In this blog, you will learn about kube-bench and how to run Kubernetes CIS benchmarks against a cluster using kube-bench.
When managing Kubernetes clusters for production use cases, security and compliance are crucial factors to consider. The clusters need to be securely configured to minimize the attack surface.
Additionally, every organization might have audit requirements for systems to be compliant with security standards.
What is the CIS Kubernetes benchmark?
cisecurity.org
Kubernetes CIS benchmarks cover security guidelines & recommendations for the following
- Control Plane Components: Control plane node configurations & component recommendations.
- Worker Nodes: Worker node configurations and Kubelet.
- Policies: RBAC, service accounts, Pod security standards, CNI and network policies, Secret Management, etc.
The following image shows the example list of CIS guidelines for the Kubernetes API server.
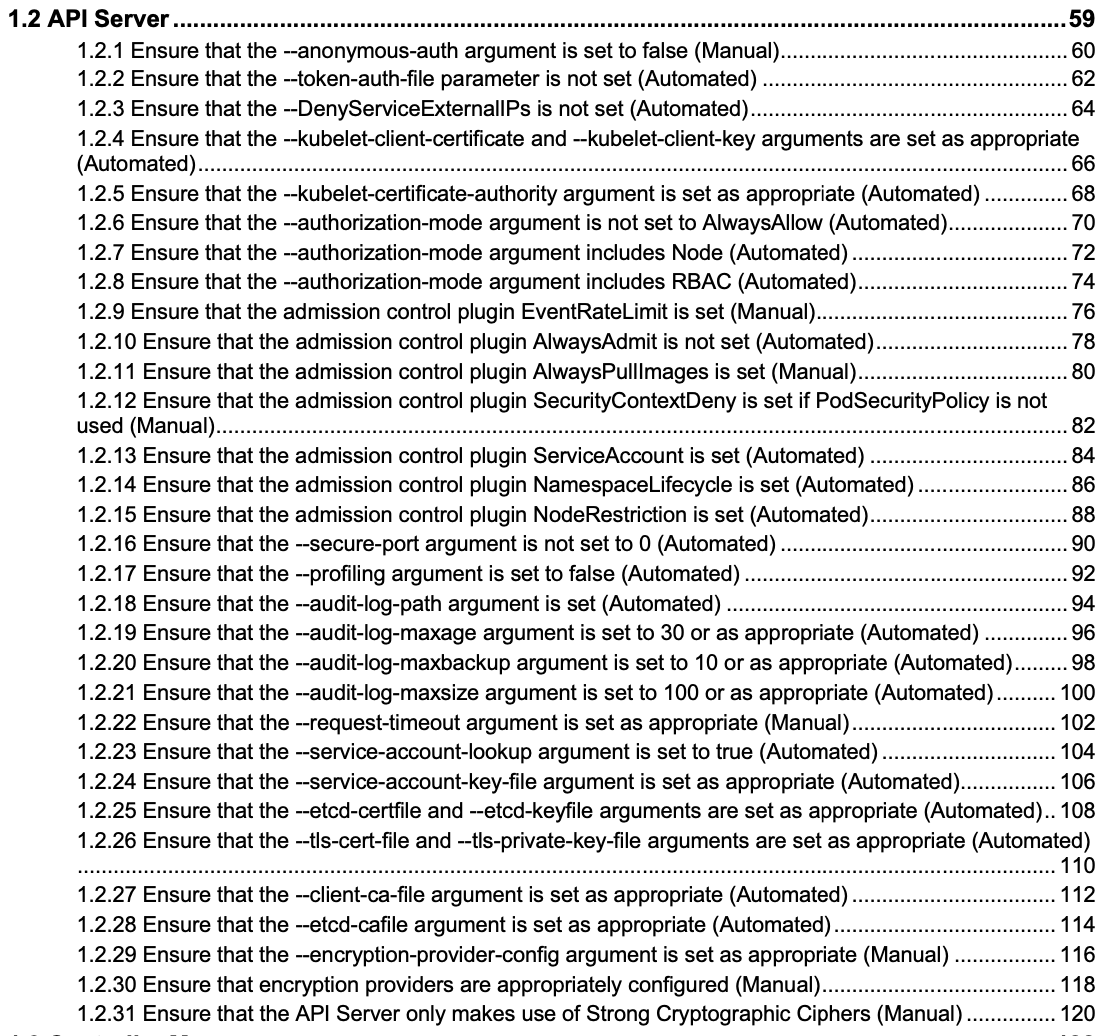
What is Kube-bench?
