Prometheus is an open-source monitoring system which is very lightweight and has a good alerting mechanism.
Install and Configure Prometheus
This guide explains how to install and configure the latest Prometheus on a Linux VM.
If you would like to install Prometheus on a Kubernetes cluster, please see the Prometheus on kubernetes guide.
Before You Begin
- Ensure that you have sudo access to the Linux server because the commands used in this guide require elevated privileges.
- The server has access to the internet for downloading the Prometheus binary.
- Most importantly, firewall rules opened for accessing Prometheus port 9090 on the server.
Setup Prometheus Binaries
Step 1: Update the yum package repositories.
sudo yum update -yStep 2: Go to the official Prometheus downloads page and get the latest download link for the Linux binary.
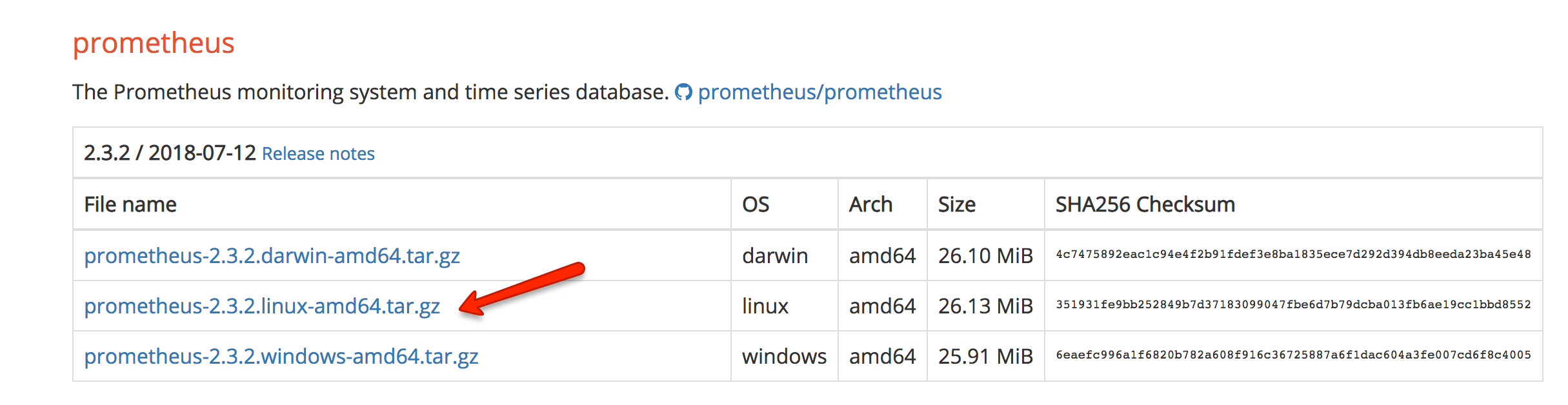
Step 3: Download the source using curl, untar it, and rename the extracted folder to prometheus-files.
curl -LO url -LO https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.22.0/prometheus-2.22.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xvf prometheus-2.22.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
mv prometheus-2.22.0.linux-amd64 prometheus-filesStep 4: Create a Prometheus user, required directories, and make Prometheus the user as the owner of those directories.
sudo useradd --no-create-home --shell /bin/false prometheus
sudo mkdir /etc/prometheus
sudo mkdir /var/lib/prometheus
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /var/lib/prometheusStep 5: Copy prometheus and promtool binary from prometheus-files folder to /usr/local/bin and change the ownership to prometheus user.
sudo cp prometheus-files/prometheus /usr/local/bin/
sudo cp prometheus-files/promtool /usr/local/bin/
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /usr/local/bin/prometheus
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /usr/local/bin/promtoolStep 6: Move the consoles and console_libraries directories from prometheus-files to /etc/prometheus folder and change the ownership to prometheus user.
sudo cp -r prometheus-files/consoles /etc/prometheus
sudo cp -r prometheus-files/console_libraries /etc/prometheus
sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/consoles
sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/console_librariesSetup Prometheus Configuration
All the prometheus configurations should be present in /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml file.
Step 1: Create the prometheus.yml file.
sudo vi /etc/prometheus/prometheus.ymlStep 2: Copy the following contents to the prometheus.yml file.
global:
scrape_interval: 10s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'prometheus'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9090']Step 3: Change the ownership of the file to prometheus user.
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/prometheus.ymlSetup Prometheus Service File
Step 1: Create a prometheus service file.
