Do you want dockerized Jenkins which includes the configuration for build slaves also as Docker containers? So that you can run this image using docker command, then bang, everything is ready to run your Jenkins job on docker slave. Now let's make this happen.
Install Jenkins as docker container
Go to jenkins website (https://jenkins.io/doc/book/getting-started/installing/) and find "Docker" section, before executing the command docker run -d -p 49001:8080 -v $PWD/jenkins:/var/jenkins_home -t jenkins/jenkins, we need to let "jenkins" be the owner of the jenkins directory on host using its UUID:
sudo chown -R 1000:1000 /opt/jenkins_homeOtherwise, you will find the jenkins docker container cannot be started, just exit after the container created, that's because the jenkins container user by default is "jenkins",
Now you can access Jenkins from your browser, for example: http://[your Jenkins ip]:49001/, create job and build your project from your Jenkins master container
Setup Build Slave as docker container
Although you can add VM as build slave in Jenkins, it's more flexible and convenient to make build slave as docker container, because you don't need to maintain each slave VM, you can just give Jenkins a slave host's IP and slave's docker image template, then Jenkins can create slave as docker container on that host. Jenkins make this happen by a plugin called DockerPlugin.
Let's see how to install and configure this plugin.
Install the plugin
Navigate to the Manage Jenkins > Manage Plugins page in the web UI. Find DockerPlugin and install it. See https://jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/plugins/ for reference.
Plugin Configuration
Create your slave image.
Step 1: Find steps in official site https://wiki.jenkins.io/display/JENKINS/Docker+Plugin, see the section "Creating a docker image", commands include:
docker pull ubuntu
docker run -i -t ubuntu /bin/bash
apt-get update
apt-get install openssh-server
mkdir /var/run/sshd
apt-get install openjdk-6-jdk
adduser jenkins
/usr/sbin/sshd
exitHowever, the steps are insufficient if your build slave needs to build your project's docker image, create docker container and build your project because you can not run docker command in the ubuntu container after these steps. The aim is not docker-in-docker, i.e., docker container running in another docker container, which is another more complicated case. We just need to install the docker binary in docker container and mount the docker socket (by volume "/var/run/docker.sock") so as docker command can be executed in the container. So add the below steps
- To let docker daemon can be found in docker container, install docker binary inside the ubuntu container (mount docker socket step will leave to DockerPlugin because DockerPlugin will create slave container automatically when running a job):
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh- Add Jenkins user in docker group in the ubuntu container so as DockerPlugin can access docker binary to execute docker command by "jenkins" user: user mod -a -G docker jenkins.
- Commit the ubuntu container as docker image, for example, make the image name as jenkins-slave:
docker commit [container ID] jenkins-slaveStep 2: On docker host, to expose docker's TCP port so DockerPlugin can access docker host and create build slave container, edit /etc/default/docker to modify the value of DOCKER_OPTS as (note that 4243 is the default TCP port for docker):
DOCKER_OPTS='-H tcp://0.0.0.0:4243 -H unix:///var/run/docker.sock’.3. Now we can return back to Jenkins Web UI and configure Jenkins: Manage Jenkins > Configure system > Cloud > docker:
- Input docker URL: tcp://[your host ip]:4243
If click "Test Connection", you can see docker API version shown on UI.