Kube-bench is an open-source tool to assess the security of Kubernetes clusters by running checks against the Center for Internet Security (CIS) Kubernetes benchmark. It was developed in GoLang by Aqua Security, a provider of cloud-native security solutions.
Kube-bench can help with the following.
- Cluster hardening: Kube-bench automates the process of checking the cluster configuration as per the security guidelines outlined in CIS benchmarks.
- Policy Enforcement: Kube-bech checks for RBAC configuration to ensure the necessary least privileges are applied to service accounts, users, etc. it also checks for pod security standards and secret management.
- Network segmentation: Kube-bench checks for CNI and its support for network policy to ensure that network policies are defined for all namespaces.
When it comes to the use of kube-bench by organizations, a security survey conducted by Red Hat found that 24% of the respondents use it.
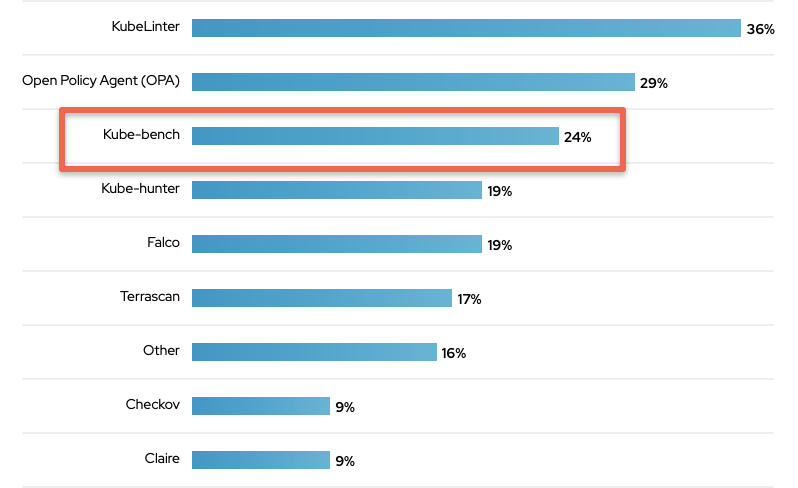
You can run kube-bench checks against a cluster in two ways.
- From the command line using kube-bench CLI
- Run inside a pod
Let's look at both options.
Running Kube-bench From Command Line
If you are preparing for CKS certification, running kube-bench from the command line is one of the important tasks.
Step 1: Log in to the control plane(master) node and create a kube-bench directory
sudo mkdir -p /opt/kube-benchStep 2: Go to the kube-bench releases page and choose the latest Linux binary link.
curl -L https://github.com/aquasecurity/kube-bench/releases/download/v0.13.0/kube-bench_0.13.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz -o /opt/kube-bench.tar.gzStep 3: Untar the binary to /opt/kube-bench folder
tar -xvf kube-bench.tar.gz -C /opt/kube-benchIf you check the /opt/kube-bench directory, You will see the kube-bench executable and cfg folder that contains the benchmark variations for different versions and versions of managed kubernetes services GKE, EKS, AKS, etc as shown in the following tree structure.
vagrant@master-node:~$ tree
.