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.serviceStep 2: Copy the following content to the file.
[Unit]
Description=Prometheus
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
User=prometheus
Group=prometheus
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \
--config.file /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
--storage.tsdb.path /var/lib/prometheus/ \
--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \
--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetStep 3: Reload the systemd service to register the prometheus service and start the prometheus service.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
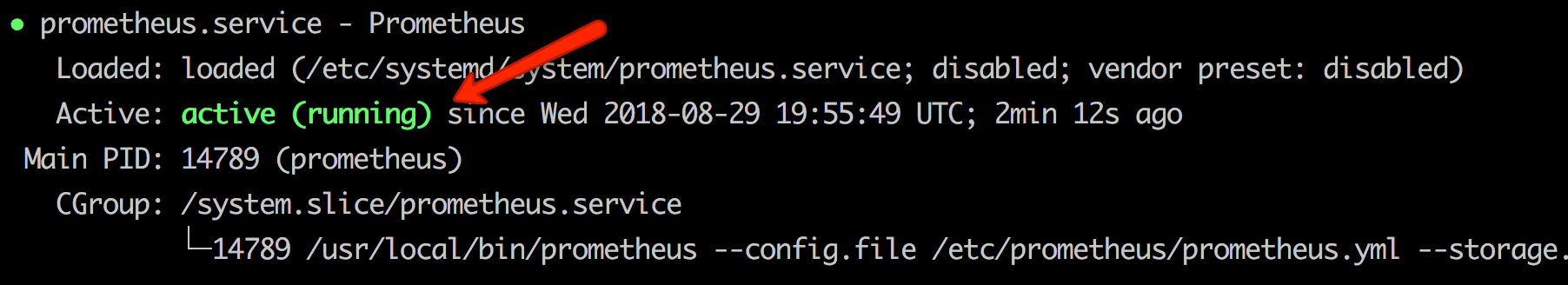
sudo systemctl start prometheusCheck the prometheus service status using the following command.
sudo systemctl status prometheusThe status should show the active state as shown below.
Access Prometheus Web UI
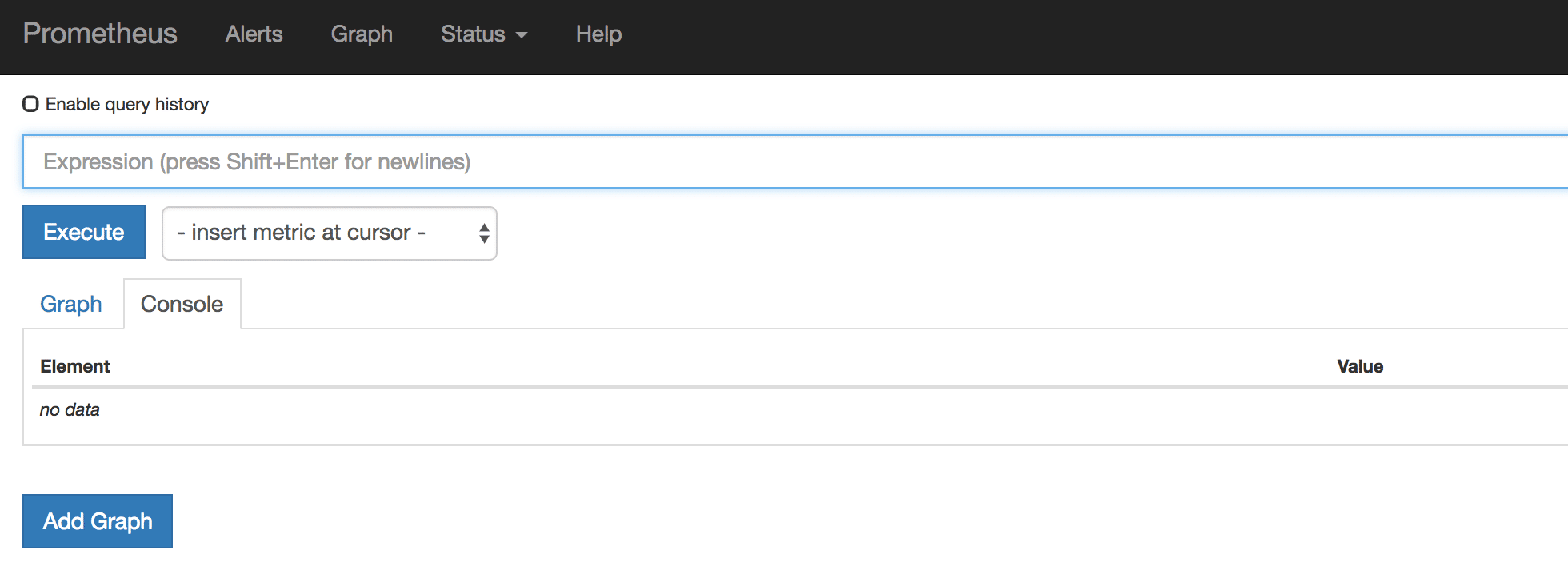
Now you will be able to access the prometheus UI on 9090 port of the prometheus server.