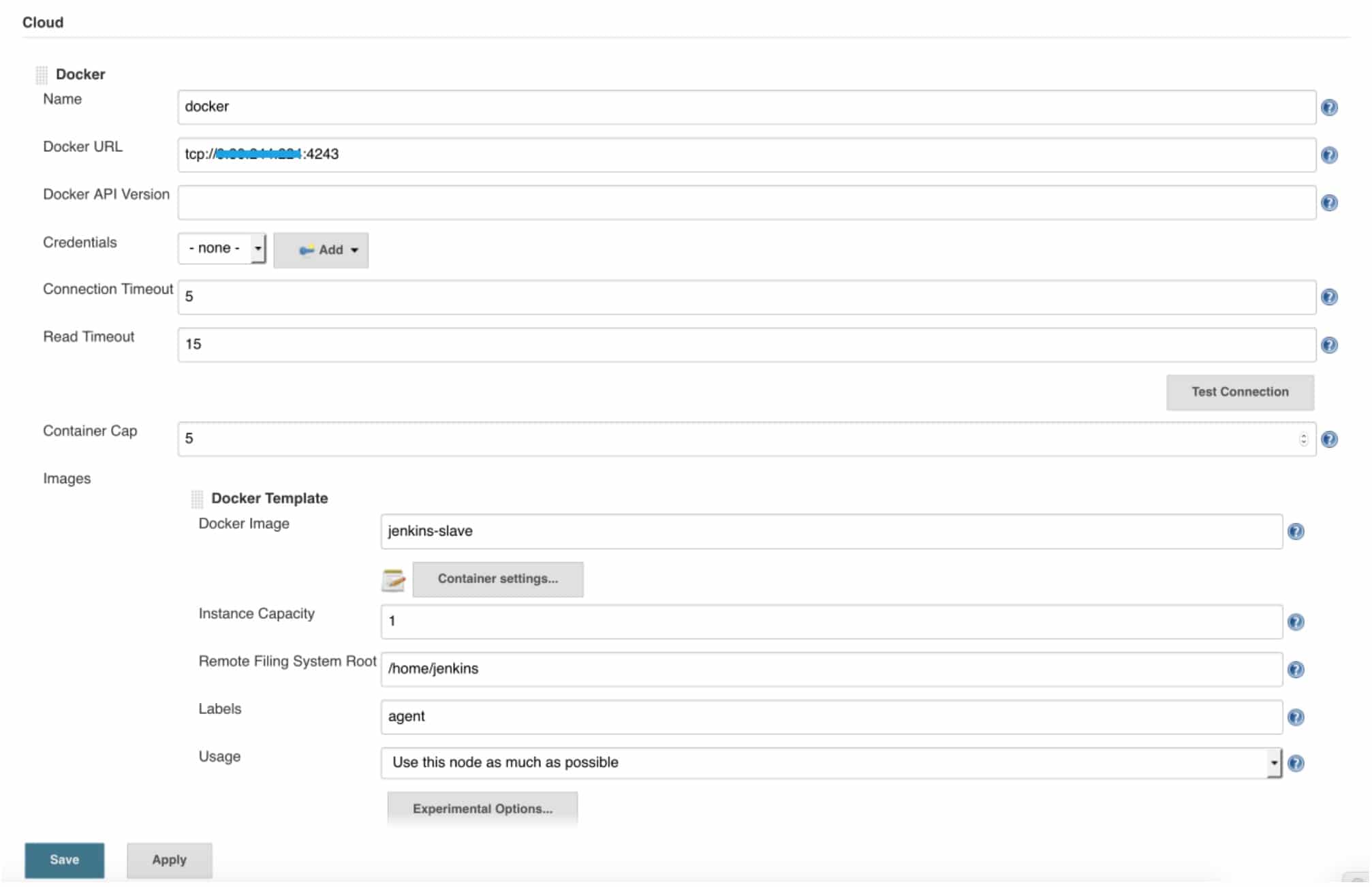
- In “Docker Template” section, click “Container settings”, input Volumes:
/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
/home/jenkins/workspaceThe volumes are volume mappings that DockerPlugin will use to create slave containers. The first volume mapping mounts docker socket into the container to enable docker command can be listened by docker daemon on the host, the second line let Jenkins find her workspace to execute the job.

