.
Uninstall Q CLI Cleanly
Once you test everything and want to remove it from the server, you can follow the steps below.
Before remove the configuration, exit from the Q CLI.
/quitTo uninstall the Q CLI, remove the Q CLI binary from the home directory.
rm ~/.local/bin/q
After this, remove the autocompletion from the ~/.bashrc
Before we wrap this up, we need to know the pricing of the Q CLI as well.
Amazon Q CLI Advantages
The following are some of the advantages of the Q CLI.
- The main advantage is that we can perform tasks on AWS, such as creating a resource or getting information about the existing resources.
- The Q CLI can even write code, test and execute them from the local machine.
- It can analyze the existing code and give suggestions to improve the code quality and security.
Even though the Q CLI has this many advantages, it still has some limitations.
For example,
If I want to analyze my current usage of a particular service and need a cost report, the Q CLI can't give the proper output.
Because, the Q CLI is a lightweight CLI tool so it doesn't have logic to reach the cost explorer or the pricing APIs, and can't create a report itself.
But we can still use Q CLI for the same query to resolve with the help of AWS MCP servers.
These MCP servers have specific logics to perform the operations to resolve the query.
So whenever we want to analyze a cost and generate a report, we can use the AWS Cost Analysis MCP server with the Q CLI.
This is how we extend the capabilities of the Q CLI with the help of the MCP server, we are covering that topic on the MCP server integration blog.
Amazon Q CLI Pricing
Amazon offers a free version of the Q CLI, that we have used for this demo.
Amazon Q Developer gives you 50 agentic chat interactions per month at no cost.
However, AWS offers paid versions called pro tier of cost 19$/month for a user, which will support upto 1000 agentic requests per month.
Pro subscription comes with many advantages. Please refer the official documentation to know more.
Security Reminder
Even AI tools meant to help must be used with caution.
In July 2025, someone inserted a dangerous instruction into version 1.84 of the Amazon Q Developer VS Code extension that would have wiped local and cloud data.
Luckily, it couldn’t run because of a syntax error. AWS responded quickly, removing the bad version and releasing a safe update (1.85)
So always review changes or pull requests even for trusted tools and limit AI agent permissions. Never give full power by default
Conclusion
This blog gives you the generic idea of the Q CLI installation and authentication.
In this we have shown a couple of real use cases, however, you can use them as per your organization's requirements.
You can even,
- Convert architecture diagrams into Terraform code.
- Convert ER diagrams into SQL schemas.
- Turn sketches into design documents.
- Generate UI wireframes from screenshots
As part of extending the Q CLI capabilities, we will be publishing blogs on the integration of the MCP servers.