├── cfg
│ ├── ack-1.0
│ │ ├── config.yaml
│ │ ├── controlplane.yaml
│ │ ├── etcd.yaml
│ │ ├── managedservices.yaml
│ │ ├── master.yaml
│ │ ├── node.yaml
│ │ └── policies.yaml
│ ├── aks-1.0
│ │ ├── config.yaml
│ │ ├── controlplane.yaml
│ │ ├── managedservices.yaml
│ │ ├── master.yaml
│ │ ├── node.yaml
│ │ └── policies.yaml
│ ├── cis-1.6-k3s
│ │ ├── config.yaml
│ │ ├── controlplane.yaml
│ │ ├── etcd.yaml
│ │ ├── master.yaml
│ │ ├── node.yaml
│ │ └── policies.yaml
│ ├── config.yaml
│ ├── eks-stig-kubernetes-v1r6
│ │ ├── config.yaml
│ │ ├── controlplane.yaml
│ │ ├── managedservices.yaml
│ │ ├── master.yaml
│ │ ├── node.yaml
│ │ └── policies.yaml
│ ├── gke-1.2.0
│ │ ├── config.yaml
│ │ ├── controlplane.yaml
│ │ ├── managedservices.yaml
│ │ ├── master.yaml
│ │ ├── node.yaml
│ │ └── policies.yaml
│ └── rh-1.0
│ ├── config.yaml
│ ├── controlplane.yaml
│ ├── etcd.yaml
│ ├── master.yaml
│ ├── node.yaml
│ └── policies.yaml
├── kube-benchStep 4: Move the kube-bench executable to the /usr/local/bin directory that is part of the system PATH
sudo mv /opt/kube-bench/kube-bench /usr/local/bin/Now you can execute kube-bench from any system location.
Step 4: Let's run the benchmark checks using kube-bench executable. We will be using the generic config.yaml to run the benchmarks using the following command. You have to run the command as sudo.
sudo kube-bench --config-dir /opt/kube-bench/cfg --config /opt/kube-bench/cfg/config.yamlThe above command will run the benchmarks checks and creates the summary of checks, remediation, and summary as shown below.
# Checks Example
[INFO] 1 Control Plane Security Configuration
[INFO] 1.1 Control Plane Node Configuration Files
[PASS] 1.1.1 Ensure that the API server pod specification file permissions are set to 644 or more restrictive (Automated)
[PASS] 1.1.2 Ensure that the API server pod specification file ownership is set to root:root (Automated)
# Remediations Example
== Remediations master ==
1.1.9 Run the below command (based on the file location on your system) on the control plane node.
For example, chmod 600 <path/to/cni/files>
1.1.12 On the etcd server node, get the etcd data directory, passed as an argument --data-dir,
from the command 'ps -ef | grep etcd'.
# Summary Example
== Summary master ==
41 checks PASS
9 checks FAIL
11 checks WARN
0 checks INFOIf you want the report in a separate file, you can direct the output to a file as shown below.
sudo kube-bench --config-dir /opt/kube-bench/cfg --config /opt/kube-bench/cfg/config.yaml > kube-bench.report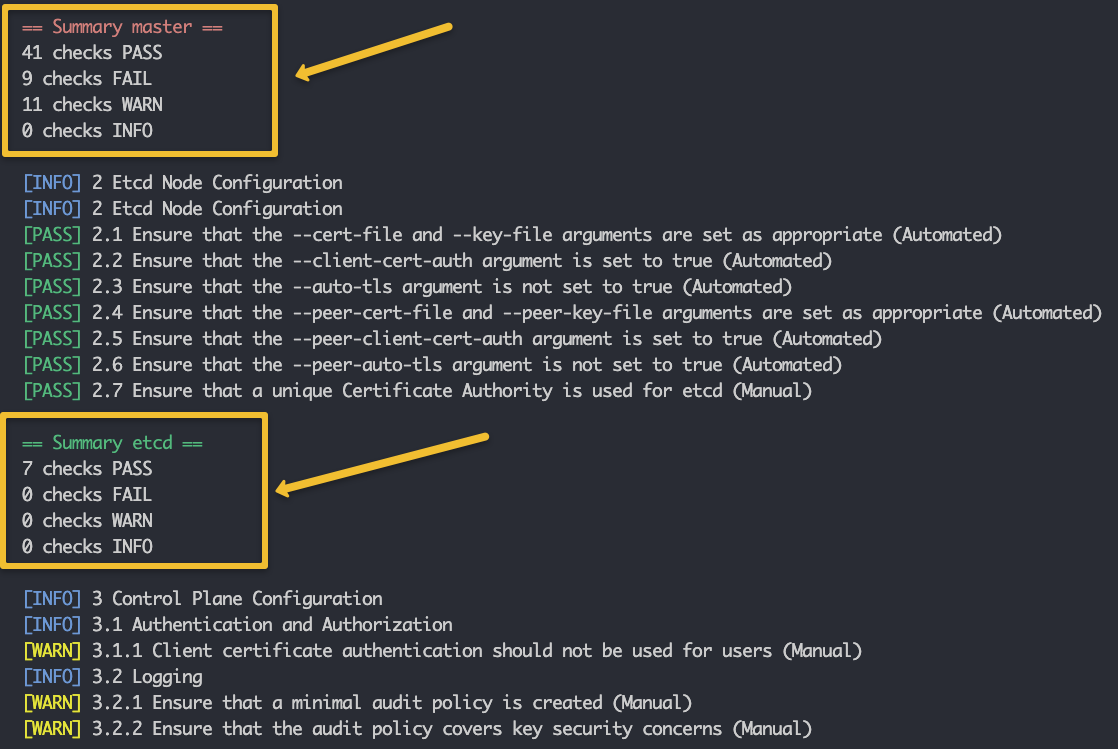
Installing Kube-bench From Package
You can also install and run kube-bench using Linux packages. On the releases page, you will find both .deb and .rpm packages.
For example, to install on Debian/Ubuntu systems, you can execute the following commands.