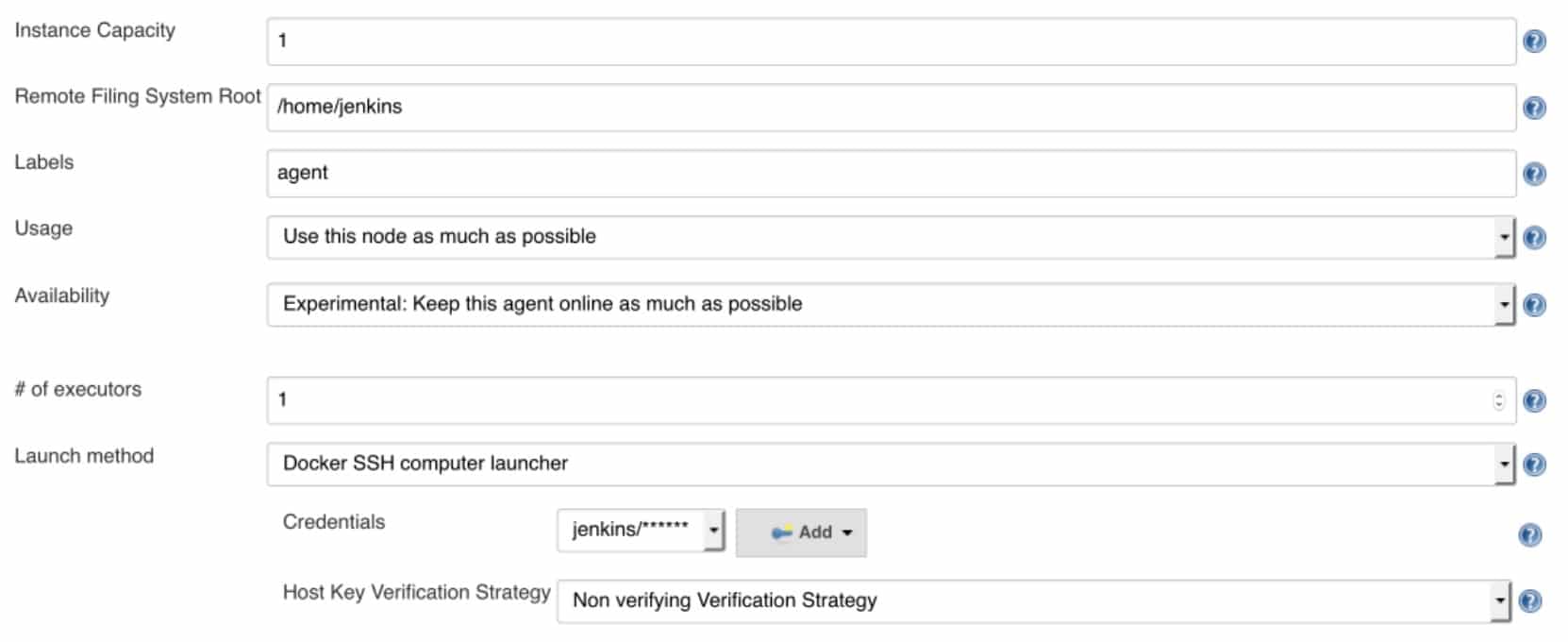
- DockerPlugin by default will destroy build slave container after each build, you can save your slave container for debugging purpose or deploy purpose. On “Container settings”, from “Availability” label, click “Experimental options”, choose “Experimental: Keep this agent online as much as possible”.