http://<prometheus-ip>:9090/graphYou should be able to see the following UI as shown below.
You can use the Prometheus query tab to query the available metrics as shown in the gig below.
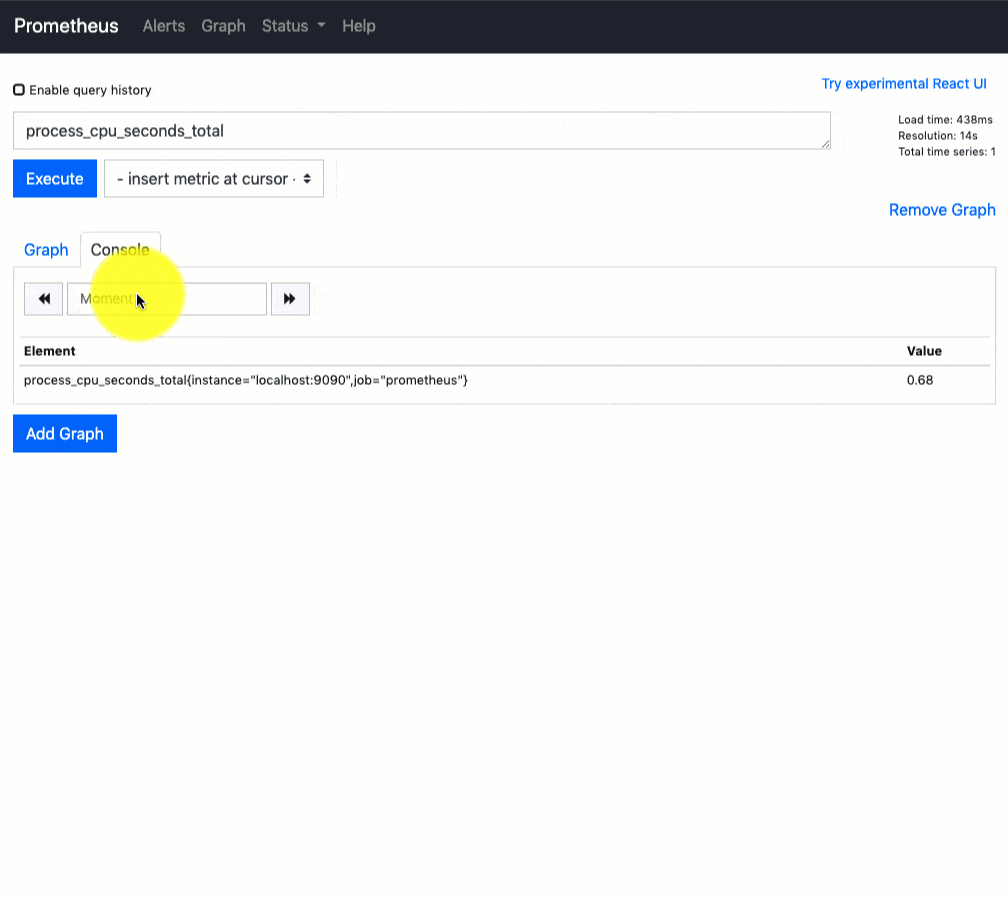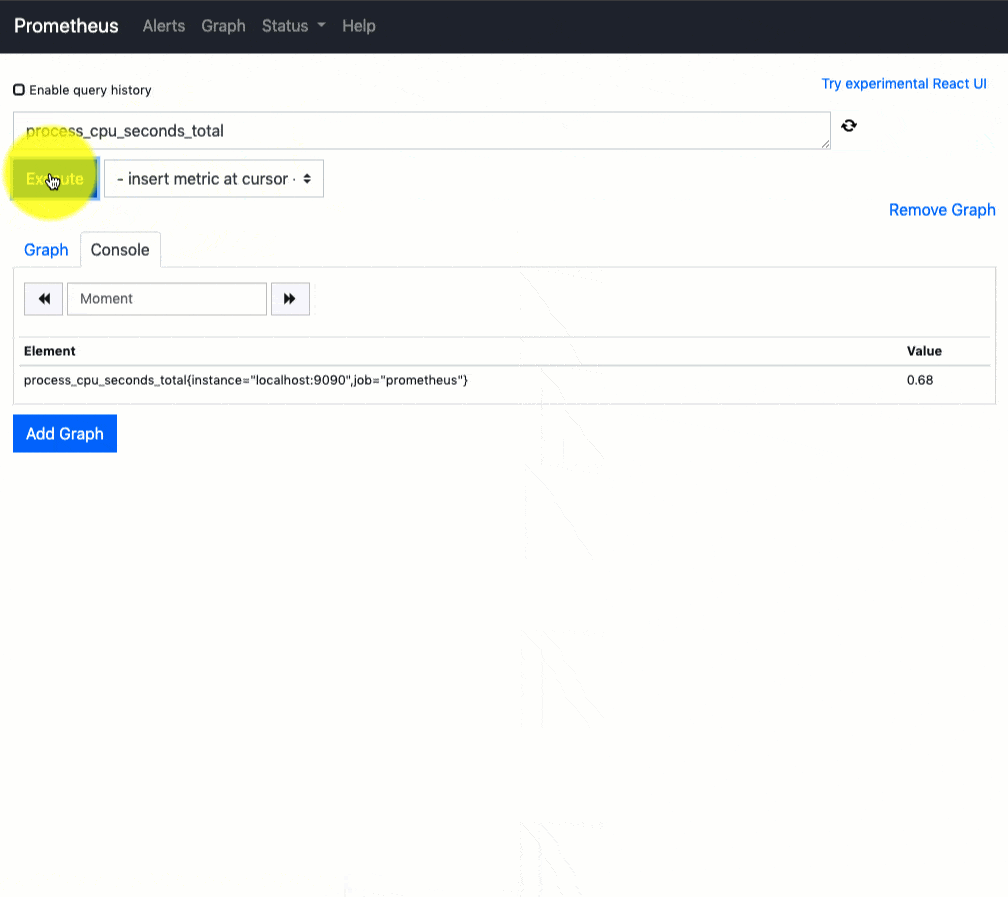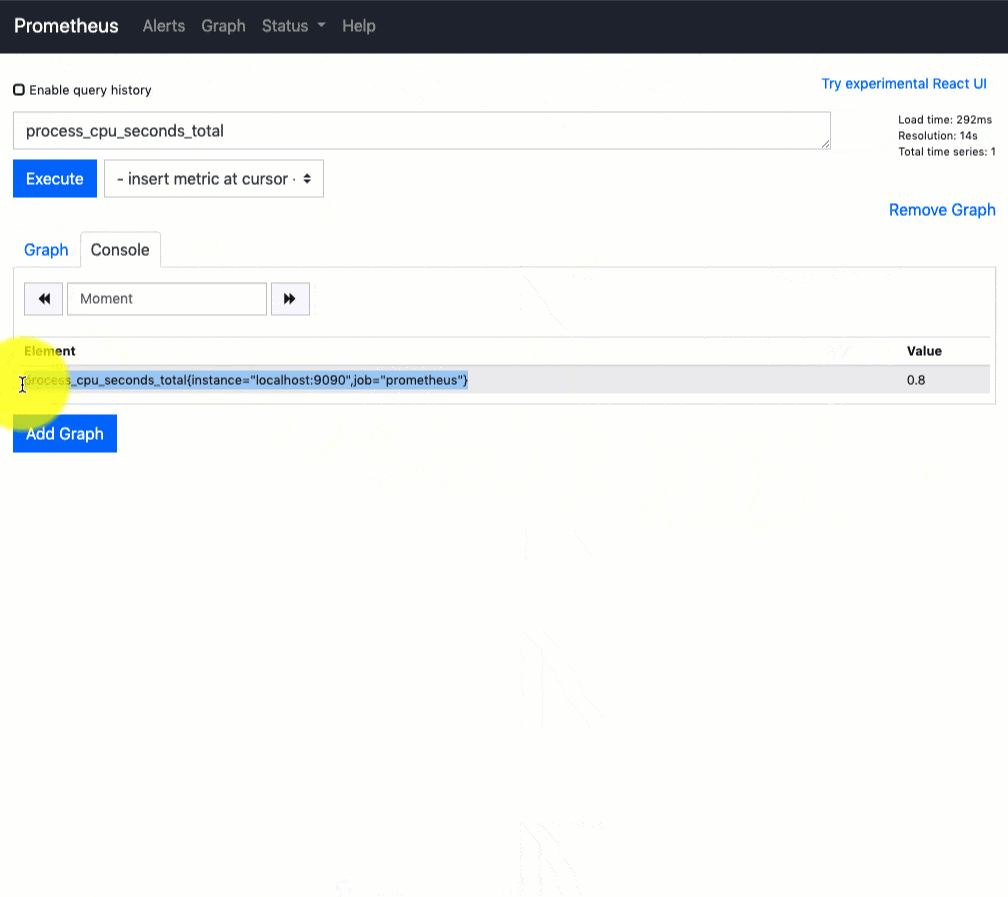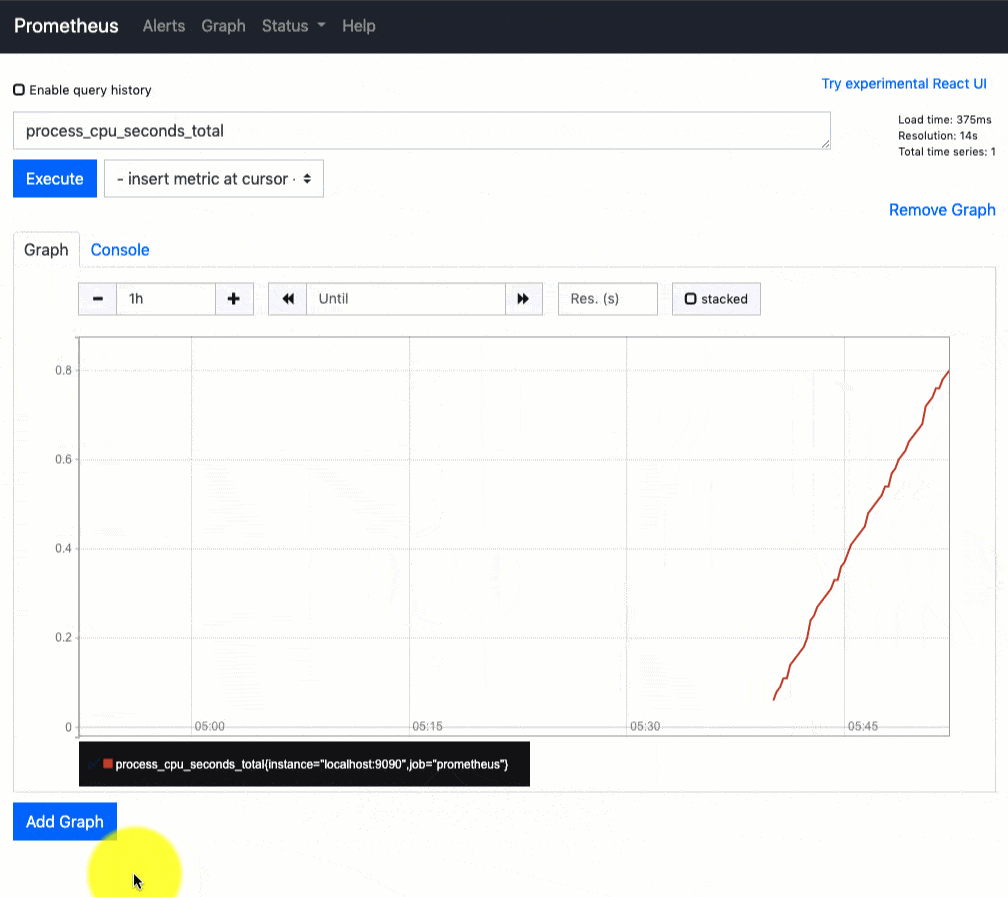
Right now, we have just configured the Prometheus server. You need to register the target in the prometheus.yml file to get the metrics from the source systems.
For example, if you want to monitor ten servers, the IP address of these servers should be added as a target in the Prometheus configuration to scrape the metrics.
The server should have Node Exporter installed to collect all the system metrics and make it available for Prometheus to scrap it.
Follow this detailed Prometheus Node Exporter Guide to setup node exporter and registering it to the Prometheus server.
You can also use this setup as lab for the Prometheus Certified Associate Certification preparation.