curl -L https://github.com/aquasecurity/kube-bench/releases/download/v0.13.0/kube-bench_0.13.0_linux_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i kube-bench.debAfter the installation, you can find the kube-bench cfg folder in the /etc/kube-bench/ directory.
Also, you can run the kube-bench checks without providing the config directory parameters as we did in the binary installation. By default, kube-bench refers the /etc/kube-bench/cfg directory.
To run the checks execute the following command.
sudo kube-benchRunning Kube-bench In a Pod
Another method to run kube-bench is by deploying it as a Kubernetes job pod. This method is particularly useful for running CIS benchmarks on managed Kubernetes clusters where root access to the control plane or worker nodes is not available.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aquasecurity/kube-bench/main/job.yamlOr if you want to modify the YAML, you can download it to a file and then apply it
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aquasecurity/kube-bench/main/job.yaml > job.yamlkubectl apply -f job.yamlThen kube-bench report will be available in the pod logs. First List the pod
kubectl get podsNow use the pod name to get the logs. Replace kube-bench-4j2bs with your pod name.
kubectl logs kube-bench-4j2bsYou can also export the kube-bench log to a file
kubectl logs kube-bench-4j2bs > kube-bench.reportKube-bench Possible Errors
unable to determine benchmark version: config file is missing 'version_mapping' sectioIf you run the kube-bench command without providing the --config-dir and --config parameters, you will get the above error.
Kube-bench for Managed Kubernetes Clusters (GKE, EKS, AKS etc)
If you look at managed Kubernetes services like GKE, EKS, or AKS, you don't get access to the control plane node to install the kube-bench utility.
All managed kubernetes services follow the shared responsibility model where the Cloud providers take care of control plane availability and security and the user needs to take care of security in terms of users, policies, etc.
Also, when you deploy the pod, it gets scheduled on a node and Kube-bench figures out that only kubelet is running on that node and it runs the checks accordingly. Meaning, it runs the tests for worker nodes. If you schedule the pod to be in the control plane, it runs all the checks required for the control plane.
kube-bench Alternatives
If you are looking for open-source alternatives for kube-bench to run CIS benchmarks, you can look at the following two tools.
- Checkov
- KubeScape
Summary
Kube-bench helps in verifying that your Kubernetes cluster is configured according to the recommendations from the Center for Internet Security (CIS).
To comply with the organization's security policies and audit requirements, you can run kube-bench to check and remediate security issues in the cluster.
If you are learning kubernetes, check out the comprehensive kubernetes tutorials.