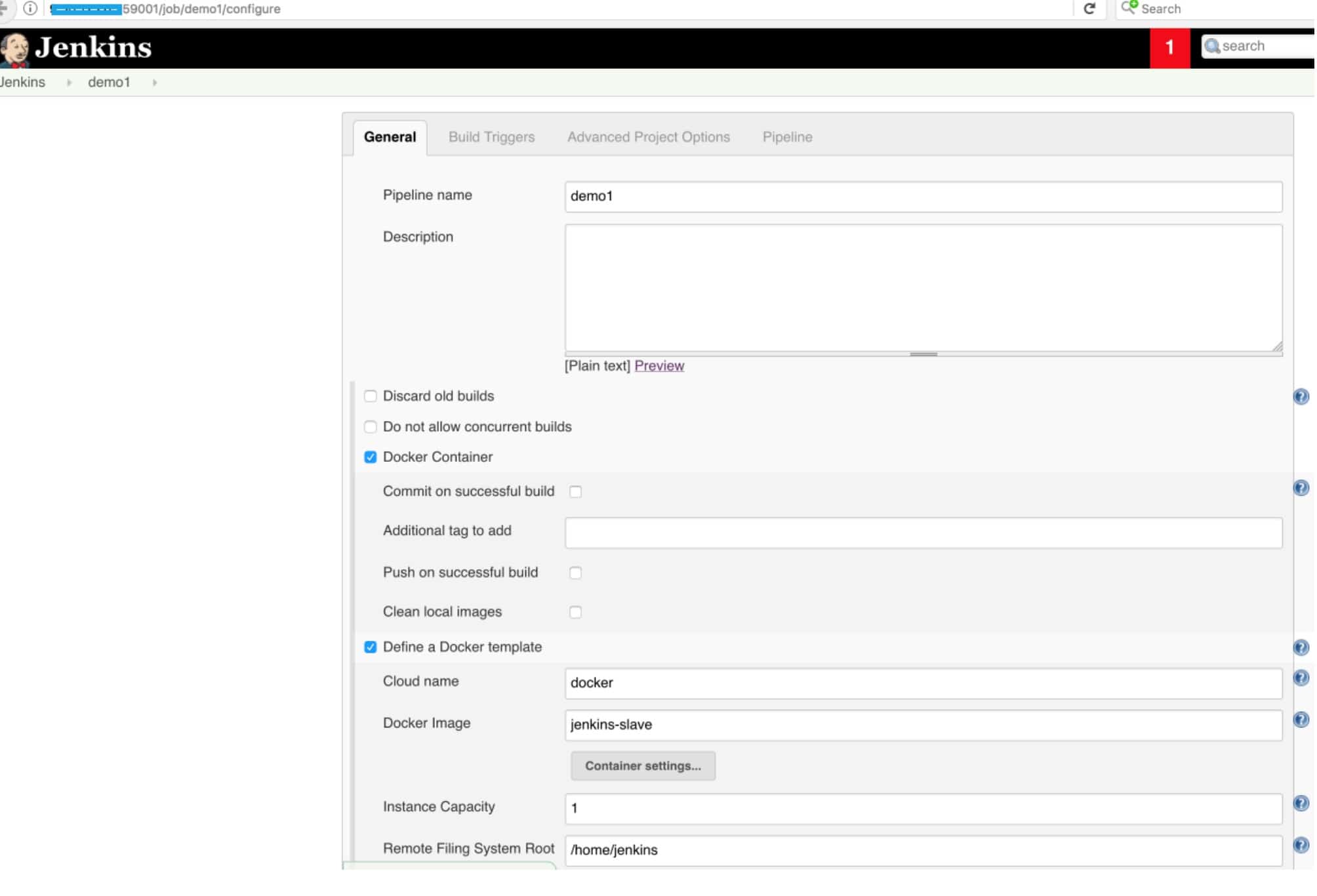
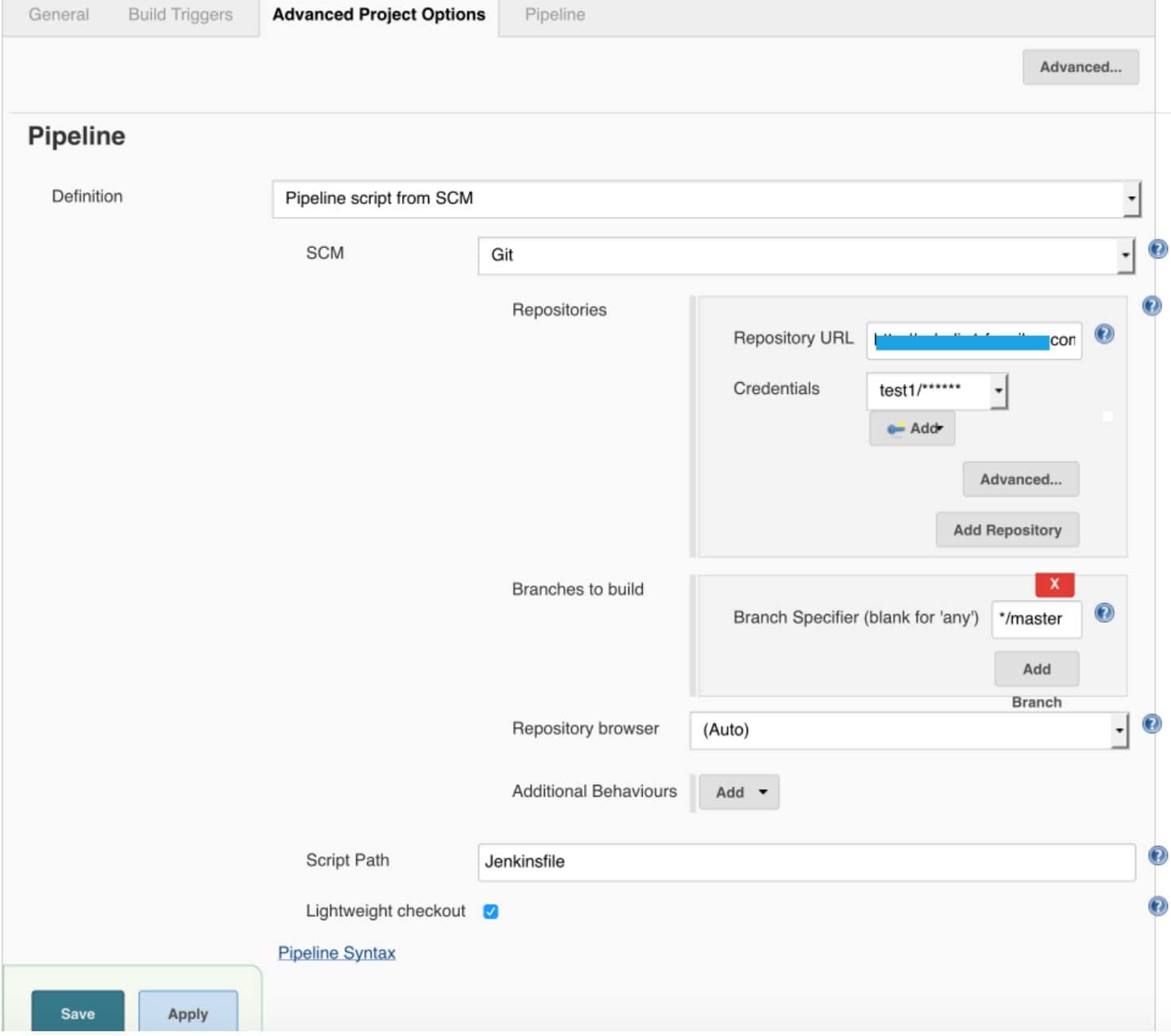
Now the docker slave configuration is complete. The whole configuration can be saved by committing the Jenkins image. To verify, you can create a job to run. Your Job configuration can be as below screenshots if you want a pipeline job in order to build from a repository (note your repository should contain a Jenkinsfile).
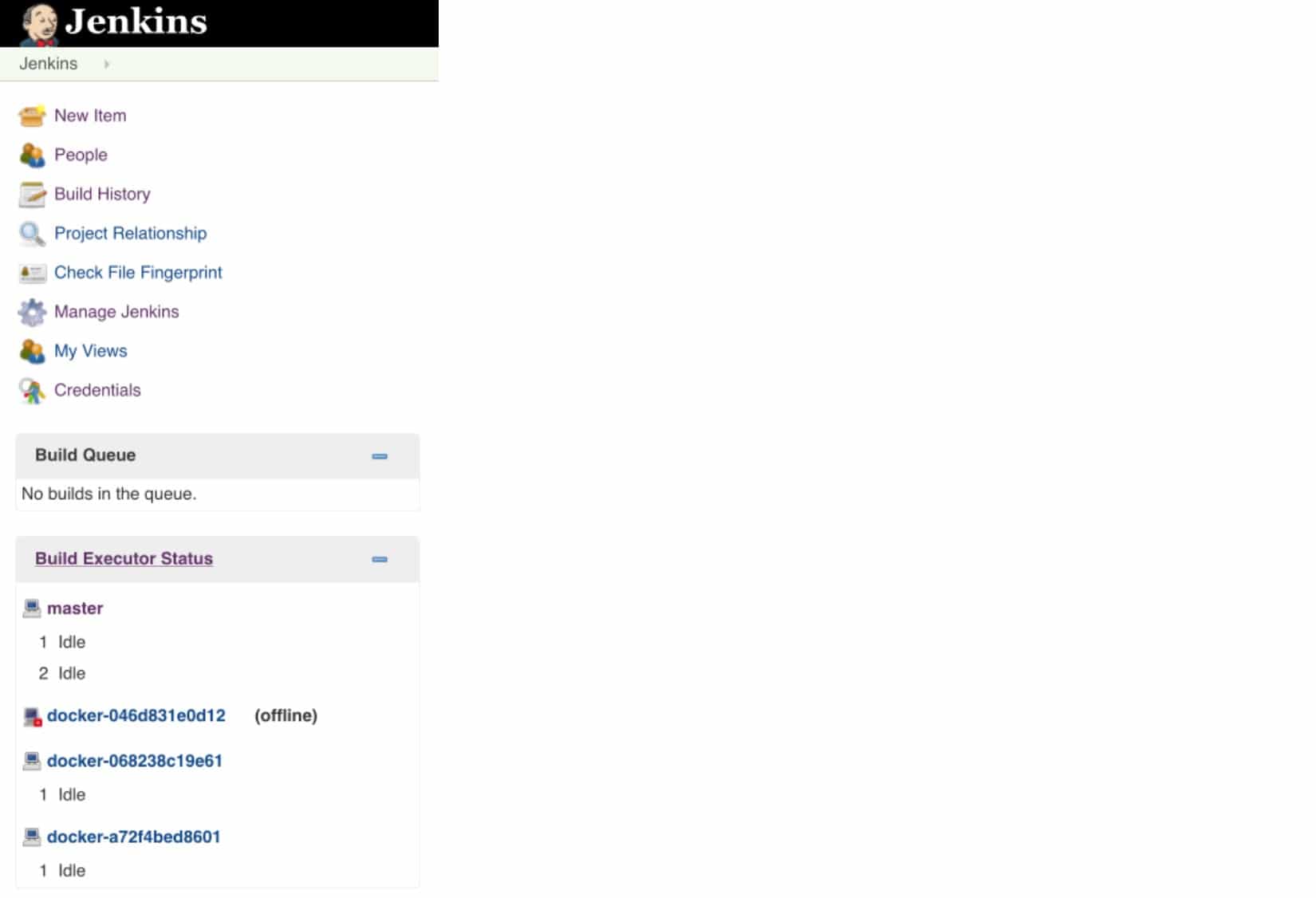
When the job is running, you can see the created slave containers from "Build Executor Status", docker-xxx is a slave container's name. After the job finished building, the container status will
be "Idle", if you destroy the container on your slave host manually, the status will be "offline".

ONLINE COURSE: Docker Technologies for DevOps and Developers
Learn how to develop and deploy web applications with Docker technologies. Take your DevOps skills to the next level.
Docker Technologies for DevOps and Developers
- Learn to containerize applications with microservices approach
- Best practices for making Dockerfiles
- Learn to build multi-node swarm cluster and learn to orchestrate applications
- In depth understanding for Docker and its workflows for complex applications